Indonesia Vegetable Market Outlook to 2030
Region:Asia
Author(s):Abhinav kumar
Product Code:KROD3667
December 2024
85
About the Report
Indonesia Vegetable Market Overview
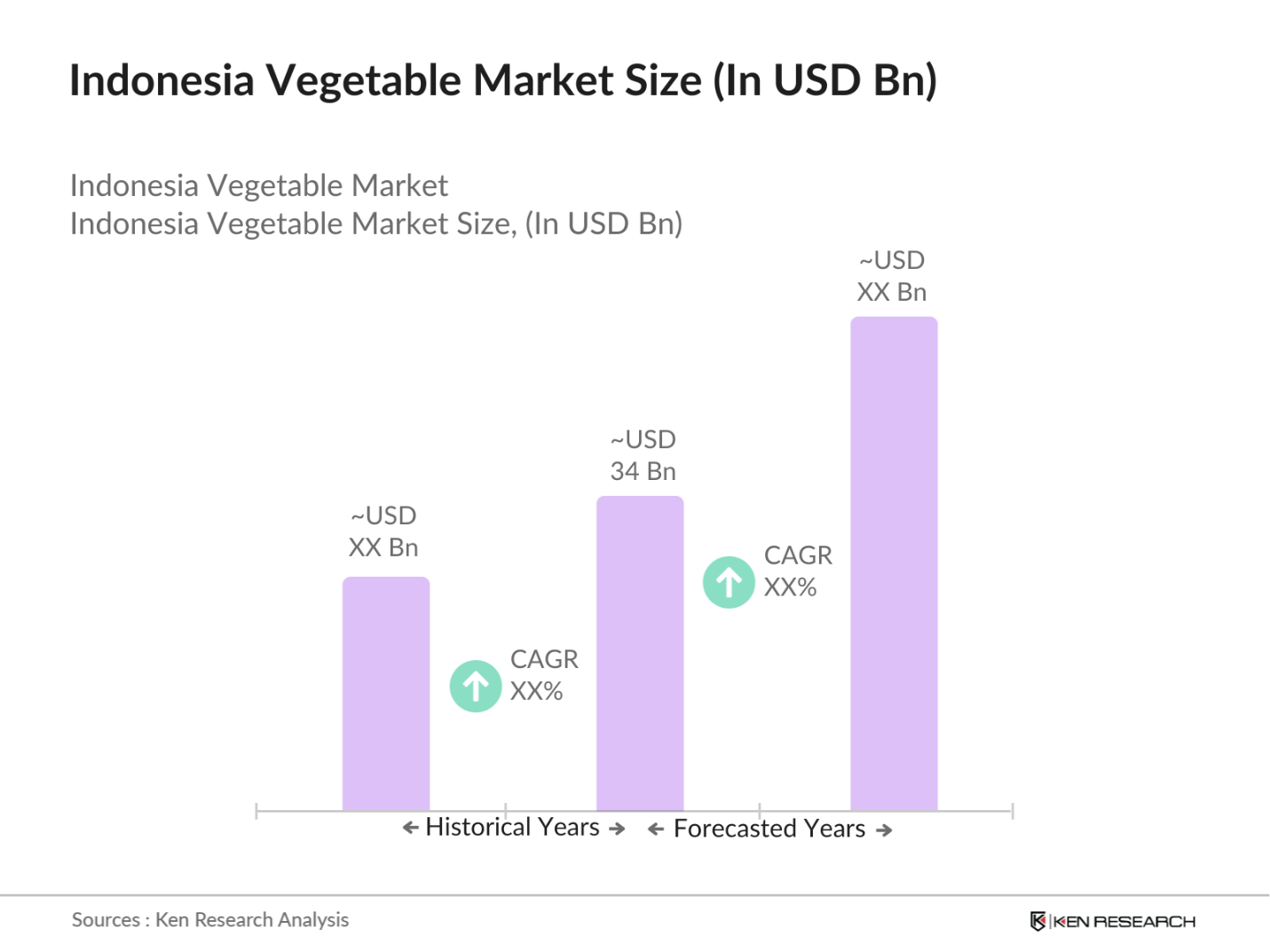
- The Indonesia Vegetable Market is valued at USD 34 billion, driven by increasing domestic consumption and export opportunities within Southeast Asia. The market has experienced consistent demand due to the rising population, growing health consciousness, and a shift toward organic and fresh produce. Government initiatives to boost agricultural output and technological advancements, such as precision farming and vertical agriculture, have further accelerated growth in the sector. These factors continue to provide strong momentum, ensuring the sustained expansion of this market.
