KSA Space Launch Service Market Outlook to 2030
Region:Middle East
Author(s):Abhinav kumar
Product Code:KROD7213
December 2024
97
About the Report
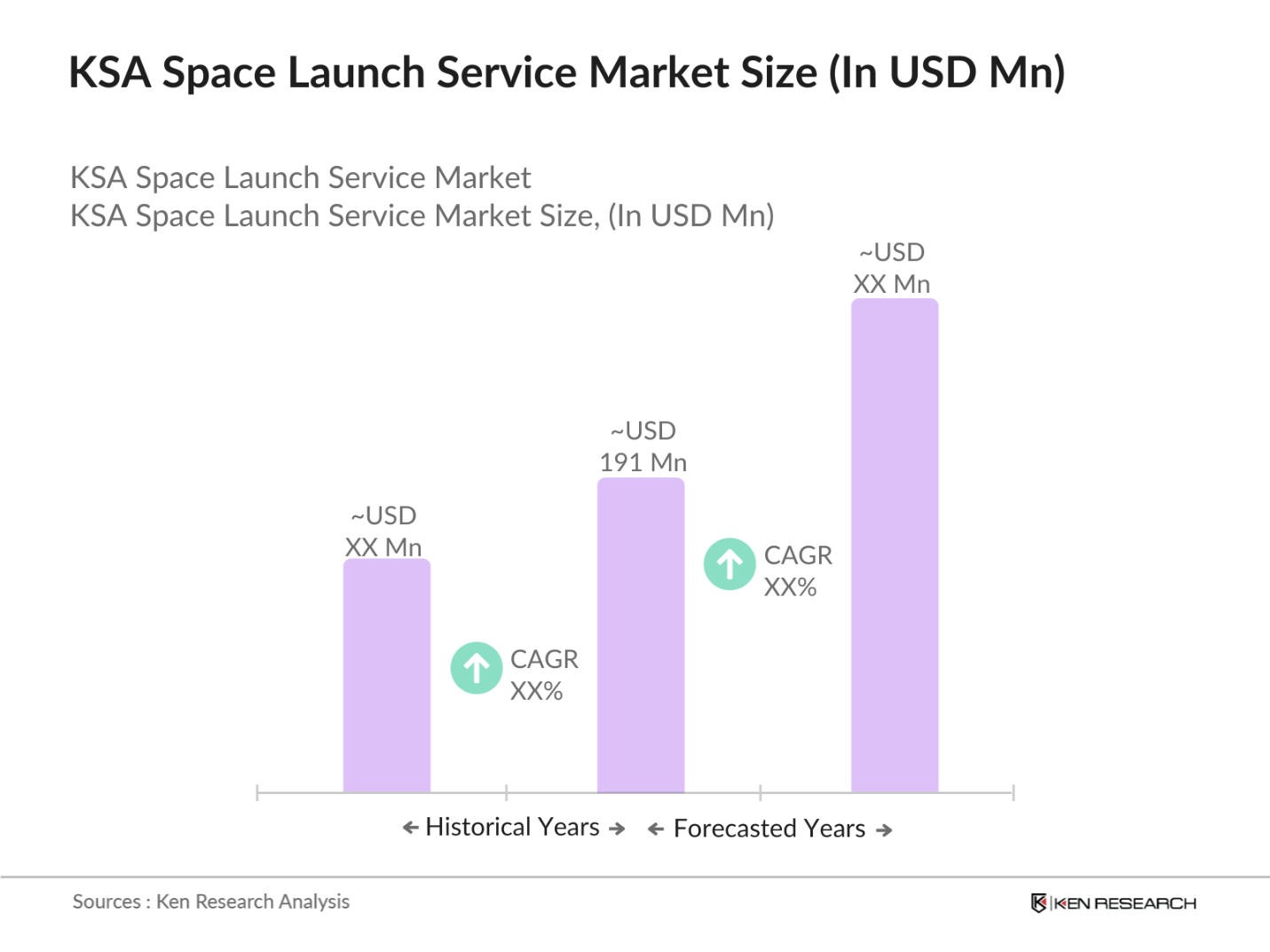
KSA Space Launch Service Market Overview
- The KSA Space Launch Service market, valued at USD 191 million based on historical analysis, is driven by significant government investments in space technology, primarily through Vision 2030 initiatives. This growth is fueled by increasing global demand for satellite launches, bolstered by Saudi Arabias ambitious plans to establish itself as a regional hub for space exploration. The nations investment in commercial space services, combined with its strategic partnerships with international space agencies, is laying the groundwork for continued market expansion in the coming years.
