Indonesia Biosimilars Market Outlook to 2030
Region:Asia
Author(s):Shreya
Product Code:KROD2573
November 2024
97
About the Report
Indonesia Biosimilars Market Overview
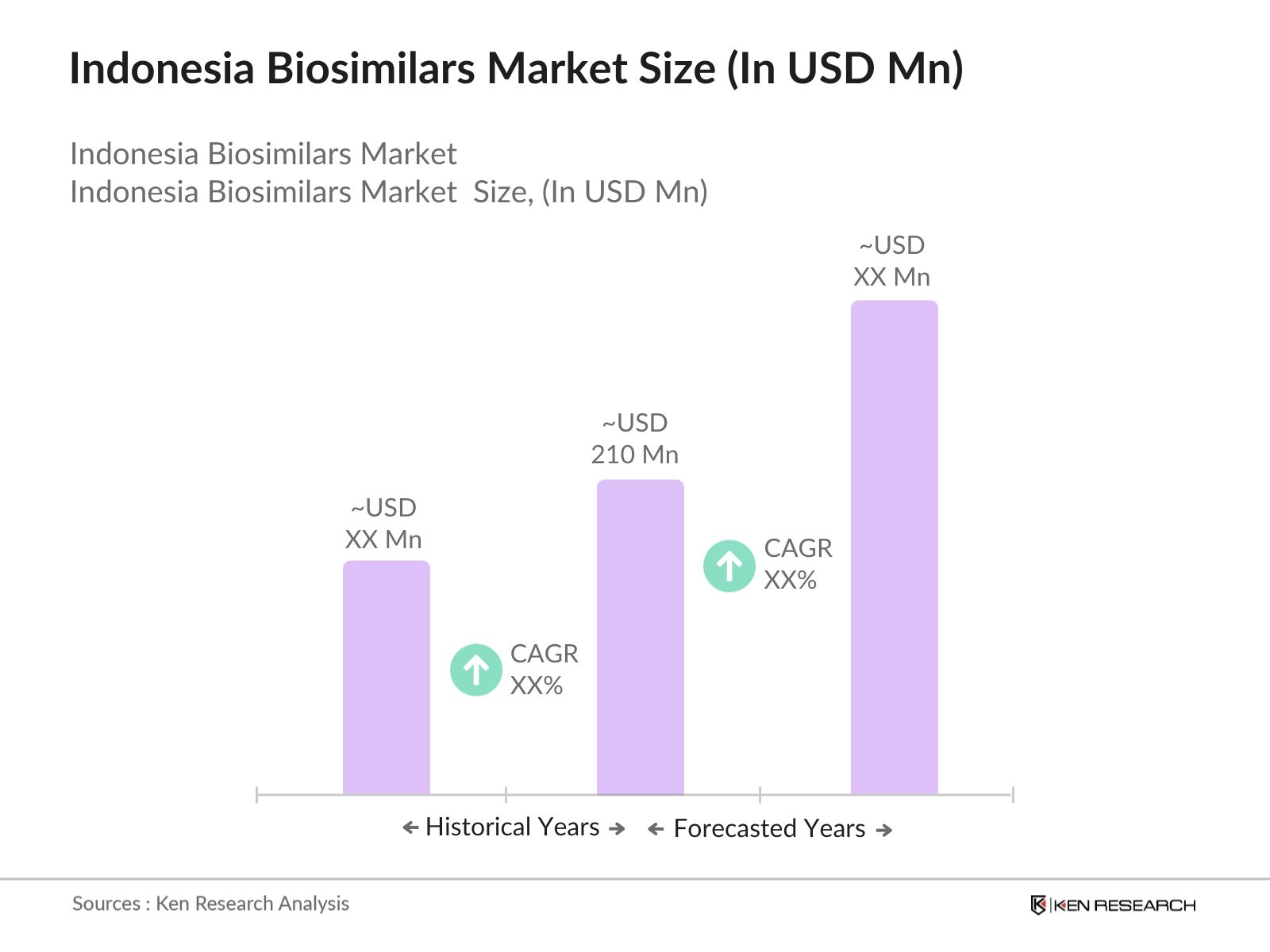
The Indonesia biosimilars market is valued at USD 210 million, based on a five-year historical analysis. This market's growth is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders, alongside rising healthcare costs, which make biosimilars a cost-effective alternative to biologics. Additionally, government policies supporting healthcare infrastructure and the expedited regulatory approval for biosimilars contribute to the market's expansion. The need for affordable therapeutic options in a growing population further drives the biosimilars demand in the country.
