Region:Global
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAA1677
Pages:97
Published On:August 2025
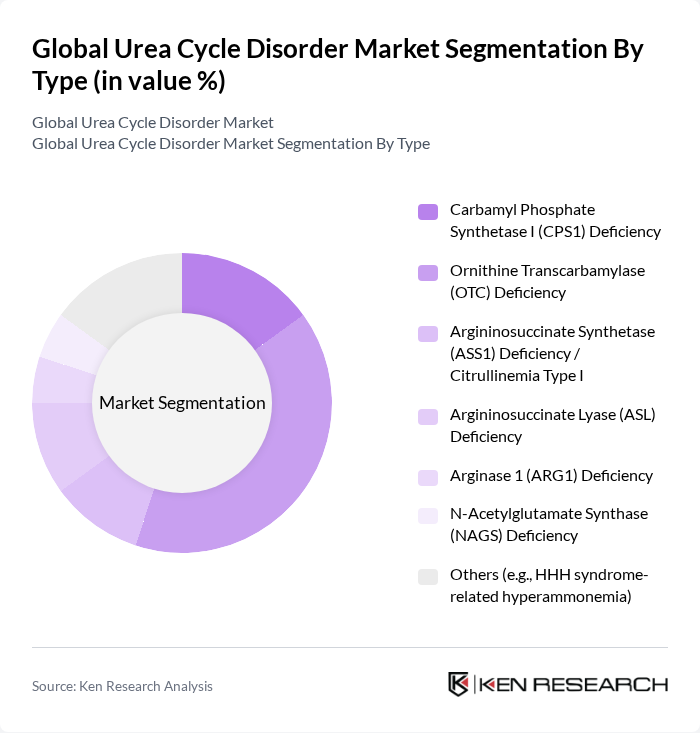
By Type:The market is segmented into various types of urea cycle disorders, including Carbamyl Phosphate Synthetase I (CPS1) Deficiency, Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) Deficiency, Argininosuccinate Synthetase (ASS1) Deficiency / Citrullinemia Type I, Argininosuccinate Lyase (ASL) Deficiency, Arginase 1 (ARG1) Deficiency, N-Acetylglutamate Synthase (NAGS) Deficiency, and Others (e.g., HHH syndrome-related hyperammonemia). Among these, OTC Deficiency is the most prevalent, accounting for a significant portion of the market due to its higher incidence rate and the critical need for effective management strategies.
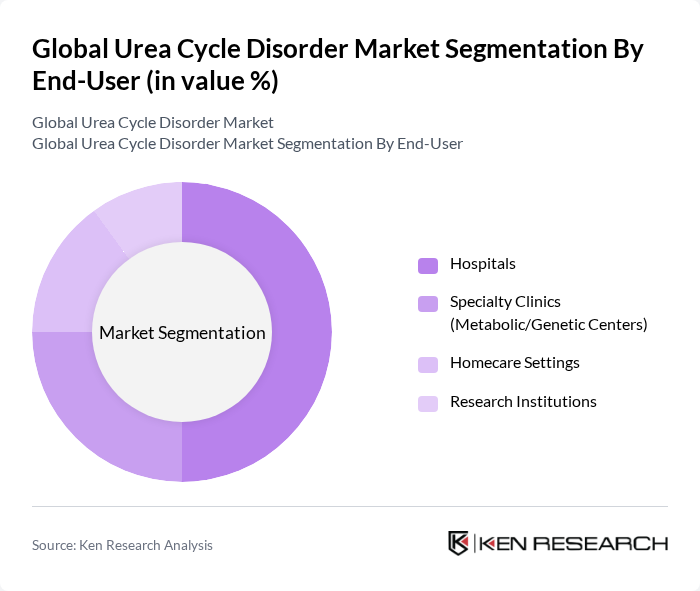
By End-User:The market is segmented by end-user into Hospitals, Specialty Clinics (Metabolic/Genetic Centers), Homecare Settings, and Research Institutions. Hospitals are the leading end-user segment, primarily due to their comprehensive facilities for diagnosis and treatment, as well as their ability to provide specialized care for patients with urea cycle disorders.