- Riyadh leads the market, supported by its role as the political and financial capital of Saudi Arabia, where most of the government agencies and corporations are headquartered. Jeddah is another key player, driven by its proximity to the Red Sea and strategic location for regional and international space logistics. These cities dominate due to their access to resources, established infrastructure, and proximity to government decision-makers who play a crucial role in shaping the space industry.
- The Saudi Space Commission (SSC) has been developing policies to regulate the Kingdom's growing space sector. In 2024, SSC introduced a new framework aimed at fostering private-sector participation in space activities, which includes launching satellites and conducting research. This policy framework ensures compliance with international standards while promoting innovation in the domestic space industry.
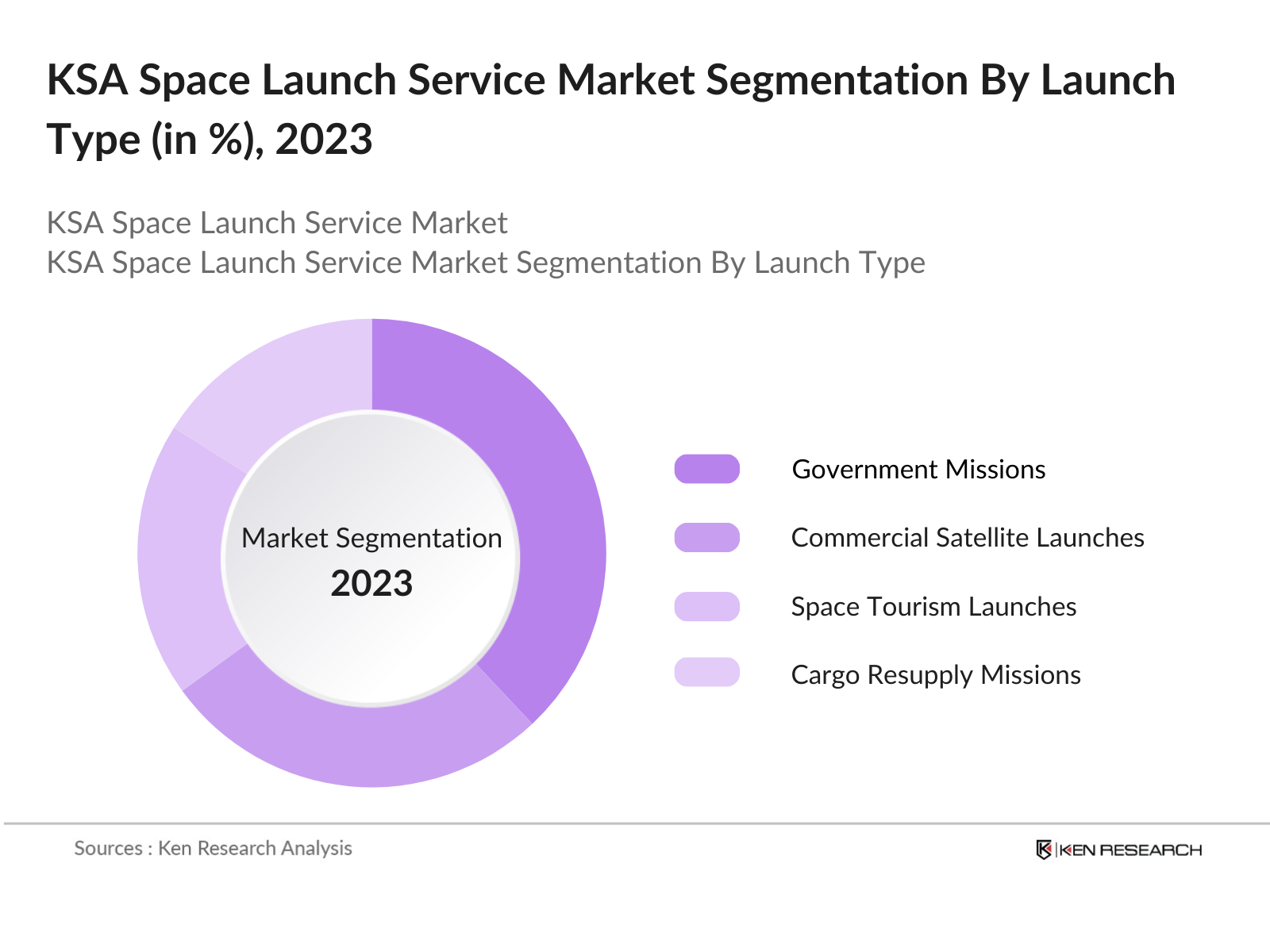
KSA Space Launch Service Market Segmentation
By Launch Type: The KSA space launch service market is segmented by launch type into government missions, commercial satellite launches, space tourism launches, cargo resupply missions, and scientific research missions. Recently, government missions have a dominant market share under this segmentation. This is primarily driven by the Saudi Space Commissions initiatives to establish the country as a leader in space technology and exploration. Government missions are also crucial for building the countrys space infrastructure and capabilities, ensuring that Saudi Arabia meets its ambitious goals under Vision 2030.