Java and Sumatra dominate the biosimilars market in Indonesia, primarily due to their robust healthcare infrastructure and concentration of major pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. These regions are home to the largest populations in the country, which increases the demand for biosimilar therapies. Moreover, government hospitals and leading private healthcare providers in these areas are focusing on offering cost-effective treatment options, making biosimilars a popular choice. Java, being Indonesia's economic hub, also benefits from higher disposable income, which further fuels market demand.
Indonesias government enforces the TKDN (Domestic Component Level) policy, which mandates that at least 40% of the components used in biosimilars must be sourced locally. This regulation, implemented in 2023, aims to boost local manufacturing and reduce dependence on imports. The TKDN policy has incentivized local pharmaceutical companies to increase production capacity and collaborate with international firms to meet these requirements, further fostering the growth of Indonesia's biosimilars market.
Indonesia Biosimilars Market Segmentation
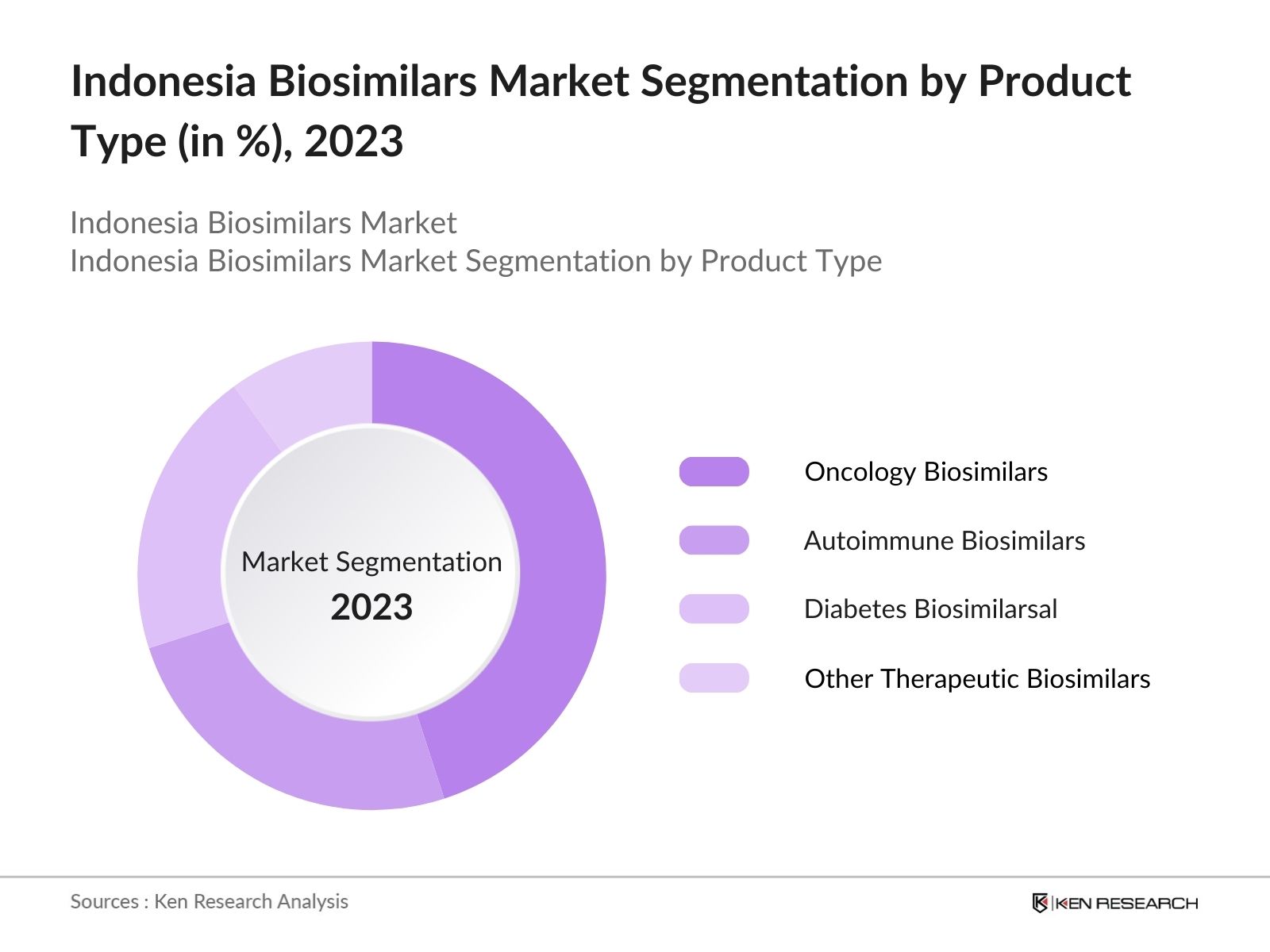