- Java and Sumatra are the dominant regions within the Indonesia vegetable market, due to their fertile agricultural lands and well-established infrastructure. Java, in particular, benefits from its proximity to major cities like Jakarta, where urban demand for fresh vegetables is high. Sumatra also plays a key role due to its large-scale farming operations, which produce a significant portion of the nations export vegetables. The dominance of these regions is attributed to optimal climatic conditions, better logistics networks, and governmental support for modern farming techniques.
- The Indonesian government offers various subsidies and support programs to enhance agricultural productivity. In 2024, approximately IDR 7 trillion (about USD 470 million) is allocated for agricultural subsidies, targeting seeds, fertilizers, and infrastructure improvements. These subsidies aim to support vegetable farmers, improve crop yields, and stabilize prices. Additionally, the government has implemented training programs to educate farmers on best practices, fostering a more resilient agricultural sector and ensuring food security.
Indonesia Vegetable Market Segmentation
By Vegetable Type: Indonesias vegetable market is segmented by vegetable type into leafy vegetables, root vegetables, fruit vegetables, and legumes. Recently, leafy vegetables hold a dominant share within this segment due to the increasing demand for healthier food options among consumers. Leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and lettuce have gained popularity owing to their nutritional benefits and the rising trend of clean eating in urban areas. Moreover, advancements in farming techniques like hydroponics have made leafy vegetables more accessible throughout the year, bolstering their market share.

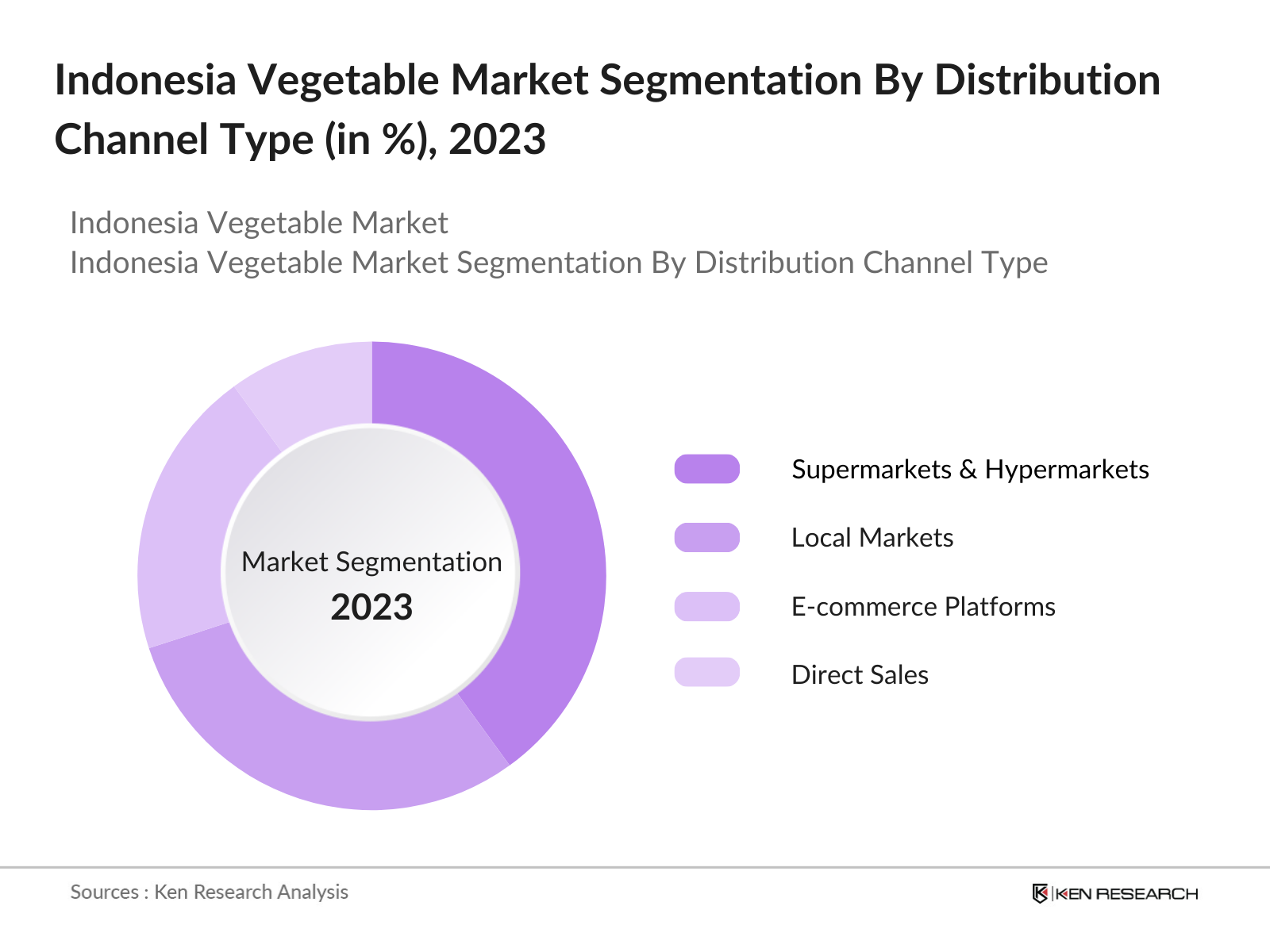
By Distribution Channel: In terms of distribution channels, the Indonesia vegetable market is segmented into supermarkets and hypermarkets, local markets, e-commerce platforms, and direct sales (farmers to consumers). Supermarkets and hypermarkets currently dominate this segment due to their extensive reach, growing urbanization, and consumer preference for one-stop shopping experiences. As more Indonesians move to cities, they increasingly rely on modern retail chains for access to fresh produce, which is why this channel holds a significant share of the distribution market.
