Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Outlook to 2029
Region:Asia
Author(s):Kartik and Nishika
Product Code:KR1485
April 2025
80-120
About the Report
Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Overview
The Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market is valued at USD 2,580 million, based on a five-year historical analysis, driven by pandemic-induced mass testing, increased healthcare awareness, and widespread private sector investments in diagnostics infrastructure, propelled by consistent demand for evidence-based treatments, rising health insurance penetration, and a continued shift toward esoteric and molecular diagnostics.

Greater Jakarta dominates the clinical laboratory market in Indonesia due to its dense population, growing geriatric demographic, and presence of corporate clientele. The region alone contributes over one-third of the independent diagnostic lab revenue. Other high-performing provinces include West Java and East Java, which benefit from a high population base and accessibility to urban healthcare infrastructure. Kalimantan is an emerging cluster due to infrastructure investments following its proposed status as Indonesias new capital.
All clinical labs in Indonesia must obtain licensing via the Pelayanan Terpadu Satu Pintu (PTSP) system. This involves document submission, GCLP certification, inspection reports, and field verification. Additionally, accreditation is mandated by the National Accreditation Committee (KAN) and includes online registration, a USD 300 assessment fee, feasibility tests, and field visits. Licenses typically require renewal every five years. In 2023, the MoH digitized this process to ensure transparency, with over 2,000 facilities onboarded under the revised licensing norms.
Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Segmentation
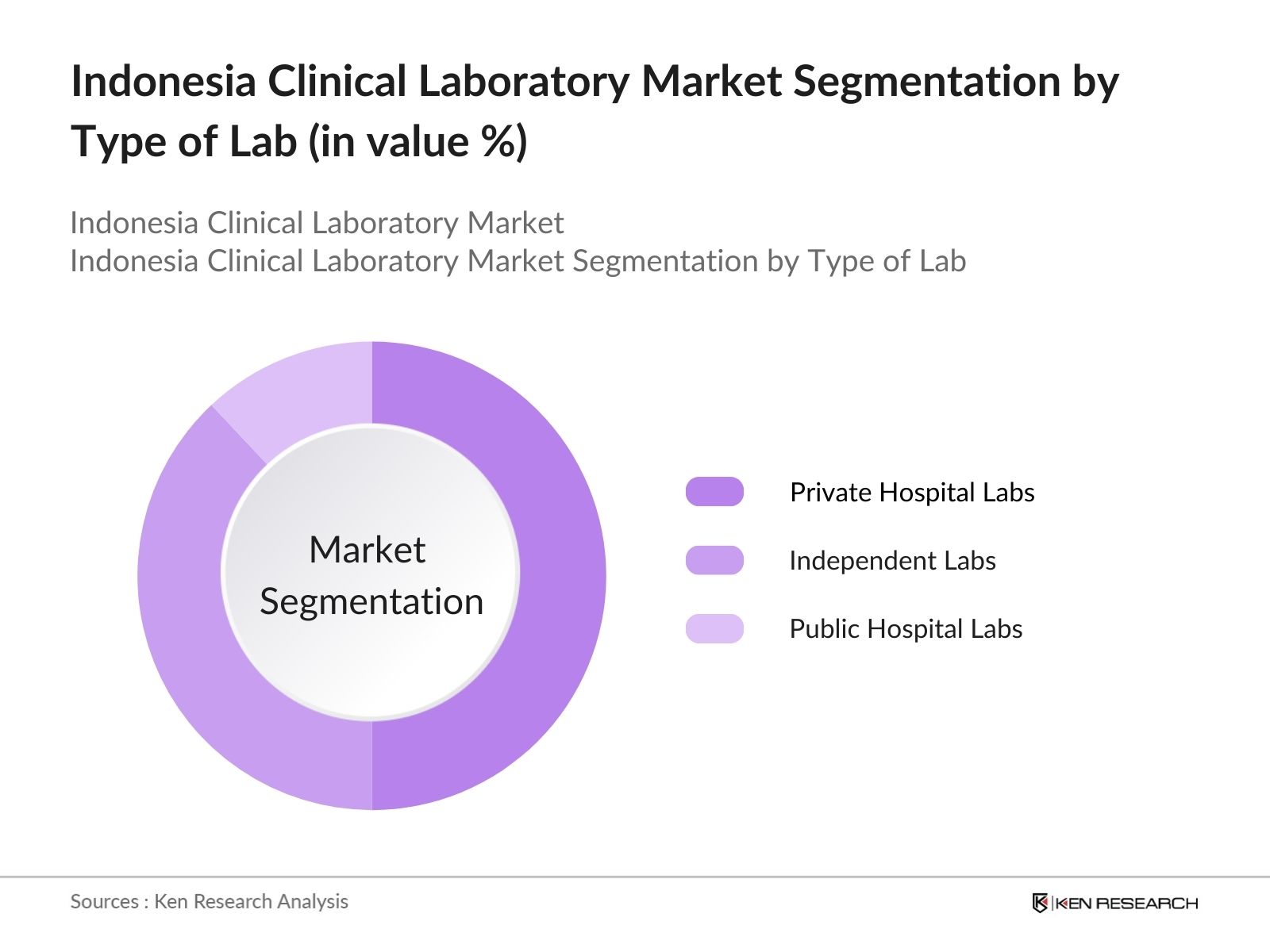
By Type of Lab: Indonesias clinical lab market is segmented by lab type into private hospital labs, independent labs, and public hospital labs. Private hospital labs dominate the market due to their established infrastructure, direct access to in-patients, and extensive third-party partnerships. Their integration with hospital systems and strong capital investment allows rapid adoption of automated diagnostic platforms and specialty testing services.
By Type of Test: The clinical laboratory market in Indonesia is segmented into routine, esoteric, and non-laboratory tests. Routine tests currently hold the dominant market share. This is primarily due to high frequency (35 tests/person annually), low cost ($615/test), and the wide availability of coverage under the JKN health insurance scheme. Urbanization and chronic lifestyle-related conditions further reinforce the reliance on routine testing.
 Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Competitive Landscape
Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Competitive Landscape
The Indonesia Clinical Lab Market is characterized by a consolidated leadership structure with players like Prodia and Kimia Farma, followed by fast-growing innovators such as CITO and Parahita. Visionary players are driving regional expansion and tech adoption, while niche players such as Bio Medika focus on corporate tie-ups and specialized diagnostics.

Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing Demand for Temperature-Sensitive Products: The UAE's rising demand for frozen meat, seafood, and confectioneries, coupled with its hot climate, has made cold storage a necessity. With 88% urbanization and increasing disposable income, consumer expectations are shifting towards quality and safety, further boosting the adoption of ambient and chilled storage for perishable goods across retail, hospitality, and pharmaceutical sectors.
Infrastructure Investments: A government-backed AED 128.5 billion investment in logistics infrastructure, including roads, hyperloop, and the Etihad Rail network, is strengthening cold chain connectivity. Free zones like Jebel Ali and Dubai South are offering incentives such as 100% FDI and expedited customs clearance, making the UAE a strategic logistics hub for cross-border cold storage operations and regional re-export distribution.
Growth of Pharma Industry: With a 21.0% share in 2024, the pharmaceutical sector is the largest cold chain user in the UAE. The market is projected to reach AED 17.3 billion by 2025, supported by 23 manufacturing units and 2,500 locally produced medicines. The sector's expansion is driving specialized infrastructure needs for vaccine, biologic, and temperature-sensitive drug storage.
Market Challenges
High Capital and Operating Costs: Setting up a mid-sized cold chain warehouse with 58,000 pallet positions can cost over AED 76 million, with forklifts alone priced at AED 1.1 lakh each. Additionally, labor and electricity account for nearly 40% of recurring costs, making profitability difficult without automation and high operational efficiency across facilities.
Entry Barriers and Profit Pressure: Cold chain players face steep entry barriers, with minimum occupancy levels of 60-62% needed to breakeven. Price competition remains intense, as larger players push average pallet rates down to AED 2.22.8 per day. These challenges limit market entry for smaller logistics providers and constrain long-term profitability margins.
Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market is expected to experience sustained growth led by insurance-led demand, automation, and molecular innovation. The governments increased healthcare budget of USD 12 billion, alongside reforms such as telepathology and international partnerships for genomic research, will drive market expansion. Emerging players will focus on underserved regions like Kalimantan and Sulawesi, while established labs are expected to increase test volumes and specialization.
Market Opportunities
Tech-Driven Transformation: Emerging technologies like IoT, Blockchain, and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are revolutionizing the cold chain industry by offering real-time traceability and fraud reduction. Automation through AGVs and ASRS systems is enabling companies to minimize human error and reduce space utilization by up to 85%, significantly enhancing operational resilience and scalability.
Greener Logistics and Sustainability: Green initiatives such as solar-powered warehouses, EV-based delivery fleets, and advanced cooling systems are transforming logistics sustainability. Innovations like truck platooning are expected to reduce CO emissions by 10% and cut fuel costs by up to 8%, helping companies align with environmental goals while improving energy efficiency and cost savings.
Scope of the Report
|
Type of Lab |
Independent Labs |
|
Type of Test |
Routine Tests |
|
Region |
Greater Jakarta |
|
Referral Source |
Doctor Referrals |
|
Ownership Model |
In-House Labs |
Products
Key Target Audience
Private Healthcare Providers
Hospital Chains and Multi-Specialty Groups
Diagnostic Equipment Manufacturers
Digital Health and Telemedicine Startups
Government and Regulatory Bodies (Ministry of Health, BPJS Kesehatan)
Public-Private Health Partnerships (KAN, PTSP)
Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
Regional Health Insurance Providers and TPAs
Companies
Players Mentioned in the Report
Prodia
Kimia Farma Diagnostika
Diagnos
Parahita Diagnostic Center
CITO Laboratorium Klinik
Table of Contents
1. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Overview
1.1. Definition and Scope
1.2. Market Taxonomy
1.3. Healthcare Ecosystem Overview
1.4. Evolution and Lifecycle of Diagnostic Labs
1.5. Testing Volume Trend and Frequency Metrics
2. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Size (In USD Mn)