The Global Urea Cycle Disorder Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Horizon Therapeutics plc (now part of Amgen Inc.), Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Recordati S.p.A. (Recordati Rare Diseases), Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc., Eurocept Pharmaceuticals Holding (Lucane Pharma SA), Bausch Health Companies Inc., Immedica Pharma AB, Medunik USA, Acer Therapeutics Inc. (now Zevra Therapeutics, Inc.), Dipharma SA, Relief Therapeutics Holding SA, Nestlé S.A. (Vitaflo International Ltd.), Orpharma Pty Ltd., Arcturus Therapeutics Holdings Inc., Selecta Biosciences, Inc. (Selecta-IGM Biosciences, Inc.) contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Urea Cycle Disorder market appears promising, driven by ongoing advancements in genetic research and the development of innovative therapies. As healthcare systems increasingly adopt personalized medicine approaches, the focus will shift towards tailored treatment plans that address individual patient needs. Additionally, the integration of digital health technologies is expected to enhance patient monitoring and management, improving overall outcomes and accessibility in the None region.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Carbamyl Phosphate Synthetase I (CPS1) Deficiency Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) Deficiency Argininosuccinate Synthetase (ASS1) Deficiency / Citrullinemia Type I Argininosuccinate Lyase (ASL) Deficiency Arginase 1 (ARG1) Deficiency N-Acetylglutamate Synthase (NAGS) Deficiency Others (e.g., HHH syndrome-related hyperammonemia) |
| By End-User | Hospitals Specialty Clinics (Metabolic/Genetic Centers) Homecare Settings Research Institutions |
| By Treatment Type | Dietary Management (protein restriction, essential amino acids) Pharmacological Treatments (ammonia scavengers, amino acid supplements) Gene Therapy and RNA-based Therapies Liver Transplantation |
| By Distribution Channel | Hospital Pharmacies Specialty Pharmacies Retail Pharmacies Online Pharmacies |
| By Region | North America Europe Asia-Pacific Latin America Middle East & Africa |
| By Age Group | Pediatric Patients (including neonatal-onset) Adolescent & Adult Patients (late-onset) Geriatric Patients |
| By Severity | Mild Cases Moderate Cases Severe Cases (acute hyperammonemia) Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Providers | 120 | Metabolic Disorder Specialists, Pediatricians |
| Patient Advocacy Groups | 90 | Patient Advocates, Family Members of Affected Individuals |
| Pharmaceutical Companies | 70 | Product Managers, R&D Directors |
| Health Insurance Providers | 60 | Policy Analysts, Claims Managers |
| Research Institutions | 50 | Clinical Researchers, Geneticists |
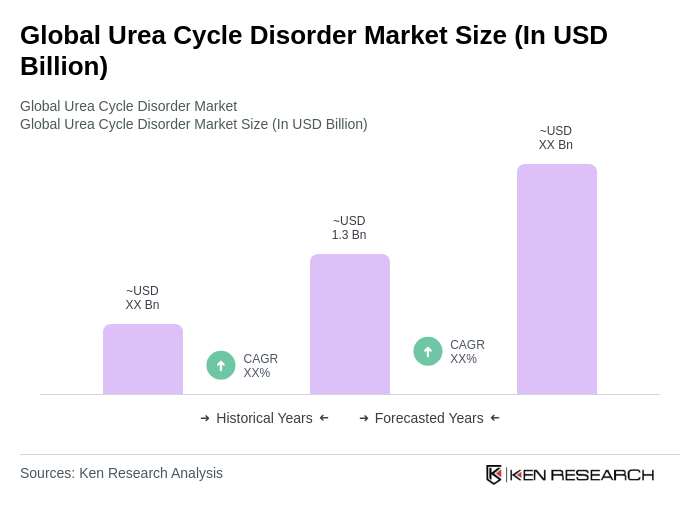
The Global Urea Cycle Disorder Market is valued at approximately USD 1.3 billion, reflecting a significant growth driven by increased awareness of genetic disorders, advancements in diagnostic methods, and the development of ammonia-lowering therapies.