Indonesia Vegetable Market Competitive Landscape
The Indonesia vegetable market is dominated by a mix of local and international players, with companies like PT East West Seed Indonesia and PT TaniHub Group holding significant influence. The market is characterized by a robust competitive ecosystem, with both domestic and multinational firms vying for market share by leveraging their extensive distribution networks, strong brand presence, and diverse product portfolios. The consolidation of these players highlights their ability to meet the growing consumer demand while ensuring quality and scalability in production.
|
Company Name |
Establishment Year |
Headquarters |
No. of Employees |
Revenue (USD) |
Market Penetration |
Key Product Type |
Distribution Channel |
Sustainability Initiatives |
|
PT East West Seed Indonesia |
1982 |
Purwakarta, Indonesia |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
PT TaniHub Group |
2016 |
Jakarta, Indonesia |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
PT Sumber Tani Agung |
1971 |
Medan, Indonesia |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
PT BISI International Tbk |
1983 |
Kediri, Indonesia |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
PT Sewu Segar Nusantara |
1995 |
Jakarta, Indonesia |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Indonesia Vegetable Industry Analysis
Growth Drivers
- Urbanization and Population Growth: Indonesia's rapid urbanization is a significant driver of vegetable demand. By 2025, the urban population is projected to exceed 56% of the total population, increasing the demand for fresh produce. The World Bank reports that urbanization contributes to enhanced access to markets and better infrastructure, facilitating vegetable distribution. Furthermore, with a population expected to reach approximately 277 million by 2024, the demand for vegetables will rise correspondingly. Urban areas typically experience higher consumption rates of fresh produce, supporting local farmers and increasing the market for vegetables.