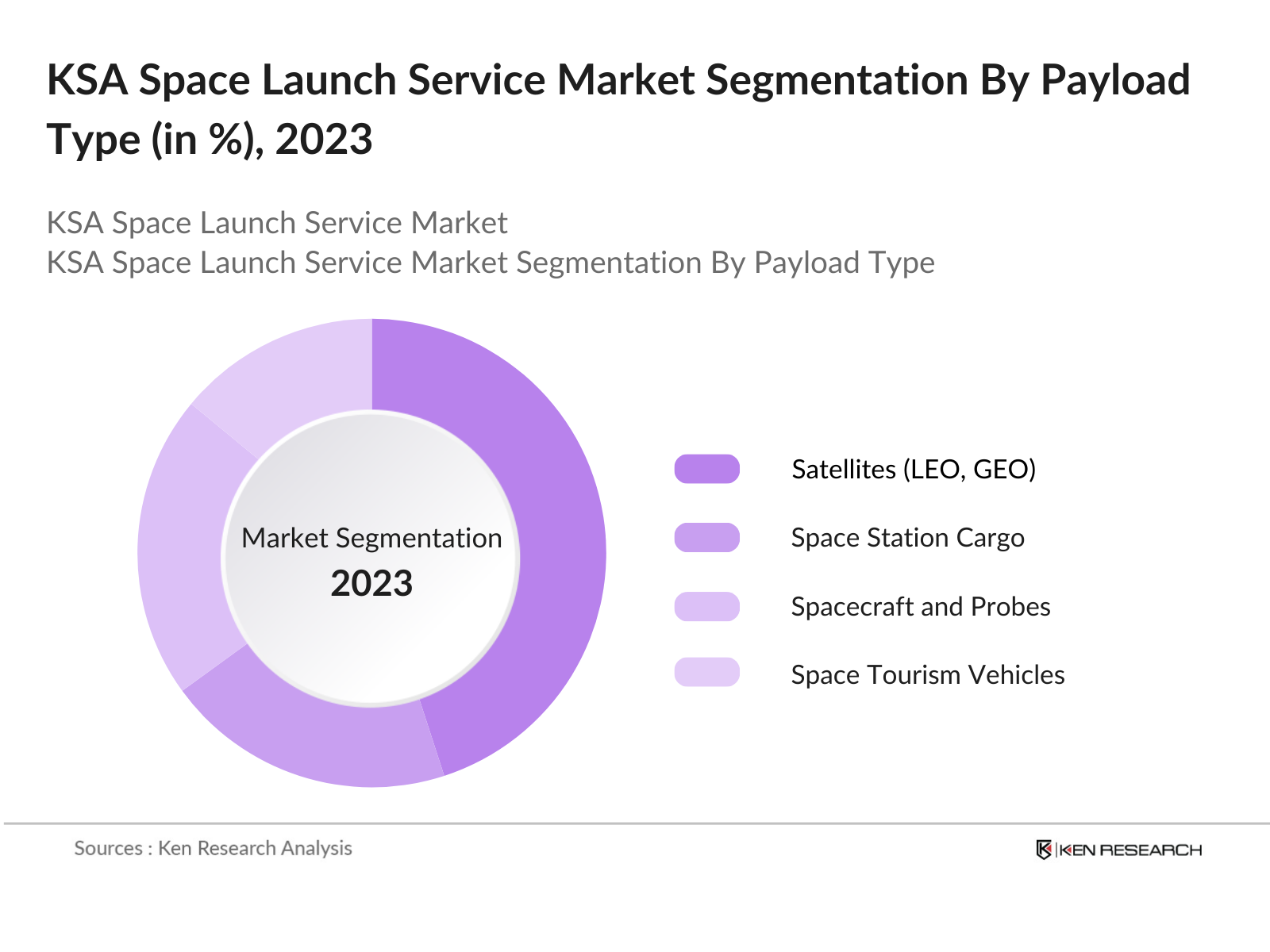
By Payload Type: In terms of payload type, the market is divided into satellites (LEO, GEO, MEO, Nano, Micro), space station cargo, spacecraft and probes, and space tourism vehicles. Among these, satellites dominate the market due to the increasing demand for telecommunications, Earth observation, and scientific research. The surge in the global demand for data connectivity and satellite-based internet services has pushed the deployment of various satellite types, especially in the LEO (Low Earth Orbit) segment, making it the most active in terms of launches and overall contribution to market growth.
KSA Space Launch Service Market Competitive Landscape
The KSA space launch service market is competitive and dominated by a combination of international giants and emerging local players. Global players such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Arianespace have a significant influence due to their technological advancements and established reputations. Saudi Arabia, through its Saudi Space Commission, is actively partnering with these global firms to enhance its capabilities. The market sees a consolidation around key players who have both the technical know-how and financial backing to meet the increasing demand for commercial and government launch services.
|
Company Name |
Establishment Year |
Headquarters |
Launch Success Rate |
Payload Capacity (tons) |
R&D Investments |
Technological Integration |
Key Partnerships |
Reusability of Launch Systems |
|
SpaceX |
2002 |
California, USA |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
|
Blue Origin |
2000 |
Washington, USA |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
|
Arianespace |
1980 |
Evry, France |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
|
Saudi Space Commission |
2018 |
Riyadh, KSA |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
|
Virgin Galactic |
2004 |
California, USA |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
_ |
KSA Space Launch Service Industry Analysis
Growth Drivers
National Vision 2030 Initiatives: Saudi Arabias Vision 2030 prioritizes the growth of the space sector, aiming to establish a robust space economy. By 2024, the Saudi Space Commission (SSC) has outlined plans to advance space research and development, launch initiatives, and contribute to the global space market. SSC has committed $2 billion in funding for domestic space technology programs as part of Vision 2030, which aims to increase non-oil sector GDP contributions. The SSC's cooperation with international space agencies has been vital for boosting R&D activities, which will drive the growth of KSAs space launch services.
Government Investments in Space Technology: The Saudi government is heavily investing in space technology, with allocations for space initiatives through its 2024 budget nearing $4 billion. This funding is channeled towards building satellite infrastructure, research centers, and commercial launch capabilities. The establishment of King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) has accelerated satellite launches, boosting local technical expertise. These investments are designed to drive long-term self-reliance in space technology, aligning with Vision 2030 objectives.
