What is Stopping India from Mass Adoption Industry 5.0?
Download the Full Consulting POV Now













Overview
India’s manufacturing sector stands at the edge of a transformative shift. As the global economy shifts toward, the focus is no longer just on automation but on human-centric, sustainable, and resilient manufacturing. The global Industry 5.0 implementation potential is projected to exceedUSD 64 billion by 2030, with India well-positioned to emerge as a leader, if it can overcome structural inefficiencies and skill gaps.
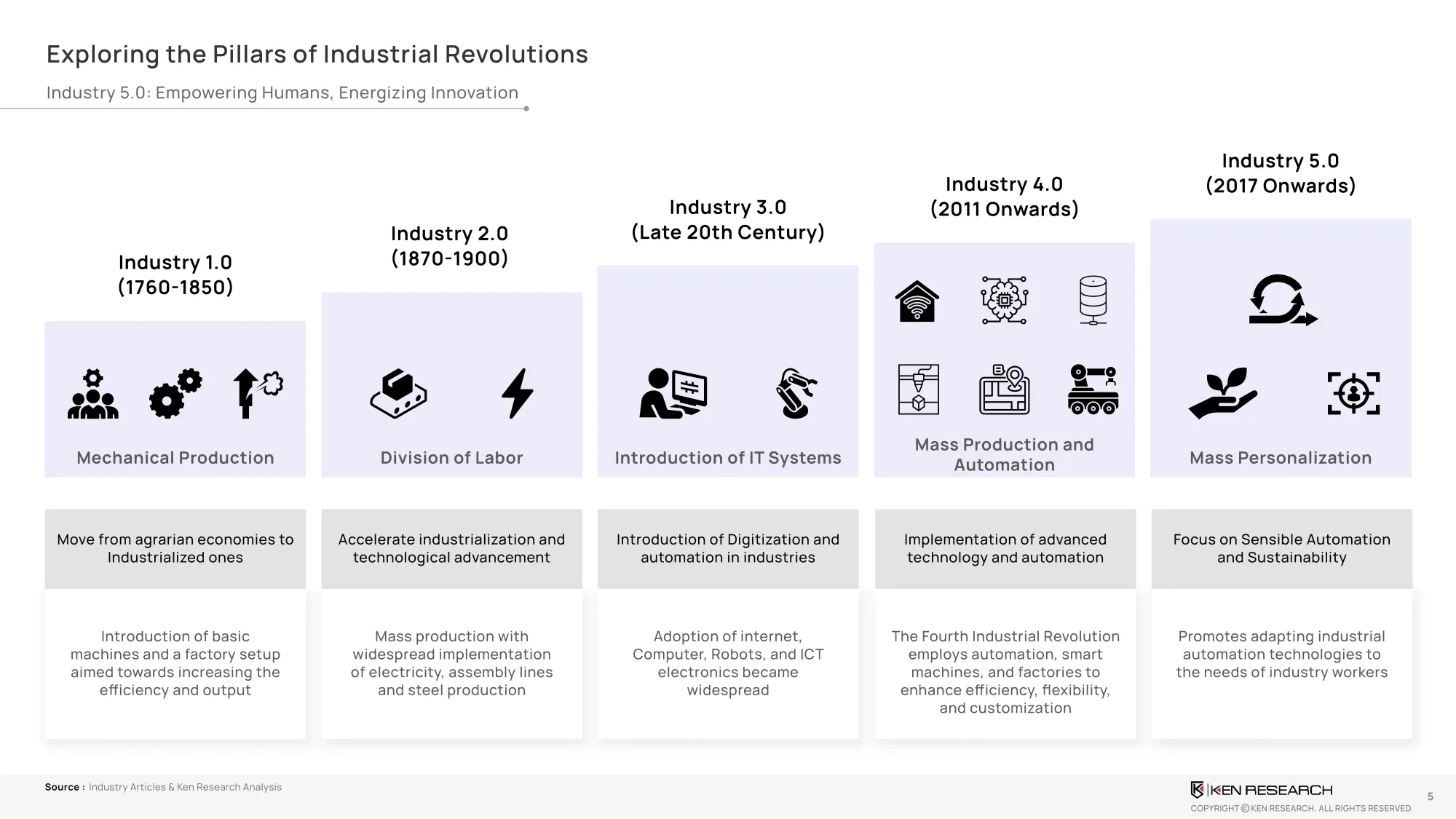
- Adoption remains limited due to high integration costs, workforce skill mismatches, and safety concerns around human-machine collaboration. However, with strategic investments in digital twins, traceability solutions, AI-powered safety systems, and government-backed skilling initiatives, India can advance into this next industrial era.
