Region:Asia
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAA3214
Pages:97
Published On:September 2025
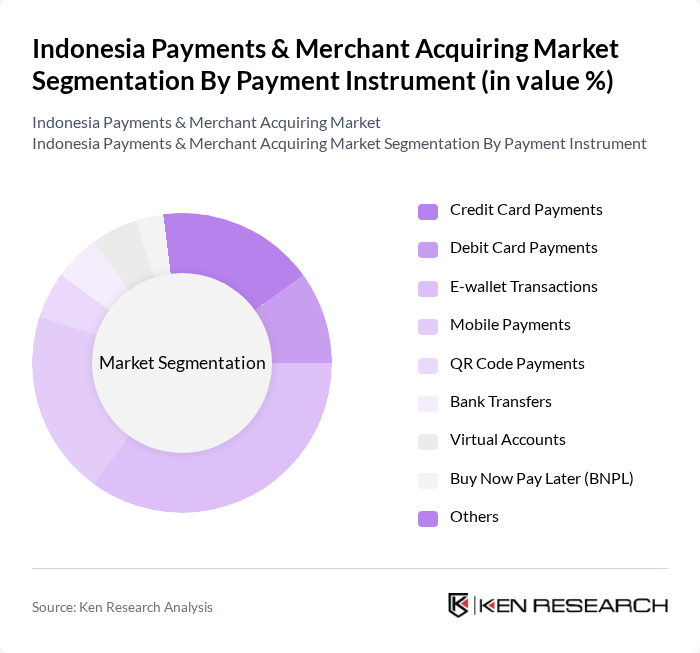
By Payment Instrument:The payment instrument segmentation includes various methods through which transactions are processed. The subsegments are Credit Card Payments, Debit Card Payments, E-wallet Transactions, Mobile Payments, QR Code Payments, Bank Transfers, Virtual Accounts, Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL), and Others. Among these, E-wallet Transactions have gained significant traction due to their convenience, interoperability through QRIS, and the growing trend of cashless payments, particularly among younger consumers and MSMEs .
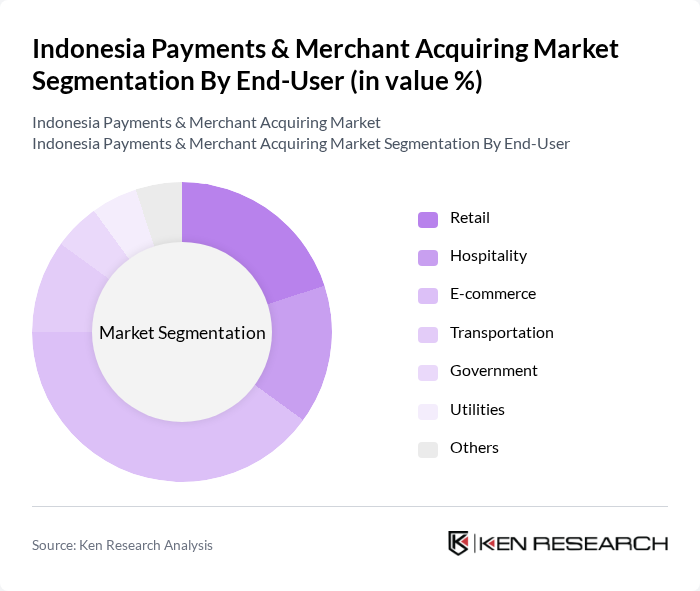
By End-User:The end-user segmentation encompasses various sectors utilizing payment solutions, including Retail, Hospitality, E-commerce, Transportation, Government, Utilities, and Others. The E-commerce sector is particularly dominant, driven by the increasing number of online shoppers, the convenience of digital payment methods, and the rapid expansion of online marketplaces and cross-border commerce .
The Indonesia Payments & Merchant Acquiring Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Bank Mandiri, BCA (Bank Central Asia), DOKU, OVO, GoPay, LinkAja, Xendit, Jenius, CIMB Niaga, Dana, GrabPay, Paytren, ShopeePay, BRI (Bank Rakyat Indonesia), Bank Negara Indonesia (BNI) contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of Indonesia's payments and merchant acquiring market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and increasing consumer acceptance of digital transactions. The integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology is expected to enhance payment security and efficiency. Additionally, the government's commitment to promoting cashless transactions will likely foster a more inclusive financial ecosystem. As the market evolves, collaboration between fintech companies and traditional banks will be crucial in addressing regulatory challenges and expanding service offerings to underserved populations.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Payment Instrument | Credit Card Payments Debit Card Payments E-wallet Transactions Mobile Payments QR Code Payments Bank Transfers Virtual Accounts Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) Others |
| By End-User | Retail Hospitality E-commerce Transportation Government Utilities Others |
| By Payment Channel | Online Payments In-store Payments Recurring Payments Peer-to-Peer Payments Cross-border Payments Others |
| By Merchant Size | Micro Merchants Small Merchants Medium Merchants Large Merchants Others |
| By Industry Vertical | Food and Beverage Fashion and Apparel Electronics Health and Beauty Travel and Tourism Others |
| By Transaction Value | Low Value Transactions Medium Value Transactions High Value Transactions Others |
| By Payment Frequency | Daily Transactions Weekly Transactions Monthly Transactions Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| SME Payment Solutions | 120 | Business Owners, Financial Managers |
| Consumer Payment Preferences | 140 | General Consumers, Tech-Savvy Users |
| Payment Gateway Providers | 80 | Product Managers, Business Development Executives |
| Merchant Acquiring Services | 60 | Sales Directors, Operations Managers |
| Regulatory Impact Assessment | 40 | Compliance Officers, Legal Advisors |
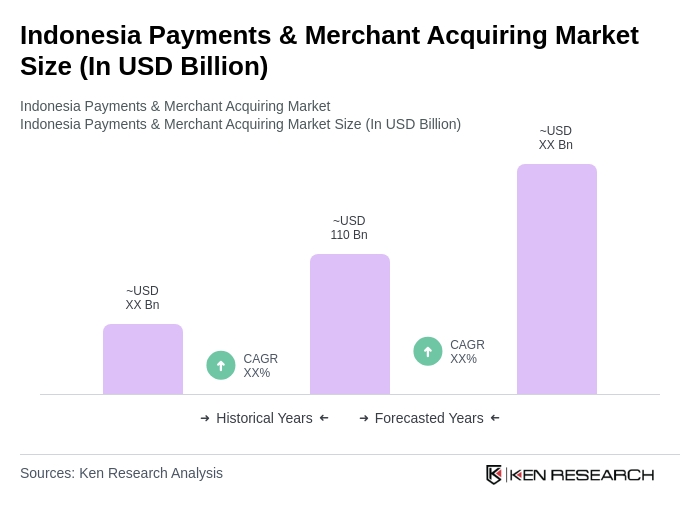
The Indonesia Payments & Merchant Acquiring Market is valued at approximately USD 110 billion, driven by digitalization, increased smartphone usage, and a shift towards cashless transactions among consumers.