Increasing Global Demand for Satellites: The global demand for satellite launches has increased, driven by the expansion of communications, Earth observation, and military satellite needs. By 2024, over 6,500 active satellites are orbiting Earth, many launched by developing space nations like Saudi Arabia. The KSA is positioning itself to benefit from this demand, aiming to service a portion of the satellite launch market with its growing infrastructure. The government is focused on launching more domestically produced satellites to reduce reliance on foreign technology.
Market Challenges
High Operational Costs: The high costs associated with space launch services pose a challenge for Saudi Arabia. Operational expenses, which include satellite construction, launch services, and ground support, often exceed $50 million per launch. This level of expenditure can be a barrier for emerging markets like Saudi Arabia that are developing their launch capabilities. Although government subsidies alleviate some pressure, the continued reliance on international launch vehicles for larger payloads limits cost efficiency and scalability.
Limited Domestic Infrastructure: Saudi Arabias domestic space launch infrastructure is still developing, with limited availability of launch pads and manufacturing facilities. By 2024, there are only two major launch sites in the country, and most large-scale projects require collaboration with international spaceports. The lack of indigenous launch vehicles means that KSA depends on foreign suppliers for critical components and services, limiting the scope of fully domestic space missions.
KSA Space Launch Service Market Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the KSA Space Launch Service market is expected to experience substantial growth, driven by continuous government support, advancements in reusable launch technologies, and a burgeoning interest in space tourism and satellite services. Saudi Arabias ambition to become a global leader in the space sector is propelling heavy investments in infrastructure, such as domestic launch facilities and research institutions. Moreover, collaborations with international players will further solidify the nations foothold in the industry. The future will also witness an increased focus on Low Earth Orbit (LEO) missions, which are becoming more prominent due to the demand for satellite internet services and commercial space endeavors. As the Kingdom scales its space capabilities, there is a clear opportunity for local companies to emerge as key players in this evolving market.
Opportunities
- Strategic Partnerships with Global Space Agencies: Saudi Arabia has the opportunity to deepen its collaborations with established space agencies like NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). In 2024, SSC signed a new agreement with NASA for joint research on space missions, focusing on advanced satellite technology and reusable launch systems. These partnerships enable technology transfers and provide KSA with access to cutting-edge launch technologies, opening opportunities for domestic launch services.
- Technological Advancements in Reusable Launch Systems: Reusable launch technology presents a significant opportunity for Saudi Arabias space program. In 2024, Saudi Arabia is studying reusable launch vehicles (RLVs) in collaboration with global partners. RLVs can drastically reduce launch costs, with estimates showing potential savings of up to 70%. This would make satellite deployment more economically viable for the Kingdom, positioning KSA as a key player in the global space launch market.
Scope of the Report
|
Launch Type |
Government Missions Commercial Satellite Launches Space Tourism Launches Cargo Resupply Missions Scientific Research Missions |
|
Payload Type |
Satellites Space Station Cargo Spacecraft and Probes Space Tourism Vehicles |
|
Vehicle Type |
Small-Lift Launch Vehicles Medium-Lift Launch Vehicles Heavy-Lift Launch Vehicles Reusable Launch Vehicles |
|
End-User |
Government Agencies Private Space Companies Research Organizations Commercial Satellite Operators |
|
Region |
Riyadh Jeddah Eastern Province Al-Qassim Makkah |
Products
Key Target Audience
Government and Regulatory Bodies (Saudi Space Commission, General Authority for Civil Aviation)
Satellite Companies
Launch Service Industries
Space Tourism Companies
Telecommunications Companies
Military and Defense Industries
Investor and Venture Capitalist Firms