The Core Challenge
Despite years of progress under Industry 4.0,India manufacturing sectorbase remains largely automation-focused andill-equipped for the human-machine collaboration required in Industry 5.0. The problem lies in transitioning from machine-centric productivity to intelligent systems that empower human labour while achieving sustainable and resilient operations.
Sub-Issues at Play
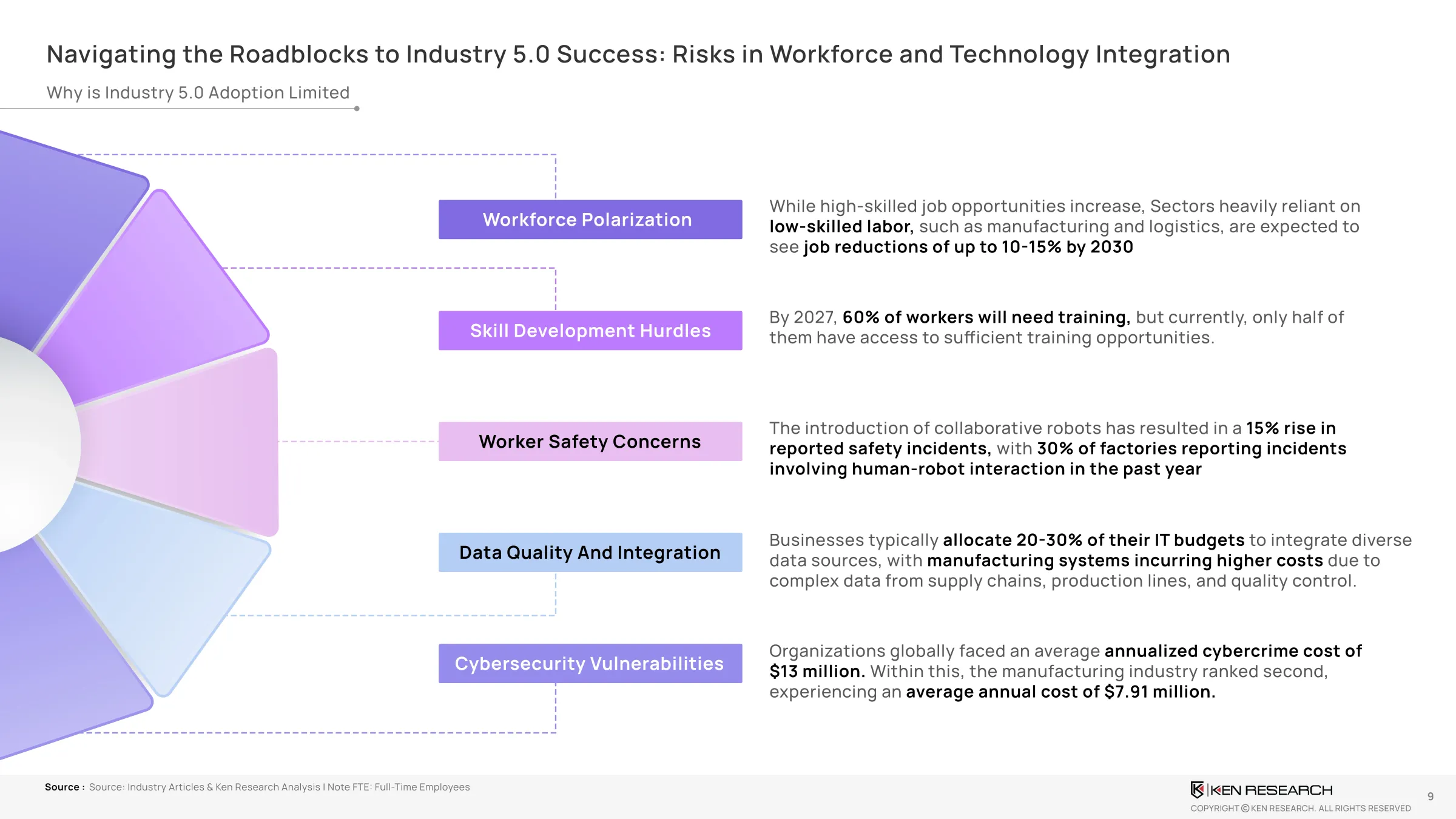
- Limited Adoption:Less than 20% of manufacturers have initiated pilots in Industry 5.0technologies like AR/VR safety systems, wearables, or digital twins, indicating a slow transition toward human-centric and sustainable manufacturing despite growing global momentum.
