Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAD2933
Pages:99
Published On:November 2025
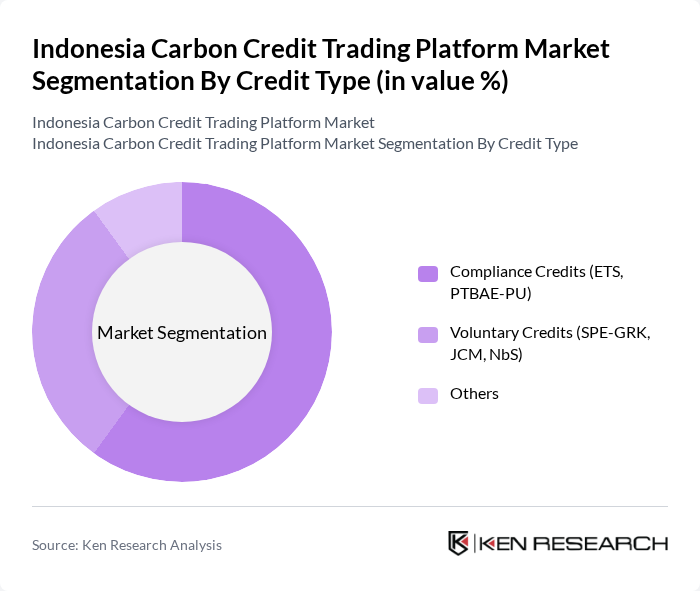
By Credit Type:The market is segmented into Compliance Credits, Voluntary Credits, and Others. Compliance Credits are primarily driven by regulatory requirements, while Voluntary Credits cater to companies looking to enhance their sustainability profiles beyond legal obligations. The Compliance Credits segment is currently leading the market due to stringent government regulations and increasing corporate accountability towards emissions reduction. Indonesia’s national carbon registry, Sistem Registri Nasional (SRN), tracks all compliance and voluntary credits, ensuring transparency and traceability .
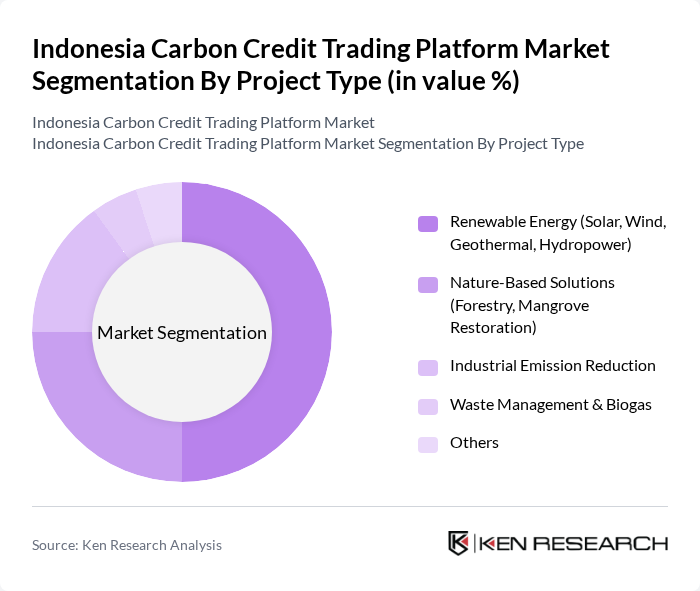
By Project Type:The market is categorized into Renewable Energy, Nature-Based Solutions, Industrial Emission Reduction, Waste Management, and Others. Renewable Energy projects, particularly solar and wind, are gaining traction due to government incentives and technological advancements. Nature-Based Solutions are also significant, as they align with global sustainability goals. The Renewable Energy segment is currently the dominant force in the market, driven by increasing investments and public interest in sustainable energy sources. Indonesia’s vast forest and peatland resources also support a growing number of nature-based carbon projects, which are increasingly sought after by international buyers , .