By Product Type: The market is segmented by product type into oncology biosimilars, autoimmune biosimilars, diabetes biosimilars, and other therapeutic biosimilars. Recently, oncology biosimilars hold a dominant market share in Indonesia under the product type segmentation. This dominance is due to the rising incidence of cancer and the growing need for cost-effective cancer treatments. Biosimilars offer an affordable alternative to branded biologics, making them more accessible to a larger portion of the population.
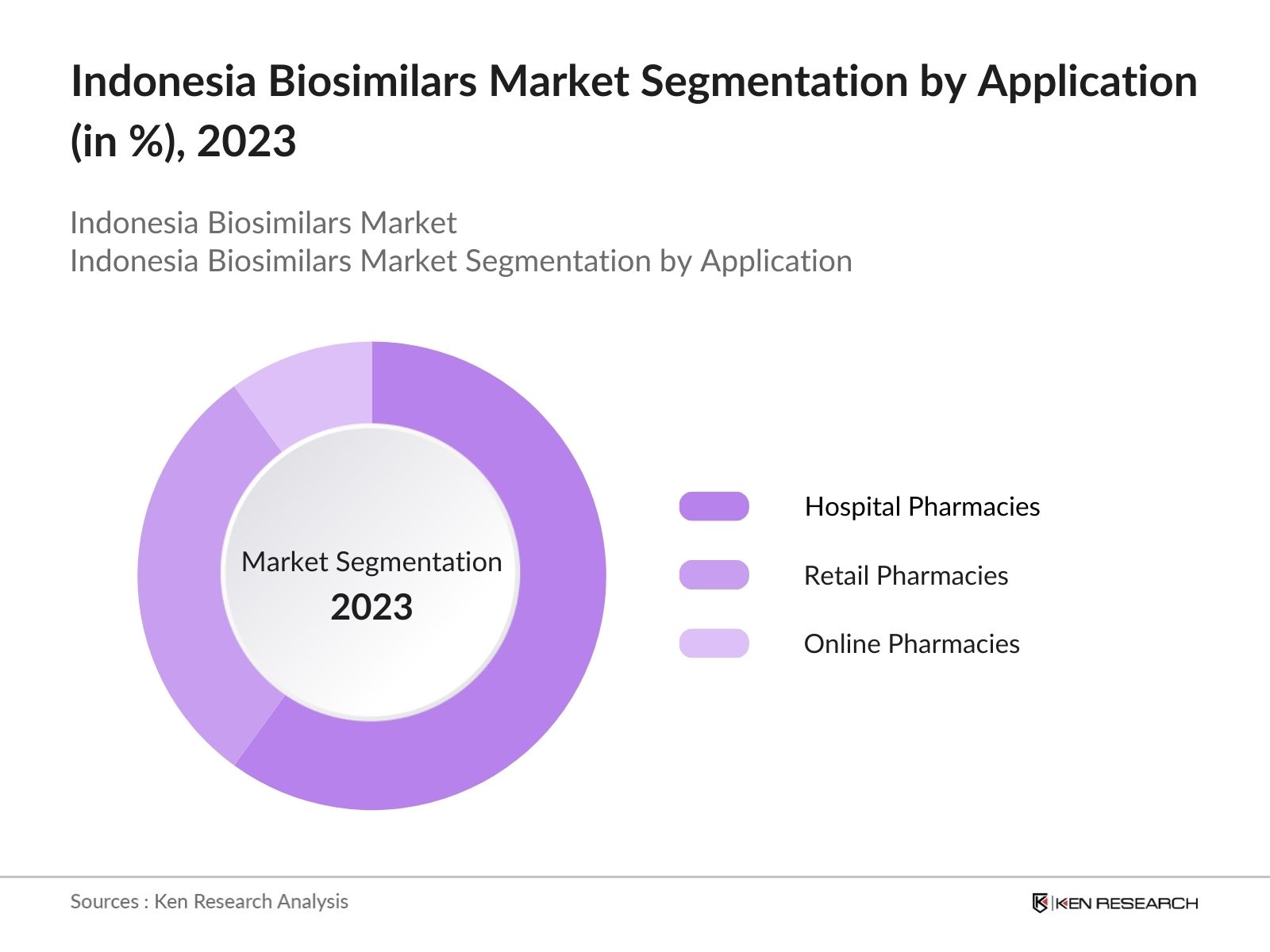
By Application: The market is segmented by application into hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and online pharmacies. Hospital pharmacies lead the market under the application segmentation. This is attributed to hospitals being the primary point of care for patients requiring biologics and biosimilars. Furthermore, hospitals in Indonesia are partnering with biosimilar manufacturers to provide affordable treatments to patients, especially those with chronic conditions requiring long-term therapy. The availability of healthcare professionals in hospitals to guide patients on biosimilar use further boosts hospital pharmacies as the dominant distribution channel.
Indonesia Biosimilars Market Competitive Landscape