- Workforce Readiness:While60% of workers will require upskilling by 2027, only half have access to adequate training, creating a significant bottleneck in adopting emerging technologies like AI, robotics, and collaborative manufacturing systems.
- Safety Concerns:Human-robot collaboration has led to a15% rise in safety incidents, with30% of factories reporting robot-human conflictsin the past year, emphasizing the urgent need for better safety protocols and smarter co-working systems.
- Cyber Risks:Manufacturing ranks second globally in cyberattack exposure, with average annual losses atUSD 7.91 millionper company. This poses a major threat to the stability of integrated, data-driven Industry 5.0 environments.
Global Benchmarks
- GermanyandJapanare ahead, integrating predictive maintenance, cobots, and blockchain for traceability.
- Indian factories lag in AR/VR adoption and remain heavily reliant on manual oversight and legacy infrastructure.
Root Cause Analysis
Structural and Systemic Barriers
- Fragmented IT Infrastructure:Manufacturing firms allocate20–30% of IT budgetsjust to integrate siloed data systems from production lines, supply chains, and quality controls.
- Capital Constraints:The high upfront cost of smart contracts, blockchain integration, and digital twin infrastructure inhibits adoption among mid-sized players.
- Policy Mismatch:Existing policies under Make in India and PLI schemes emphasize automationand export competitiveness but lack targeted support for Industry 5.0 pillars like human safety and carbon neutrality.
- Skilling Gap:Vocational training curriculums are outdatedand not aligned with modern tools like collaborative robots, blockchain systems, or AR/VR-based plant simulation.
The India Advantage & Potential Solutions
India’s Strategic Strengths
- Demographic Edge:India’s working-age population, which is projected to be around 64% (920 Mn)of the total population (1.42 Bn), can be a global hub for hybrid human-machine collaboration if upskilled.
- Startup Ecosystem: India’s innovation landscape is thriving, with over 300 deep-tech startups focused on industrial automation, robotics, and AI. This creates a fertile ground for rapid prototyping, pilot deployment, and scaling of Industry 5.0 technologies across manufacturing value chains.
- Policy Momentum:Existing government programs like the National Manufacturing Policy and SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0provide a strong foundation, which can be strategically expanded to support Industry 5.0 initiatives, particularly around human-machine collaboration, sustainability, and resilient digital infrastructure.