Ground Control and Space Infrastructure Companies
Companies
List of Major Players in the KSA Space Launch Service Market
SpaceX
Blue Origin
Arianespace
Northrop Grumman
Lockheed Martin
United Launch Alliance (ULA)
Rocket Lab
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Sierra Nevada Corporation
Saudi Space Commission
Virgin Galactic
Boeing Defense, Space & Security
China Great Wall Industry Corporation (CGWIC)
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
Russian Space Agency (Roscosmos)
Table of Contents
1. KSA Space Launch Service Market Overview
1.1. Definition and Scope
1.2. Market Taxonomy
1.3. Market Growth Rate
1.4. Market Segmentation Overview
2. KSA Space Launch Service Market Size (In USD Bn)
2.1. Historical Market Size
2.2. Year-On-Year Growth Analysis
2.3. Key Market Developments and Milestones
3. KSA Space Launch Service Market Analysis
3.1. Growth Drivers
3.1.1. National Vision 2030 Initiatives
3.1.2. Government Investments in Space Technology
3.1.3. Increasing Global Demand for Satellites
3.1.4. Expansion of Commercial Space Activities
3.2. Market Challenges
3.2.1. High Operational Costs
3.2.2. Limited Domestic Infrastructure
3.2.3. Regulatory and Compliance Barriers
3.2.4. Dependence on International Partners
3.3. Opportunities
3.3.1. Strategic Partnerships with Global Space Agencies
3.3.2. Technological Advancements in Reusable Launch Systems
3.3.3. Establishment of Domestic Launch Capabilities
3.3.4. Space Tourism Potential
3.4. Trends
3.4.1. Rise of Small Satellite Launches
3.4.2. Focus on Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Missions
3.4.3. Use of Autonomous Launch Systems
3.4.4. Integration of AI and Big Data in Launch Operations
3.5. Government Regulation
3.5.1. Saudi Space Commission (SSC) Policies
3.5.2. Licensing and Compliance Requirements
3.5.3. International Space Law Compliance
3.5.4. Bilateral Agreements with Global Space Agencies
3.6. SWOT Analysis
3.7. Stakeholder Ecosystem (Launch Operators, Satellite Providers, Ground Services)
3.8. Porters Five Forces (Supplier Power, Buyer Power, Competition, New Entrants, Substitutes)
3.9. Competition Ecosystem (Vertical Integration, Launch Providers, Services Providers)
4. KSA Space Launch Service Market Segmentation
4.1. By Launch Type (In Value %)
4.1.1. Government Missions
4.1.2. Commercial Satellite Launches
4.1.3. Space Tourism Launches
4.1.4. Cargo Resupply Missions
4.1.5. Scientific Research Missions
4.2. By Payload Type (In Value %)
4.2.1. Satellites (LEO, GEO, MEO, Nano, Micro)
4.2.2. Space Station Cargo
4.2.3. Spacecraft and Probes
4.2.4. Space Tourism Vehicles
4.3. By Vehicle Type (In Value %)
4.3.1. Small-Lift Launch Vehicles
4.3.2. Medium-Lift Launch Vehicles
4.3.3. Heavy-Lift Launch Vehicles
4.3.4. Reusable Launch Vehicles
4.4. By End-User (In Value %)
4.4.1. Government Agencies
4.4.2. Private Space Companies
4.4.3. Research Organizations
4.4.4. Commercial Satellite Operators
4.5. By Region (In Value %)
4.5.1. Riyadh
4.5.2. Jeddah
4.5.3. Eastern Province
4.5.4. Al-Qassim
4.5.5. Makkah
5. KSA Space Launch Service Market Competitive Analysis
5.1 Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
5.1.1. SpaceX
5.1.2. Blue Origin
5.1.3. Arianespace
5.1.4. Northrop Grumman
5.1.5. Lockheed Martin
5.1.6. United Launch Alliance (ULA)
5.1.7. Rocket Lab
5.1.8. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
5.1.9. Sierra Nevada Corporation
5.1.10. Saudi Space Commission
5.1.11. Virgin Galactic
5.1.12. Boeing Defense, Space & Security
5.1.13. China Great Wall Industry Corporation (CGWIC)
5.1.14. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
5.1.15. Russian Space Agency (Roscosmos)
5.2 Cross Comparison Parameters
5.2.1. Launch Success Rate
5.2.2. Launch Frequency
5.2.3. Payload Capacity
5.2.4. Cost per Launch
5.2.5. Launch Infrastructure
5.2.6. Technology Integration (AI, Reusability)
5.2.7. Environmental Impact
5.2.8. Global Market Share
5.3. Market Share Analysis
5.4. Strategic Initiatives (Joint Ventures, Global Collaborations)
5.5. Mergers and Acquisitions
5.6. Investment Analysis
5.7. Venture Capital Funding
5.8. Government Grants
5.9. Private Equity Investments
6. KSA Space Launch Service Market Regulatory Framework
6.1. National Space Policy
6.2. Safety and Compliance Standards
6.3. Certification Processes
7. KSA Space Launch Service Future Market Size (In USD Bn)
7.1. Future Market Size Projections
7.2. Key Factors Driving Future Market Growth
8. KSA Space Launch Service Future Market Segmentation
8.1. By Launch Type (In Value %)
