Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAB0229
Pages:100
Published On:August 2025
By Payment Mode:The payments market in South Korea is segmented into various modes, including mobile payments, contactless payments, online payments, point-of-sale (POS) systems, bank transfers, prepaid cards, cryptocurrency payments, and others. Among these, mobile payments have gained significant traction due to the widespread use of smartphones, the convenience of QR code-based solutions, and the integration of payment apps with e-commerce platforms. Contactless payments are also on the rise, driven by consumer demand for quick and secure transactions, especially in retail and transportation. Online payments continue to grow, particularly in the e-commerce sector, as more consumers prefer shopping online and businesses increasingly offer digital checkout options .

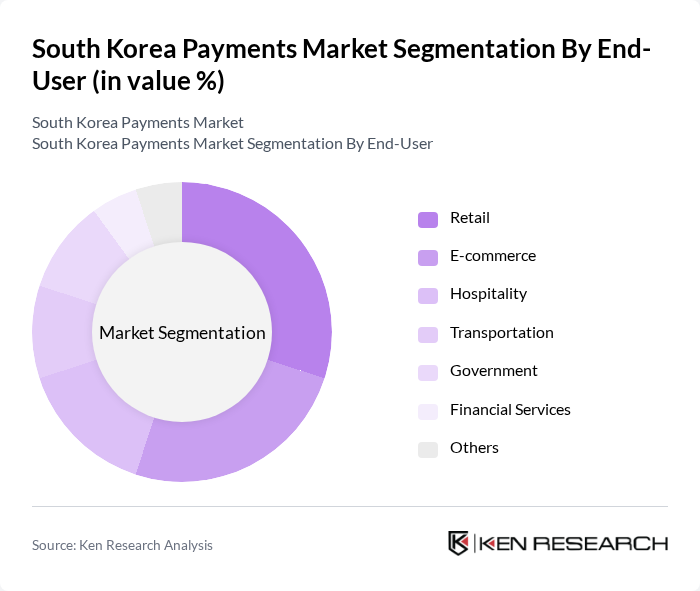
By End-User:The end-user segmentation of the payments market includes retail, e-commerce, hospitality, transportation, government, financial services, and others. The retail and e-commerce sectors are the most significant contributors, driven by the increasing trend of online shopping, digital wallets, and the need for efficient payment solutions. The hospitality and transportation sectors are also rapidly adopting digital payments, enhancing customer experiences and operational efficiency through real-time and contactless payment options .
The South Korea Payments Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Samsung Pay, Kakao Pay, Naver Pay, Viva Republica (Toss), NHN Payco, LG Uplus, Shinhan Bank, KB Kookmin Bank, Hana Bank, Woori Bank, NH Nonghyup Bank, Citibank Korea, Standard Chartered Bank Korea, KEB Hana Card, Bithumb, Coinone, and Korbit contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korea payments market is poised for continued evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. The integration of artificial intelligence in payment processing is expected to enhance transaction efficiency and security. Additionally, the growing trend of sustainability in payment solutions will likely influence consumer choices, prompting providers to adopt eco-friendly practices. As these trends unfold, the market will adapt, presenting new opportunities for innovation and growth in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Payment Mode | Mobile Payments Contactless Payments Online Payments Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems Bank Transfers Prepaid Cards Cryptocurrency Payments Others |
| By End-User | Retail E-commerce Hospitality Transportation Government Financial Services Others |
| By Payment Type | Domestic Payments Cross-Border Payments |
| By Enterprise Size | Large Enterprises Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
| By Industry Vertical | BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) Manufacturing IT and Telecom Retail & E-commerce Healthcare Education Energy and Utilities Others |
| By Customer Segment | Individual Consumers Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Large Enterprises Government Entities Others |
| By Geographic Distribution | Seoul Capital Area Yeongnam (Southeastern Region) Honam (Southwestern Region) Hoseo (Central Region) Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Payment Preferences | 150 | General Consumers, Tech-Savvy Users |
| Merchant Payment Solutions | 100 | Small Business Owners, Retail Managers |
| Mobile Payment Adoption | 80 | Millennials, Gen Z Users |
| Cross-Border Payment Trends | 70 | International Business Executives, Export Managers |
| Regulatory Impact on Payments | 40 | Compliance Officers, Financial Analysts |
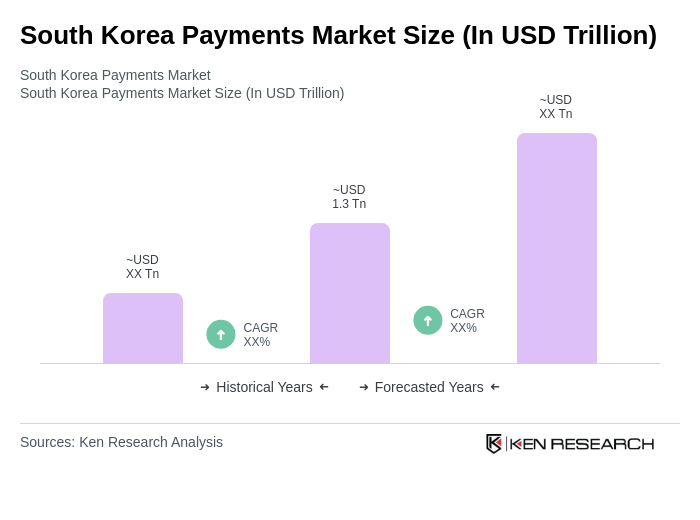
The South Korea Payments Market is valued at approximately USD 1.3 trillion, driven by the rapid adoption of digital payment solutions, increased smartphone penetration, and a shift towards cashless transactions among consumers and businesses.