Opportunity Areas (USD Potential by 2030)
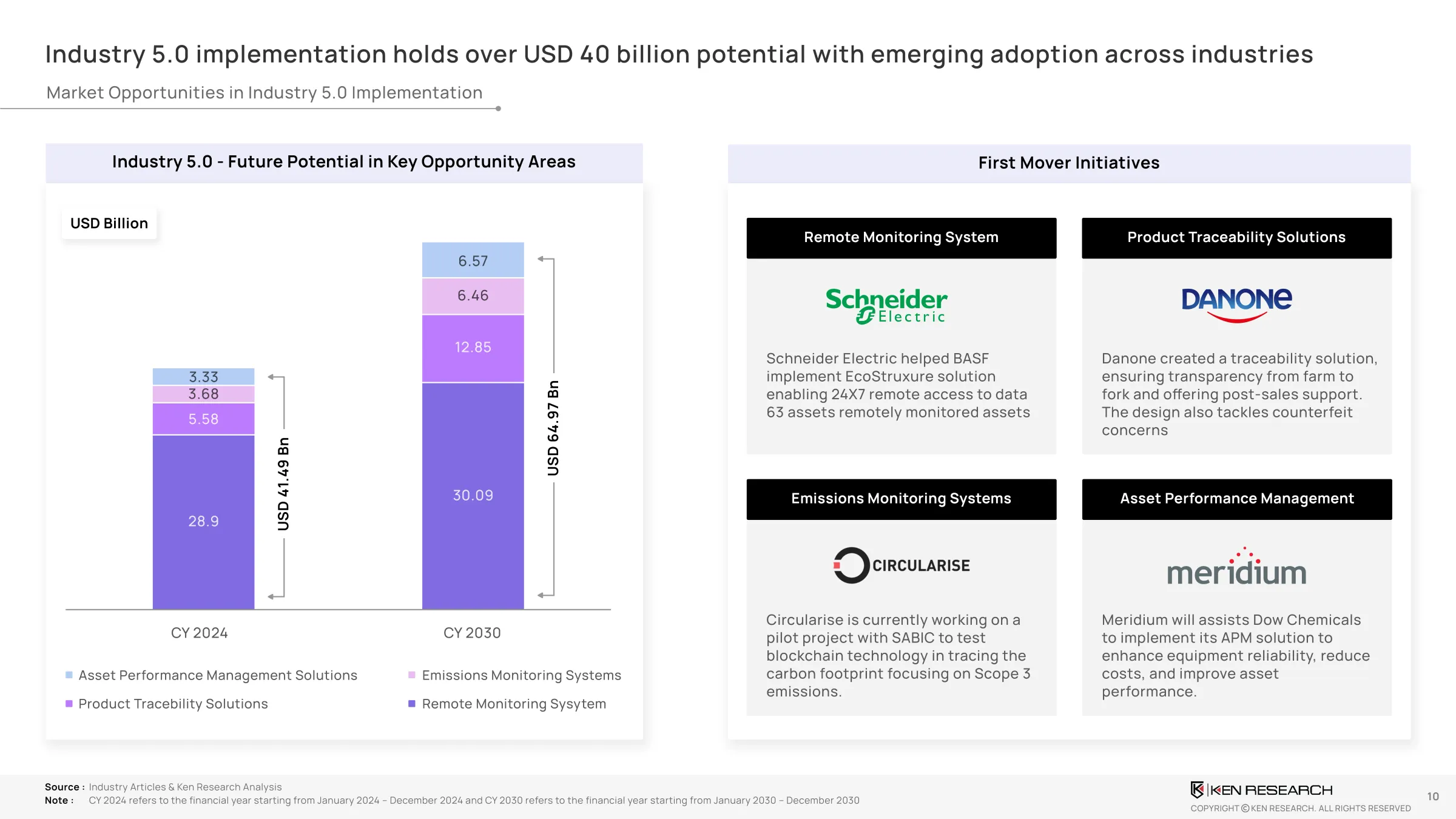
With Remote Monitoring Systems and Product Traceability Solutions expected to be the dominant contributors to this surge, the industry 5.0 opportunities are anticipated to expand from USD 41.49 billion in 2024 to USD 64.97 billion by 2030.
Strategic Recommendations
- Policy Initiatives:
- Business Strategies:
- Investment Opportunities:
Roadmap for Execution
Step-by-Step Implementation Plan
What Does the Future Hold?
Industry 5.0 marks a systematic shift from automation for efficiency to intelligent co-working for resilience, customization, and human empowerment. India has a unique opportunity to lead this shift by embedding sustainability, digital innovation, and workforce enablement into its manufacturing DNA.
With focused policy reforms, tech innovation, and cross-industry collaboration, India can not only enhance its industrial competitiveness but also emerge as aglobal inspiration for inclusive and conscious manufacturing. India’s long-term success will depend on its ability to scale early pilots, invest in workforce transformation, and encourage collaborative innovation across stakeholders.















