Region:Middle East
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAD3940
Pages:94
Published On:November 2025
By Type:The market is segmented into various types of testing methodologies, including cell-based assays, biochemical assays, organ-on-a-chip technologies, high-throughput screening, in silico models, and others. Among these, cell-based assays are leading the market due to their relevance in drug development and toxicity testing, providing more accurate and predictive results compared to traditional methods. The adoption of organ-on-a-chip and high-throughput screening technologies is also increasing, driven by the need for more physiologically relevant and scalable testing platforms .

By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, academic and research institutions, contract research organizations (CROs), diagnostics laboratories, and others. Pharmaceutical companies dominate this segment, driven by their need for efficient drug development processes and compliance with regulatory standards, which necessitate extensive toxicology testing. Biotechnology firms and academic institutions are also significant contributors, reflecting the region’s growing emphasis on translational research and innovation .

The Qatar In Vitro Toxicology Testing Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Qatar University, Qatar Biomedical Research Institute (QBRI), Sidra Medicine, Hamad Medical Corporation, Qatar Science & Technology Park (QSTP), Weill Cornell Medicine – Qatar, Gulf Pharmaceutical Industries (Julphar), Qatar National Research Fund (QNRF), Doha Institute for Graduate Studies, Qatar Foundation, Qatar Toxicology Laboratory, Qatar Clinical Research Center, Qatar Institute for Environmental and Energy Research, Qatar Medical Center, Qatar Health Authority contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Qatar in vitro toxicology testing market appears promising, driven by ongoing advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on regulatory compliance. As the demand for alternative testing methods continues to rise, laboratories are expected to invest in innovative solutions that enhance efficiency and accuracy. Furthermore, collaborations between academic institutions and industry players are likely to foster research initiatives, paving the way for new methodologies and applications in toxicology testing.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Cell-based assays Biochemical assays Organ-on-a-chip technologies High-throughput screening In silico models Others |
| By End-User | Pharmaceutical companies Biotechnology firms Academic and research institutions Contract research organizations (CROs) Diagnostics laboratories Others |
| By Application | Drug development Environmental testing Cosmetic testing Chemical safety assessment Food safety testing Others |
| By Technology | In vitro assays Computational toxicology Microfluidics D cell culture OMICS-based platforms Others |
| By Region | Doha Al Rayyan Umm Salal Al Wakrah Others |
| By Investment Source | Government funding Private equity Venture capital Corporate investments International grants Others |
| By Policy Support | Grants and subsidies Tax incentives Research funding programs Regulatory support initiatives Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Testing Services | 60 | Laboratory Directors, R&D Managers |
| Cosmetic Safety Assessments | 40 | Product Safety Officers, Regulatory Affairs Managers |
| Chemical Toxicity Testing | 50 | Quality Control Managers, Compliance Officers |
| Environmental Toxicology Studies | 45 | Environmental Scientists, Policy Makers |
| Academic Research Collaborations | 40 | University Researchers, Lab Technicians |
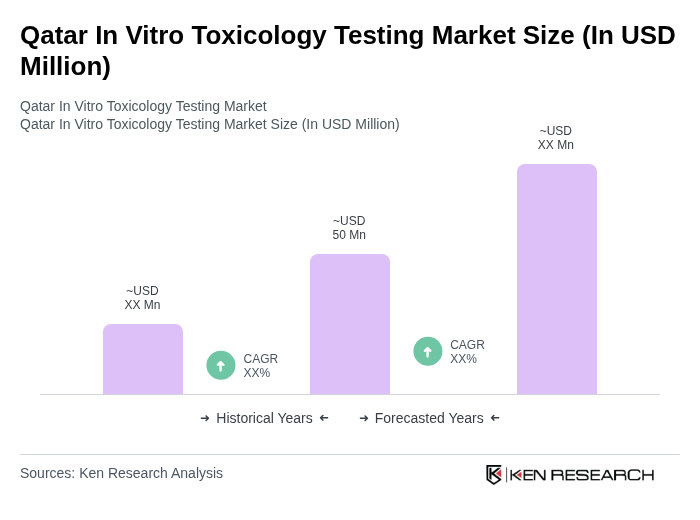
The Qatar In Vitro Toxicology Testing Market is valued at approximately USD 50 million, reflecting a significant growth trend driven by the demand for alternative testing methods and a focus on drug safety and efficacy.