The Indonesia biosimilars market is dominated by a few key players, including both international pharmaceutical giants and domestic manufacturers. Companies such as Biocon, Pfizer, and Samsung Bioepis are prominent due to their vast portfolios of biosimilars and their strong distribution networks in the region. Local manufacturers are also making significant inroads, benefiting from government support aimed at promoting local production and reducing dependence on imported biologics.
|
Company |
Established |
Headquarters |
Specialization |
Market Presence |
R&D Focus |
Key Products |
Strategic Partnerships |
Distribution Strength |
Revenue |
|
PT Kalbio Global Medika |
2010 |
Jakarta |
|||||||
|
Novartis |
1996 |
Switzerland |
|||||||
|
Sanbe Farma |
1975 |
Jakarta |
|||||||
|
Roche |
1896 |
Switzerland |
|||||||
|
Biocon |
1978 |
India |
Indonesia Biosimilars Industry Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Cost-effective Biologics: Biosimilars offer an economically viable solution in Indonesia's healthcare system, which is struggling with rising costs of biologic therapies. The World Bank indicates that Indonesias healthcare expenditure reached IDR 1,800 trillion in 2023, with biologics accounting for a substantial portion. Biosimilars provide a cheaper alternative, often priced 30-40% lower than their reference biologics. This price difference is crucial in expanding access to life-saving treatments for underserved populations, helping the government to manage healthcare costs more effectively.