8.2. By Payload Type (In Value %)
8.3. By Vehicle Type (In Value %)
8.4. By End-User (In Value %)
8.5. By Region (In Value %)
9. KSA Space Launch Service Market Analysts Recommendations
9.1. TAM/SAM/SOM Analysis
9.2. Customer Cohort Analysis
9.3. Marketing Initiatives
9.4. White Space Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first step involved identifying key variables such as government policy changes, technological advancements, and international collaboration in the KSA Space Launch Service market. This was accomplished through comprehensive desk research and data collection from governmental and private industry sources.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data on KSA space launches, payload capacity, and successful mission percentages were analyzed. These metrics were used to build a framework for understanding the market's current dynamics, focusing on trends such as reusable launch systems and payload delivery efficiency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses were validated through interviews with industry experts and stakeholders, including engineers and analysts within Saudi space agencies. Their insights were instrumental in refining the projections and ensuring data accuracy.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final step involved synthesizing the research through a combination of bottom-up and top-down approaches, ensuring that the analysis accounted for both global trends and region-specific nuances. This method ensured a comprehensive, validated view of the KSA Space Launch Service market.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. How big is the KSA Space Launch Service Market?
The KSA Space Launch Service market is valued at USD 191 million based on a five-year historical analysis. The market is expanding due to increasing government investment and international partnerships aimed at strengthening the nations space capabilities.
02. What are the challenges in the KSA Space Launch Service Market?
Challenges include high operational costs, reliance on international partners for advanced technology, and the need for significant investment in domestic infrastructure to support large-scale space missions.
03. Who are the major players in the KSA Space Launch Service Market?
Major players include SpaceX, Blue Origin, Saudi Space Commission, Virgin Galactic, and Arianespace. These companies dominate the market due to their technological prowess and established global presence.
04. What are the growth drivers of the KSA Space Launch Service Market?
The market is driven by government initiatives under Vision 2030, growing demand for satellite services, and the development of reusable launch systems that reduce the overall cost of space missions.
05. What are the opportunities in the KSA Space Launch Service Market?
Opportunities lie in the development of domestic launch facilities, collaboration with international space agencies, and the expansion of space tourism services, which are expected to generate significant revenue in the coming years.
Why Buy From Us?

What makes us stand out is that our consultants follows Robust, Refine and Result (RRR) methodology. i.e. Robust for clear definitions, approaches and sanity checking, Refine for differentiating respondents facts and opinions and Result for presenting data with story

We have set a benchmark in the industry by offering our clients with syndicated and customized market research reports featuring coverage of entire market as well as meticulous research and analyst insights.

While we don't replace traditional research, we flip the method upside down. Our dual approach of Top Bottom & Bottom Top ensures quality deliverable by not just verifying company fundamentals but also looking at the sector and macroeconomic factors.

With one step in the future, our research team constantly tries to show you the bigger picture. We help with some of the tough questions you may encounter along the way: How is the industry positioned? Best marketing channel? KPI's of competitors? By aligning every element, we help maximize success.

Our report gives you instant access to the answers and sources that other companies might choose to hide. We elaborate each steps of research methodology we have used and showcase you the sample size to earn your trust.

If you need any support, we are here! We pride ourselves on universe strength, data quality, and quick, friendly, and professional service.















