Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAA4944
Pages:89
Published On:September 2025

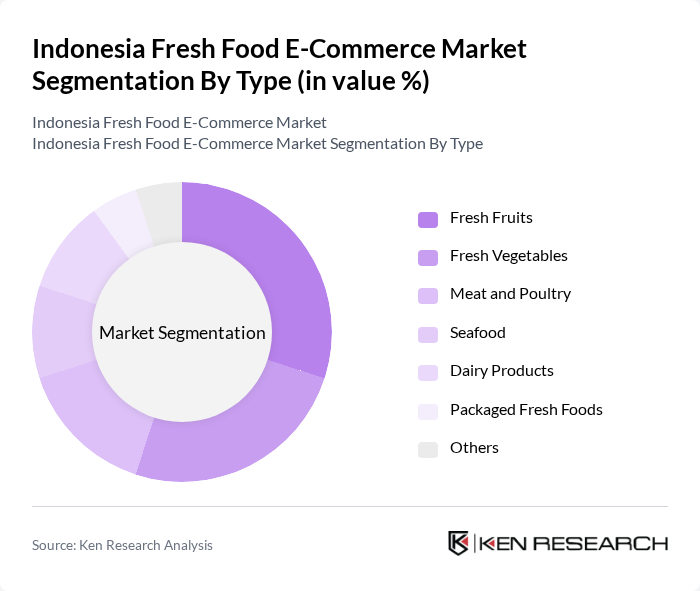
By Type:The fresh food e-commerce market is segmented into various types, including fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, meat and poultry, seafood, dairy products, packaged fresh foods, and others. Among these, fresh fruits and vegetables are the most popular due to their essential role in daily diets and the increasing demand for healthy eating. The convenience of online shopping for these products has led to a significant rise in their sales, particularly in urban areas where consumers seek quick and easy access to fresh produce.
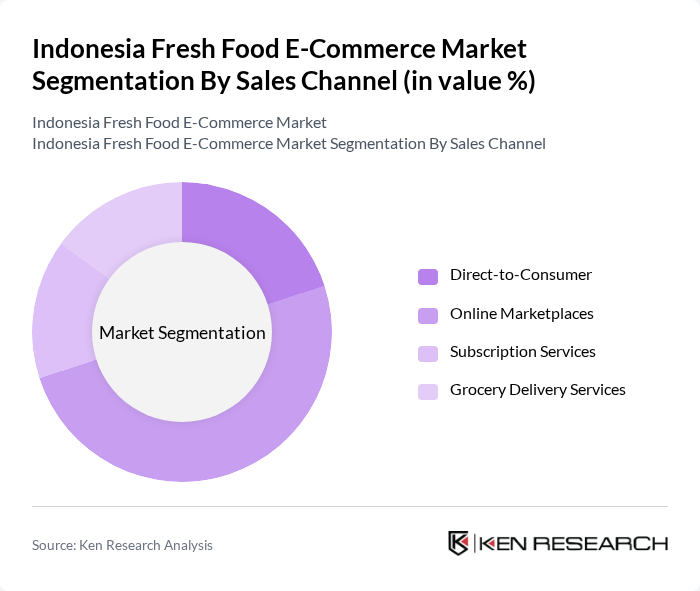
By Sales Channel:The sales channels for fresh food e-commerce include direct-to-consumer, online marketplaces, subscription services, and grocery delivery services. Online marketplaces are particularly dominant due to their wide reach and established customer bases. Consumers prefer these platforms for their variety and competitive pricing, while subscription services are gaining traction among health-conscious individuals seeking regular deliveries of fresh produce.
The Indonesia Fresh Food E-Commerce Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Gojek, Grab, HappyFresh, Sayurbox, TaniHub, Red Dot Payment, Kecipir, BliBli, Tokopedia, Bukalapak, Alfamart, Indomaret, Shopee, Lazada, Farmaku contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
As the Indonesian fresh food e-commerce market evolves, several trends are expected to shape its future. The integration of advanced technologies, such as AI for supply chain optimization, will enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, the growing emphasis on sustainability will drive demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions. With increasing consumer preference for direct-to-consumer sales, businesses that adapt to these trends will likely capture a larger market share, fostering a more competitive landscape in the future.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Fresh Fruits Fresh Vegetables Meat and Poultry Seafood Dairy Products Packaged Fresh Foods Others |
| By Sales Channel | Direct-to-Consumer Online Marketplaces Subscription Services Grocery Delivery Services |
| By Consumer Segment | Households Restaurants Retailers Institutions |
| By Packaging Type | Eco-Friendly Packaging Vacuum-Sealed Packaging Modified Atmosphere Packaging Standard Packaging |
| By Delivery Mode | Same-Day Delivery Scheduled Delivery Click and Collect |
| By Price Range | Budget Mid-Range Premium |
| By Region | Java Sumatra Bali Kalimantan Sulawesi Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Preferences in Fresh Food E-Commerce | 150 | Online Shoppers, Grocery Buyers |
| Supply Chain Insights from Fresh Food Distributors | 100 | Logistics Managers, Supply Chain Coordinators |
| Market Trends from E-Commerce Platform Operators | 80 | Product Managers, Marketing Directors |
| Consumer Behavior Analysis in Urban Areas | 120 | Urban Consumers, Tech-Savvy Shoppers |
| Insights from Agricultural Producers | 70 | Farm Owners, Agricultural Cooperative Leaders |
The Indonesia Fresh Food E-Commerce Market is valued at approximately USD 5 billion, driven by increasing online shopping adoption, consumer preferences for fresh and organic products, and the rise of mobile payment solutions.