Government Support and Regulatory Approvals: The Indonesian government has been instrumental in fostering biosimilars adoption through regulatory and policy support. In 2024, the National Agency of Drug and Food Control (BPOM) fast-tracked the approval of 15 new biosimilars, allowing for quicker market entry. The governments support is backed by its aim to reduce dependence on expensive imported biologics and promote local manufacturing of biosimilars. Additionally, incentives such as tax exemptions and reduced regulatory barriers have encouraged domestic and foreign pharmaceutical companies to invest in the production and distribution of biosimilars.
Expanding Healthcare Infrastructure: Indonesias healthcare infrastructure is rapidly improving, with the government committing over IDR 300 trillion to healthcare development in 2023. This expansion has led to the construction of more hospitals, clinics, and healthcare facilities, improving access to advanced treatments like biosimilars. By 2024, the number of hospitals in Indonesia is expected to reach 3,500, up from 2,870 in 2021. This improvement in healthcare services has directly contributed to the growing demand for biosimilars, which are essential for treating chronic diseases in these expanding facilities.
Market Challenges
Stringent Regulatory Pathways: The regulatory approval process for biosimilars in Indonesia remains stringent. The National Agency of Drug and Food Control (BPOM) imposes rigorous clinical testing and documentation requirements. On average, it takes 5-7 years for biosimilars to gain full regulatory approval, causing delays in market entry. Moreover, the cost associated with fulfilling these regulatory requirements is often high, adding to the financial burden on manufacturers. This lengthy process discourages smaller companies from entering the market, reducing the overall availability of biosimilars for patients.
High Manufacturing Costs: Manufacturing biosimilars is a complex and expensive process. Although biosimilars are typically less costly than biologics, the development and production still require significant financial resources. In Indonesia, local companies face high operational costs, with biosimilar production costs exceeding IDR 10 billion per batch, owing to the need for specialized facilities and skilled labor. These high costs limit the number of domestic producers, which in turn affects the supply of biosimilars in the Indonesian market.
Indonesia Biosimilars Market Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Indonesia biosimilars market is expected to grow significantly, driven by government support for healthcare infrastructure, an increasing number of biosimilar approvals, and rising public awareness regarding the affordability of biosimilars compared to branded biologics. Technological advancements in biosimilar production and international collaborations with local manufacturers are also anticipated to fuel market growth. The expansion of healthcare services in rural and underserved areas of Indonesia will further contribute to the growing demand for biosimilars across the country.
Future Market Opportunities
International Biosimilar Launches in Indonesia: Indonesia is becoming an attractive market for global pharmaceutical companies launching biosimilars. In 2024, global giants like Pfizer and Amgen introduced 5 new biosimilars in Indonesia, targeting oncology and autoimmune diseases. This influx of international biosimilars is expected to boost competition and provide patients with more treatment options. The government's commitment to faster regulatory approvals for foreign biosimilars has also contributed to this opportunity, with many more launches expected over the next few years.
Expanding Biosimilar Portfolio by Domestic Companies: Local pharmaceutical companies in Indonesia are expanding their biosimilar portfolios to meet growing demand. PT Kalbe Farma and PT Bio Farma have introduced 3 new biosimilar drugs into the Indonesian market by mid-2024, focusing on oncology and diabetes treatments. These domestic companies are expected to play a vital role in reducing Indonesia's dependency on imported biosimilars and making these treatments more affordable and accessible to local populations. The expansion of domestic portfolios aligns with the governments push to support local production.