2.1. Historical Revenue Performance (Revenue, Testing Volume, Avg. Price per Test)
2.2. Growth Phases: Stable, Surge, Stabilization (Pandemic Surge, Diversification, Esoteric Uptake)
2.3. Volume-Based Growth: Annual Tests per Lab, Labs per Region
2.4. Key Milestones: Insurance Reforms, Health Budget Allocation, NCD Trends
2.5. Investment Trends in Lab Infrastructure and Equipment Upgradation
3. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Analysis
3.1. Growth Drivers
3.1.1. National Insurance (JKN) Coverage Expansion
3.1.2. Urban Health Awareness & Lifestyle Shift
3.1.3. Rise in NCDs, Geriatric Population & Chronic Disease Prevalence
3.1.4. Government Budget Push for Health Tech
3.2. Restraints
3.2.1. Shortage of Medical Specialists (0.17 per 1,000)
3.2.2. Accreditation Gaps in Private Labs (Only 16% KAN Certified)
3.2.3. Regulatory Delays & Lab Licensing Challenges
3.3. Opportunities
3.3.1. Telepathology Expansion in Rural Indonesia
3.3.2. Digital Health Transformation & Home Collection Integration
3.3.3. Partnerships for Genomic Research & Molecular Diagnostics
3.4. Trends
3.4.1. AI & Machine Learning in Predictive Diagnostics
3.4.2. Rapid Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) in Outpatient Units
3.4.3. Online Healthcare Platforms Integration (e.g., Halodoc, YesDok)
3.5. Government Regulation
3.5.1. PTSP Licensing via Surat Izin Praktik (SIP)
3.5.2. KAN Accreditation Flow (Online Registration to Field Audit)
3.5.3. Mandatory Compliance with CDAKB & GCLP Guidelines
3.5.4. BPJS & e-Catalogue Lab Service Inclusion
3.6. SWOT Analysis
3.7. Stakeholder Ecosystem Mapping (MOH, BPJS, Lab Chains, Insurers)
3.8. Porters Five Forces Analysis
3.9. Competition & Innovation Ecosystem (New Tech Adoption, Collaboration Patterns)
4. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Segmentation
4.1. By Type of Lab (In Revenue %)
4.1.1. Independent Labs
4.1.2. Private Hospital Labs
4.1.3. Public Hospital Labs
4.2. By Type of Test (In Revenue %)
4.2.1. Routine Tests (CBC, BMP, HbA1c)
4.2.2. Esoteric Tests (Endocrine, Oncology, Infectious Disease, Genetic)
4.2.3. Non-Laboratory Services (X-Ray, Imaging, Colonoscopy)
4.3. By Region (In Revenue %)
4.3.1. Greater Jakarta
4.3.2. West Java
4.3.3. Central & East Java
4.3.4. Sumatra (North, Central, South)
4.3.5. Kalimantan & Sulawesi
4.4. By Referral Source (In Revenue %)
4.4.1. Doctor Referral
4.4.2. Corporate Clients
4.4.3. Walk-ins
4.4.4. Online & External Referrals
4.5. By Ownership Model (In Revenue %)
4.5.1. In-House Labs
4.5.2. Third Party Tie-Ups
4.5.3. Chain-Based vs. Franchise-Based Operations
5. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Competitive Analysis
5.1. Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
5.1.1. Prodia
5.1.2. Kimia Farma Diagnostika
5.1.3. Parahita Diagnostic Center
5.1.4. Klinik Laboratorium CITO
5.1.5. Diagnos
5.2. Cross Comparison Parameters (Headquarters, Year of Establishment, No. of Labs, No. of Tests/Year, Automation Level, Accreditation Status, In-House or Franchise, Digital Interface Availability)
5.3. Market Share Analysis (Revenue and Test Volume)
5.4. Strategic Initiatives (Lab Expansion, Partnerships, Automation)
5.5. Mergers & Acquisitions (Lab Consolidations in Urban Centers)
5.6. Investor Analysis (Foreign & Domestic Funding Patterns)
5.7. VC & PE Trends in Health Diagnostics
5.8. Government Tenders & Lab Service Bidding (e-Catalogue)
5.9. Collaborations with Hospitals, Insurers, and Online HealthTech Platforms
6. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Regulatory & Compliance Landscape
6.1. Role of PTSP, BPJS, and MoH in Licensing
6.2. KAN Accreditation Metrics and Certification Bodies
6.3. CDAKB, TKDN & Halal Certification Compliance
6.4. Insurance Integration through BPJS and Ministry Guidelines
6.5. Lab Safety Standards and GCLP Compliance Checks
7. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Future Market Size (In USD Mn)
7.1. Revenue and Test Volume Forecasts (Tests per Capita, Lab Penetration Growth)
7.2. Regional Demand Forecast (Kalimantan, East Java, Greater Jakarta)
7.3. Expansion of Esoteric & Molecular Diagnostics
7.4. Healthcare Digitization and Policy-Driven Forecast
8. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Future Market Segmentation
8.1. By Type of Lab (In Revenue %)
8.2. By Type of Test (In Revenue %)
8.3. By Region (In Revenue %)
8.4. By Referral Source (In Revenue %)
8.5. By Ownership Model (In Revenue %)
9. Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Analysts Recommendations