- Changing Dietary Preferences: There is a notable shift towards healthier dietary choices in Indonesia, characterized by an increased demand for fresh produce and vegetarian diets. As per the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the per capita consumption of vegetables has increased to approximately 37 kilograms annually as of 2022. This trend aligns with global health movements promoting plant-based diets. Moreover, a 2022 survey indicated that 28% of Indonesian consumers are adopting vegetarian diets, signaling a substantial market opportunity for vegetable growers. This changing preference is expected to continue influencing market dynamics positively.
- Government Initiatives for Agricultural Development: The Indonesian government has implemented various initiatives to enhance agricultural productivity, including vegetable farming. The Ministry of Agriculture has allocated approximately IDR 15 trillion (about USD 1 billion) for agricultural development in 2024, focusing on improving farmer access to resources and technology. These initiatives aim to increase vegetable yields and enhance food security. Moreover, government programs promoting agricultural innovation, such as the National Agricultural Extension Program, play a crucial role in fostering a competitive vegetable market.
Market Challenges
- Climate Variability and Natural Disasters: Indonesia's geographic vulnerability to climate change presents significant challenges for the vegetable market. The frequency of natural disasters, such as floods and droughts, has increased, disrupting supply chains and affecting crop yields. In 2022, the National Disaster Management Authority reported that extreme weather events impacted approximately 500,000 hectares of agricultural land, causing substantial losses. This unpredictability can lead to decreased vegetable availability and increased prices, creating challenges for both farmers and consumers in the market.
- Limited Infrastructure and Cold Chain Facilities: Infrastructure deficiencies hinder the efficiency of vegetable distribution in Indonesia. Many rural areas lack adequate transportation and cold chain facilities, resulting in post-harvest losses estimated at 30% for vegetables. The World Bank highlights that improving rural infrastructure is crucial for reducing waste and ensuring fresh produce reaches urban markets efficiently. The government is currently investing IDR 20 trillion (about USD 1.3 billion) in infrastructure projects aimed at enhancing connectivity and supply chains, yet challenges remain prevalent.
Indonesia Vegetable Market Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Indonesia vegetable market is expected to witness significant growth, driven by increasing health awareness among consumers, continued government support for agricultural productivity, and the adoption of innovative farming techniques. Technological advancements such as precision farming and vertical agriculture are anticipated to improve yield and quality, while sustainability efforts such as organic farming practices will play a major role in meeting both domestic and export demand.
Market Opportunities
- Export Potential to ASEAN and Global Markets: Indonesia's vegetable sector holds substantial export potential, particularly to ASEAN and global markets. In 2022, the country's vegetable exports reached IDR 4 trillion (approximately USD 270 million), with significant opportunities for growth identified in countries like Singapore and Malaysia. As global demand for fresh produce increases, especially for organic vegetables, Indonesian farmers can capitalize on this trend. The government is working on trade agreements and improving quality standards to facilitate exports further, enhancing market prospects for local producers.
- Adoption of Organic Farming Practices: The rise in consumer awareness regarding health and sustainability is driving the adoption of organic farming practices in Indonesia. As of 2023, approximately 10% of vegetable producers are transitioning to organic methods, with organic vegetable sales expected to grow. The Ministry of Agriculture supports this shift by providing training and subsidies for organic certification, with an aim to increase the organic farming area to 500,000 hectares by 2025. This trend aligns with global sustainability goals and positions Indonesian vegetables favorably in international markets.