Scope of the Report
|
Segment |
Sub-segments |
|---|---|
|
Product Type |
Oncology Biosimilars Autoimmune Biosimilars Diabetes Biosimilars Other Therapeutic Biosimilars |
|
Application |
Hospital Pharmacies Retail Pharmacies Online Pharmacies |
|
Manufacturing Type |
In-house Manufacturing Outsourced Manufacturing |
|
Region |
Java Sumatra Sulawesi Kalimantan Papua |
Major Players in the Indonesia Biosimilars Market
- Biocon
- Pfizer
- Samsung Bioepis
- Celltrion
- Mylan
- Dr. Reddys Laboratories
- Amgen
- Zydus Cadila
- Novartis (Sandoz)
- Eli Lilly
- Fresenius Kabi
- Aurobindo Pharma
- Reliance Life Sciences
- Apotex
- Cipla
Products
Key Target Audience
Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
Biosimilar Developers
Healthcare Providers
Hospital Networks
Government and Regulatory Bodies (Indonesia FDA, Ministry of Health)
Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
Banks and Financial institutes
Local Distributors
Public Health Organizations
Table of Contents
1. Indonesia Biosimilars Market Overview
1.1. Definition and Scope
1.2. Market Taxonomy
1.3. Market Growth Rate
1.4. Market Segmentation Overview
2. Indonesia Biosimilars Market Size (In USD Bn)
2.1. Historical Market Size
2.2. Year-On-Year Growth Analysis
2.3. Key Market Developments and Milestones
3. Indonesia Biosimilars Market Analysis
3.1. Growth Drivers
3.1.1. Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
3.1.2. Rising Demand for Cost-effective Biologics
3.1.3. Government Support and Regulatory Approvals
3.1.4. Expanding Healthcare Infrastructure
3.2. Market Challenges
3.2.1. Stringent Regulatory Pathways (Market-specific: Indonesia FDA regulations)
3.2.2. High Manufacturing Costs
3.2.3. Limited Patient Awareness and Acceptance
3.3. Opportunities
3.3.1. Emerging Biotech Partnerships
3.3.2. International Biosimilar Launches in Indonesia
3.3.3. Expanding Biosimilar Portfolio by Domestic Companies
3.4. Trends
3.4.1. Entry of Global Pharmaceutical Companies
3.4.2. Focus on Oncology and Autoimmune Diseases
3.4.3. Growing Adoption of Subcutaneous Formulations
3.5. Government Regulations
3.5.1. Local Content Requirements (Indonesia-specific: TKDN policy)
3.5.2. Accelerated Approval Process for Biosimilars
3.5.3. Public-Private Partnerships for Healthcare Innovation
3.6. SWOT Analysis
3.7. Stakeholder Ecosystem
3.8. Porters Five Forces Analysis
3.9. Competition Ecosystem
4. Indonesia Biosimilars Market Segmentation
4.1. By Product Type (In Value %)
4.1.1. Oncology Biosimilars
4.1.2. Autoimmune Biosimilars
4.1.3. Diabetes Biosimilars
4.1.4. Other Therapeutic Biosimilars
4.2. By Application (In Value %)
4.2.1. Hospital Pharmacies
4.2.2. Retail Pharmacies
4.2.3. Online Pharmacies
4.3. By Manufacturing Type (In Value %)
4.3.1. In-house Manufacturing
4.3.2. Outsourced Manufacturing
4.4. By Region (In Value %)
4.4.1. Java
4.4.2. Sumatra
4.4.3. Sulawesi
4.4.4. Kalimantan
4.4.5. Papua
5. Indonesia Biosimilars Market Competitive Analysis
5.1. Detailed Profiles of Major Competitors
5.1.1. Biocon
5.1.2. Pfizer
5.1.3. Samsung Bioepis
5.1.4. Celltrion
5.1.5. Mylan
5.1.6. Dr. Reddys Laboratories
5.1.7. Amgen
5.1.8. Zydus Cadila
5.1.9. Novartis (Sandoz)
5.1.10. Eli Lilly
5.1.11. Fresenius Kabi
5.1.12. Aurobindo Pharma
5.1.13. Reliance Life Sciences
5.1.14. Apotex
5.1.15. Cipla
5.2. Cross Comparison Parameters (No. of Employees, Headquarters, Revenue, Number of Product Approvals, Manufacturing Facilities, Therapeutic Focus, Market Share, Strategic Alliances)
5.3. Market Share Analysis
5.4. Strategic Initiatives (Product Launches, Collaborations, Partnerships)
5.5. Mergers and Acquisitions
5.6. Investment Analysis
5.7. Venture Capital Funding
5.8. Government Grants
5.9. Private Equity Investments
6. Indonesia Biosimilars Market Regulatory Framework
6.1. Local Regulatory Body Guidelines (Indonesia FDA)
6.2. Intellectual Property and Patent Landscape
6.3. Compliance Requirements
6.4. Market Entry Barriers for Foreign Manufacturers
7. Indonesia Biosimilars Future Market Size (In USD Bn)
7.1. Future Market Size Projections
7.2. Key Factors Driving Future Market Growth
8. Indonesia Biosimilars Future Market Segmentation
8.1. By Product Type (In Value %)
8.2. By Application (In Value %)
8.3. By Manufacturing Type (In Value %)
8.4. By Region (In Value %)
9. Indonesia Biosimilars Market Analysts Recommendations