9.1. Total Addressable Market (TAM) Estimation
9.2. Market Entry & Expansion Strategy (Urban vs. Rural Labs)
9.3. Investment Opportunities in Esoteric & AI Diagnostics
9.4. Business Model Optimization (Franchise vs. Centralized Labs)
9.5. Target Customer Clusters & Online Referral Optimization
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This stage involved building a comprehensive ecosystem model for Indonesias Clinical Laboratory Market by identifying test categories, lab types, and their operating structures. Regulatory insights were gathered from BPJS, PTSP, and KAN documentation.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We analyzed test volume data, average pricing, and lab-wise segmentation. Data from government databases and local health departments was integrated to ensure completeness in forecasting and trend validation.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Diagnostic professionals from 10+ clinical labs participated in structured interviews. These inputs verified the test adoption cycle, investment plans, and automation strategies of leading players.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights from private hospital and independent labs were consolidated to validate growth projections, regional expansion, and government reforms. This synthesis enabled final data modeling and policy-aligned recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. How big is the Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market?
The Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market was valued at USD 2,580 million. It is primarily driven by increased healthcare testing volumes, rising insurance adoption, and public-private diagnostic infrastructure growth.
02. What are the challenges in the Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market?
Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Key challenges include a shortage of medical professionals, with only 49,425 specialists for over 275 million citizens, and a large portion of private labs remaining unaccredited and non-compliant with BPJS reimbursement norms.
03. Who are the major players in the Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market?
The Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market is led by Prodia, Kimia Farma Diagnostika, CITO, Parahita, and Diagnos. These companies dominate through network expansion, advanced diagnostic platforms, and strategic partnerships.
04. What are the growth drivers of the Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market?
In Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Growth is driven by 90% JKN health coverage, increasing claims worth USD 4.9 billion, and a 70% surge in telemedicine consultations, showing strong diagnostics adoption across urban and rural areas.
05. What types of tests are most commonly conducted?
In Indonesia Clinical Laboratory Market Routine tests are most common, including hematology, liver/kidney function, and urinalysis. Esoteric tests such as endocrine and molecular diagnostics are gaining traction due to chronic disease prevalence.
Why Buy From Us?

What makes us stand out is that our consultants follows Robust, Refine and Result (RRR) methodology. i.e. Robust for clear definitions, approaches and sanity checking, Refine for differentiating respondents facts and opinions and Result for presenting data with story

We have set a benchmark in the industry by offering our clients with syndicated and customized market research reports featuring coverage of entire market as well as meticulous research and analyst insights.

While we don't replace traditional research, we flip the method upside down. Our dual approach of Top Bottom & Bottom Top ensures quality deliverable by not just verifying company fundamentals but also looking at the sector and macroeconomic factors.

With one step in the future, our research team constantly tries to show you the bigger picture. We help with some of the tough questions you may encounter along the way: How is the industry positioned? Best marketing channel? KPI's of competitors? By aligning every element, we help maximize success.

Our report gives you instant access to the answers and sources that other companies might choose to hide. We elaborate each steps of research methodology we have used and showcase you the sample size to earn your trust.

If you need any support, we are here! We pride ourselves on universe strength, data quality, and quick, friendly, and professional service.