Scope of the Report
|
Vegetable Type |
Leafy Vegetables Root Vegetables Fruit Vegetables Legumes |
|
Farming Technique |
Traditional Farming Organic Farming Hydroponic Farming Vertical Farming |
|
Distribution Channel |
Supermarkets and Hypermarkets Local Markets E-commerce Platforms Direct Sales |
|
End-Use |
Households Food Processing Industries Restaurants and Food Services |
|
Region |
Java Sumatra Bali and Nusa Tenggara Kalimantan Sulawesi |
Products
Key Target Audience Organizations and Entities Who Can Benefit by Subscribing to This Report:
Agricultural Commodity Companies
Fresh Produce Companies
Government and Regulatory Bodies (Ministry of Agriculture)
Investment and Venture Capitalist Firms
Food Processing Companies
Exporter Companies of Agricultural Products
E-commerce Platforms for Fresh Produce Companies
Companies
Players Mentioned in the Report:
PT East West Seed Indonesia
PT TaniHub Group
PT Sumber Tani Agung Resources
PT BISI International Tbk
PT Great Giant Pineapple
PT Agrosid Manunggal Sentosa
PT Primasindo
PT Panca Agro Mandiri
PT Sewu Segar Nusantara
Cargill Indonesia
Table of Contents
1. Indonesia Vegetable Market Overview
1.1. Definition and Scope
1.2. Market Taxonomy (Type of Vegetables, Farming Techniques, Distribution Channels)
1.3. Market Growth Rate (CAGR, Volume Growth)
1.4. Market Segmentation Overview
2. Indonesia Vegetable Market Size (In USD Bn)
2.1. Historical Market Size
2.2. Year-On-Year Growth Analysis
2.3. Key Market Developments and Milestones
3. Indonesia Vegetable Market Analysis
3.1. Growth Drivers
3.1.1. Urbanization and Population Growth
3.1.2. Changing Dietary Preferences (Increasing demand for fresh produce, vegetarian diets)
3.1.3. Government Initiatives for Agricultural Development
3.1.4. Technological Advancements in Farming (Hydroponics, Vertical Farming)
3.2. Market Challenges
3.2.1. Climate Variability and Natural Disasters
3.2.2. Limited Infrastructure and Cold Chain Facilities
3.2.3. Price Volatility
3.3. Opportunities
3.3.1. Export Potential to ASEAN and Global Markets
3.3.2. Adoption of Organic Farming Practices
3.3.3. Collaboration with International Agribusiness Firms
3.4. Trends
3.4.1. Shift towards Sustainable and Organic Farming
3.4.2. Increased Investments in Smart Agriculture (Precision Farming)
3.4.3. Expansion of E-commerce Channels for Vegetable Distribution
3.5. Government Regulations and Policies
3.5.1. Agricultural Subsidies and Support Programs
3.5.2. Trade Agreements for Vegetable Exports
3.5.3. Quality Standards and Certifications (SNI, Organic Certifications)
3.5.4. Import Tariffs and Duties on Vegetables
3.6. SWOT Analysis
3.7. Stake Ecosystem (Farmers, Distributors, Retailers, Exporters)
3.8. Porters Five Forces Analysis
3.9. Competition Ecosystem
4. Indonesia Vegetable Market Segmentation
4.1. By Vegetable Type (In Value %)
4.1.1. Leafy Vegetables
4.1.2. Root Vegetables
4.1.3. Fruit Vegetables
4.1.4. Legumes
4.2. By Farming Technique (In Value %)
4.2.1. Traditional Farming
4.2.2. Organic Farming
4.2.3. Hydroponic Farming
4.2.4. Vertical Farming
4.3. By Distribution Channel (In Value %)
4.3.1. Supermarkets and Hypermarkets
4.3.2. Local Markets
4.3.3. E-commerce Platforms
4.3.4. Direct Sales (Farmers to Consumers)
4.4. By End-Use (In Value %)
4.4.1. Households
4.4.2. Food Processing Industries
4.4.3. Restaurants and Food Services
4.5. By Region (In Value %)
4.5.1. Java
4.5.2. Sumatra
4.5.3. Bali and Nusa Tenggara
4.5.4. Kalimantan
4.5.5. Sulawesi
5. Indonesia Vegetable Market Competitive Analysis
5.1 Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
5.1.1. Indofood Sukses Makmur Tbk
5.1.2. PT East West Seed Indonesia
5.1.3. PT TaniHub Group
5.1.4. PT BISI International Tbk
5.1.5. PT Sumber Tani Agung Resources
5.1.6. PT Great Giant Pineapple
5.1.7. PT Agrosid Manunggal Sentosa
5.1.8. PT Panca Agro Mandiri
5.1.9. PT Sentra Boga Handal Tbk
5.1.10. PT Sewu Segar Nusantara
5.1.11. PT Primasindo
5.1.12. Cargill Indonesia
5.1.13. Bayer CropScience Indonesia
5.1.14. BASF Indonesia
5.1.15. PT Aneka Tani Nusantara
5.2 Cross Comparison Parameters (Market Share, Sales Volume, Distribution Reach, Number of Employees, Production Capacity, Sustainability Initiatives, Export Markets, Profit Margins)
5.3. Market Share Analysis
5.4. Strategic Initiatives
5.5. Mergers and Acquisitions
5.6. Investment Analysis
5.7. Venture Capital Funding
5.8. Government Grants
5.9. Private Equity Investments
6. Indonesia Vegetable Market Regulatory Framework
6.1. Agricultural Standards and Certifications