The Indonesia Carbon Credit Trading Platform Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as IDX Carbon (PT Bursa Efek Indonesia), CarbonX, AirCarbon Exchange (ACX Indonesia), Star Energy Geothermal, PT Pertamina (Persero), PT PLN (Persero), PT Rimba Makmur Utama, PT Mitra Hijau Indonesia, South Pole Indonesia, PT BioFuels Indonesia, PT Dharma Satya Nusantara Tbk, PT Bumi Hijau Lestari, PT Restorasi Ekosistem Riau, PT Indika Energy Tbk, PT Katingan Mentaya Project contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the carbon credit trading platform in Indonesia appears promising, driven by increasing environmental awareness and government support for sustainable practices. As more businesses adopt sustainability goals, the demand for carbon credits is expected to rise significantly. Additionally, advancements in technology and digital trading platforms will enhance market accessibility and efficiency, fostering greater participation. Collaborative efforts with international bodies will further strengthen Indonesia's position in the global carbon market, paving the way for innovative solutions and investment opportunities.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Credit Type (Compliance, Voluntary) | Compliance Credits (ETS, PTBAE-PU) Voluntary Credits (SPE-GRK, JCM, NbS) Others |
| By Project Type (Renewable Energy, Nature-Based Solutions, Industrial, Waste Management) | Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind, Geothermal, Hydropower) Nature-Based Solutions (Forestry, Mangrove Restoration) Industrial Emission Reduction Waste Management & Biogas Others |
| By End-User (Utilities, Financial Institutions, Corporates, Government, Others) | Utilities Financial Institutions Corporates Government Others |
| By Platform Type (Exchange, OTC, Auction) | Exchange (IDX Carbon) Over-the-Counter (OTC) Auction Others |
| By Region (Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Bali, Nusa Tenggara) | Java Sumatra Kalimantan Sulawesi Bali Nusa Tenggara |
| By Investment Source (Domestic, FDI, PPP, Government Schemes) | Domestic Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Government Schemes Others |
| By Policy Support (Subsidies, Tax Exemptions, RECs) | Subsidies Tax Exemptions Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Government Policy Makers | 45 | Regulatory Officials, Environmental Policy Advisors |
| Carbon Credit Project Developers | 38 | Project Managers, Sustainability Consultants |
| Corporate Sustainability Officers | 42 | CSR Managers, Environmental Compliance Officers |
| Financial Institutions Involved in Carbon Trading | 35 | Investment Analysts, Risk Management Officers |
| Environmental NGOs and Advocacy Groups | 28 | Research Analysts, Program Directors |
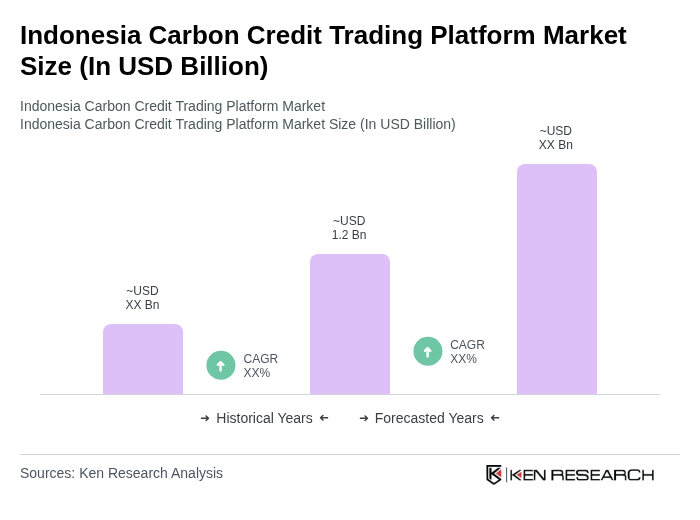
The Indonesia Carbon Credit Trading Platform Market is valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by regulatory pressures and increased awareness of climate change among businesses and consumers.