9.1. TAM/SAM/SOM Analysis
9.2. Customer Cohort Analysis
9.3. Market Penetration Strategy
9.4. White Space Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first phase entails mapping the biosimilars ecosystem in Indonesia, identifying all major stakeholders including local and international pharmaceutical companies. This is supported by extensive desk research using secondary databases, focusing on understanding the factors influencing market growth.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This phase involves the aggregation and analysis of historical data regarding biosimilar sales, market penetration, and the regulatory environment in Indonesia. The data collected is cross-referenced with national healthcare initiatives and government funding allocations.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We conduct detailed interviews with industry experts from major pharmaceutical firms, biosimilar manufacturers, and healthcare providers. These interviews validate the market data and provide key insights into the operational challenges and opportunities in the market.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Finally, a synthesis of all collected data is conducted, with inputs from industry experts ensuring the accuracy of the market projections. The report is then reviewed to ensure that it reflects a comprehensive analysis of the biosimilars market in Indonesia.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. How big is the Indonesia Biosimilars Market?
The Indonesia biosimilars market is valued at USD 210 million, driven by increasing demand for cost-effective alternatives to biologics and supported by favorable government policies.
02. What are the challenges in the Indonesia Biosimilars Market?
Challenges in the Indonesia biosimilars market include stringent regulatory pathways, high costs of biosimilar development, and a lack of patient awareness about the benefits of biosimilars compared to branded biologics.
03. Who are the major players in the Indonesia Biosimilars Market?
Key players in the Indonesia biosimilars market include Biocon, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, Celltrion, and Mylan, which dominate due to their extensive biosimilar portfolios and established distribution networks in Indonesia.
04. What are the growth drivers of the Indonesia Biosimilars Market?
The Indonesia biosimilars market is driven by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increasing healthcare costs, and supportive government policies that promote biosimilar use as a cost-effective alternative.
05. What opportunities exist in the Indonesia Biosimilars Market?
Opportunities in the Indonesia biosimilars market include increased international collaboration, the expansion of local biosimilar manufacturing facilities, and greater investment in R&D to develop new biosimilars for unmet medical needs.
Why Buy From Us?

What makes us stand out is that our consultants follows Robust, Refine and Result (RRR) methodology. i.e. Robust for clear definitions, approaches and sanity checking, Refine for differentiating respondents facts and opinions and Result for presenting data with story

We have set a benchmark in the industry by offering our clients with syndicated and customized market research reports featuring coverage of entire market as well as meticulous research and analyst insights.

While we don't replace traditional research, we flip the method upside down. Our dual approach of Top Bottom & Bottom Top ensures quality deliverable by not just verifying company fundamentals but also looking at the sector and macroeconomic factors.

With one step in the future, our research team constantly tries to show you the bigger picture. We help with some of the tough questions you may encounter along the way: How is the industry positioned? Best marketing channel? KPI's of competitors? By aligning every element, we help maximize success.

Our report gives you instant access to the answers and sources that other companies might choose to hide. We elaborate each steps of research methodology we have used and showcase you the sample size to earn your trust.

If you need any support, we are here! We pride ourselves on universe strength, data quality, and quick, friendly, and professional service.