6.2. Compliance Requirements
6.3. Certification Processes
7. Indonesia Vegetable Market Future Market Size (In USD Bn)
7.1. Future Market Size Projections
7.2. Key Factors Driving Future Market Growth
8. Indonesia Vegetable Market Future Market Segmentation
8.1. By Vegetable Type (In Value %)
8.2. By Farming Technique (In Value %)
8.3. By Distribution Channel (In Value %)
8.4. By End-Use (In Value %)
8.5. By Region (In Value %)
9. Indonesia Vegetable Market Analyst Recommendations
9.1. TAM/SAM/SOM Analysis
9.2. Customer Cohort Analysis
9.3. White Space Opportunity Analysis
9.4. Marketing Initiatives
Disclaimer
Contact Us
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first step involves constructing an ecosystem map covering all stakeholders within the Indonesia Vegetable Market. This phase leverages secondary research from industry reports, government publications, and proprietary databases to identify the critical variables that impact market growth.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, we analyze historical data, including production levels, import-export figures, and pricing trends. The objective is to build a comprehensive understanding of how various sub-segments perform and their contribution to the overall market.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are formed based on the analyzed data and validated through consultations with industry experts, farmers, and vegetable distributors. These discussions provide deeper insights into market trends and the operational dynamics at play.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final step involves synthesizing all the data collected from secondary and primary sources. We engage directly with market players to further validate findings and ensure that the report accurately reflects the state of the Indonesia Vegetable Market.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. How big is the Indonesia Vegetable Market?
The Indonesia vegetable market is valued at USD 34 billion, driven by rising consumer demand for fresh, organic produce and an expanding export market within Southeast Asia.
02. What are the challenges in the Indonesia Vegetable Market?
Challenges include climate variability, inadequate cold chain infrastructure, and price volatility, which can affect both domestic sales and export volumes.
03. Who are the major players in the Indonesia Vegetable Market?
Major players include PT East West Seed Indonesia, PT TaniHub Group, PT Sumber Tani Agung Resources, PT BISI International Tbk, and PT Sewu Segar Nusantara, each with a strong foothold in different vegetable segments.
04. What are the growth drivers of the Indonesia Vegetable Market?
Key drivers include rising health consciousness, urbanization, government support for agriculture, and technological advancements such as vertical farming and hydroponics.
05. What are the trends in the Indonesia Vegetable Market?
Trends include a shift towards organic farming, increased investment in sustainable practices, and the expansion of e-commerce as a distribution channel for fresh produce.
Why Buy From Us?

What makes us stand out is that our consultants follows Robust, Refine and Result (RRR) methodology. i.e. Robust for clear definitions, approaches and sanity checking, Refine for differentiating respondents facts and opinions and Result for presenting data with story

We have set a benchmark in the industry by offering our clients with syndicated and customized market research reports featuring coverage of entire market as well as meticulous research and analyst insights.

While we don't replace traditional research, we flip the method upside down. Our dual approach of Top Bottom & Bottom Top ensures quality deliverable by not just verifying company fundamentals but also looking at the sector and macroeconomic factors.

With one step in the future, our research team constantly tries to show you the bigger picture. We help with some of the tough questions you may encounter along the way: How is the industry positioned? Best marketing channel? KPI's of competitors? By aligning every element, we help maximize success.

Our report gives you instant access to the answers and sources that other companies might choose to hide. We elaborate each steps of research methodology we have used and showcase you the sample size to earn your trust.

If you need any support, we are here! We pride ourselves on universe strength, data quality, and quick, friendly, and professional service.















