Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAD0310
Pages:81
Published On:August 2025
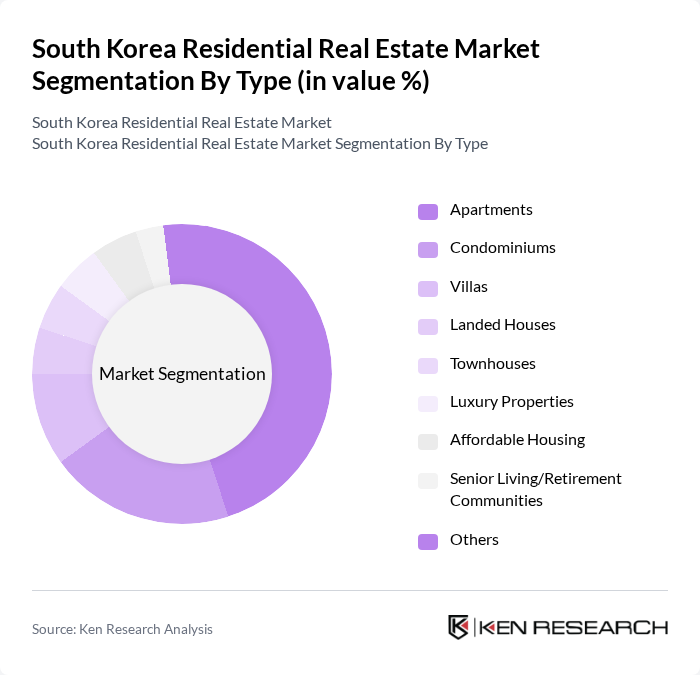
By Type:The residential real estate market in South Korea is segmented into apartments, condominiums, villas, landed houses, townhouses, luxury properties, affordable housing, senior living/retirement communities, and others. Among these,apartmentsdominate the market due to their affordability, convenience, and high demand in urban areas. The trend towards vertical living in cities has led to a significant increase in apartment developments, catering to the needs of a growing urban population. Land scarcity and high population density in metropolitan areas further drive the preference for apartment living.
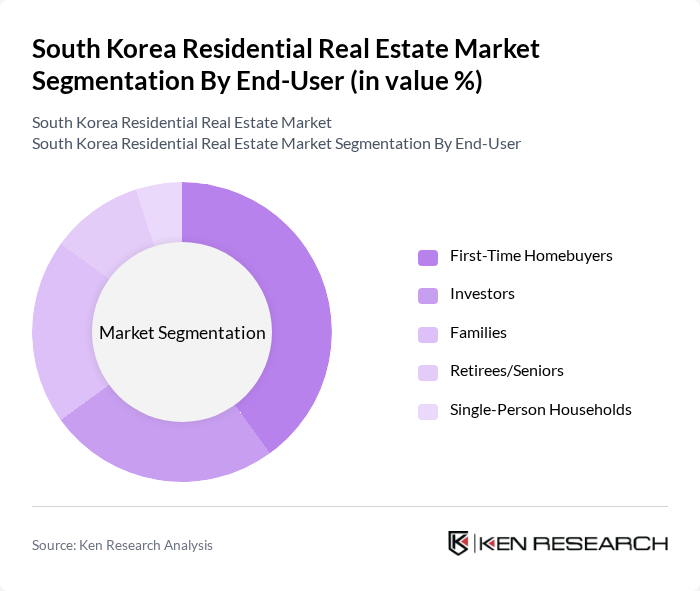
By End-User:The end-user segmentation of the residential real estate market includes first-time homebuyers, investors, families, retirees/seniors, and single-person households.First-time homebuyersrepresent a significant portion of the market, driven by favorable financing options, government incentives, and the increasing availability of affordable housing solutions. The trend toward smaller family units and single-person households is also shaping demand, especially in urban centers.
The South Korea Residential Real Estate Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Samsung C&T Corporation, Hyundai Engineering & Construction Co., Ltd., Daewoo Engineering & Construction Co., Ltd., GS Engineering & Construction Corp., SK ecoplant Co., Ltd., Hanwha Engineering & Construction Corp., POSCO E&C (POSCO Engineering & Construction Co., Ltd.), Lotte Engineering & Construction Co., Ltd., HDC Hyundai Development Company, Booyoung Group, Korea Land & Housing Corporation (LH), Kolon Global Corporation, Daelim Industrial Co., Ltd., Hyosung Corporation, Dongbu Corporation contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korean residential real estate market is poised for transformative changes driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. As urbanization continues, the demand for innovative housing solutions, such as smart homes and eco-friendly developments, is expected to rise. Additionally, the rental market is likely to expand, catering to a growing population of young professionals and expatriates. These trends will shape the market landscape, presenting both challenges and opportunities for stakeholders in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Apartments Condominiums Villas Landed Houses Townhouses Luxury Properties Affordable Housing Senior Living/Retirement Communities Others |
| By End-User | First-Time Homebuyers Investors Families Retirees/Seniors Single-Person Households |
| By Price Range | Below 300 Million KRW Million - 600 Million KRW Million - 1 Billion KRW Above 1 Billion KRW |
| By Location | Urban Areas (e.g., Seoul, Busan, Incheon) Suburban Areas Rural Areas |
| By Property Condition | New Developments Resale Properties Renovated Properties |
| By Financing Type | Mortgage Financing Cash Purchases Government Subsidized Loans |
| By Investment Purpose | Primary Residence Rental Income Vacation Homes Speculative Investment |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Property Buyers | 120 | First-time homebuyers, Investors, Relocating families |
| Real Estate Agents | 90 | Licensed real estate agents, Brokers, Market analysts |
| Property Developers | 60 | Project managers, Development executives, Financial analysts |
| Construction Firms | 50 | Site managers, Operations directors, Cost estimators |
| Urban Planners | 40 | City planners, Policy advisors, Environmental consultants |
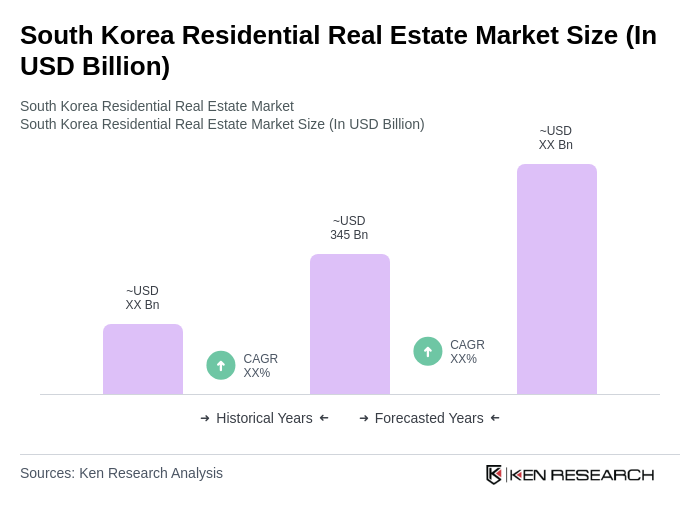
The South Korea residential real estate market is valued at approximately USD 345 billion, driven by factors such as rapid urbanization, increasing household formation, and a resilient economy that supports real estate investments.