Region:Asia
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAA0202
Pages:94
Published On:August 2025
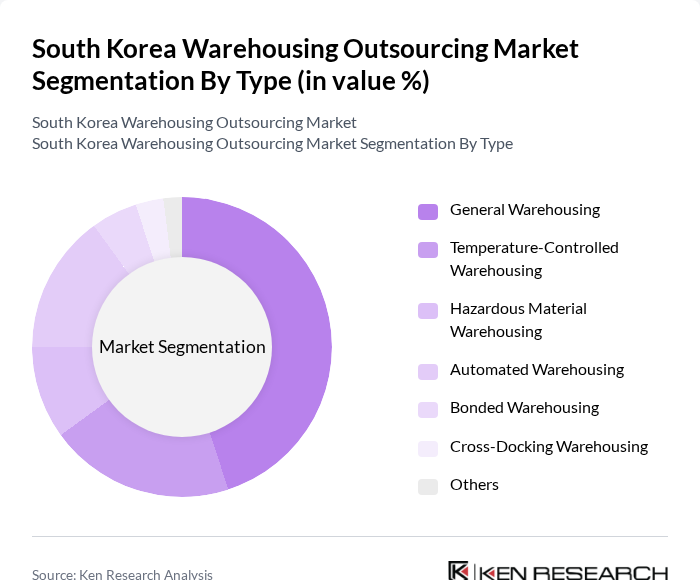
By Type:The warehousing outsourcing market is segmented into various types, including General Warehousing, Temperature-Controlled Warehousing, Hazardous Material Warehousing, Automated Warehousing, Bonded Warehousing, Cross-Docking Warehousing, and Others. Among these, General Warehousing is the most dominant segment due to its versatility and ability to cater to a wide range of industries. The increasing demand for storage solutions across sectors such as retail, manufacturing, and e-commerce has further solidified its position. Temperature-Controlled Warehousing is also gaining traction, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, where product integrity is crucial .
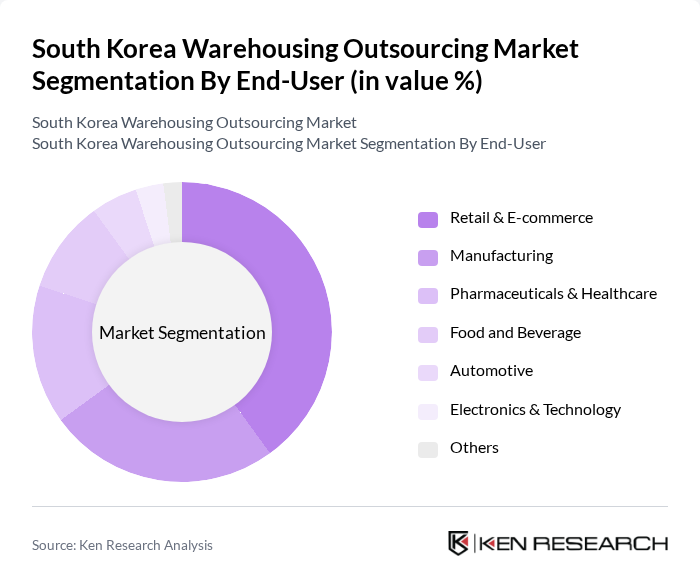
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Retail & E-commerce, Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare, Food and Beverage, Automotive, Electronics & Technology, and Others. The Retail & E-commerce segment is the largest, driven by the surge in online shopping and the need for efficient order fulfillment. The pandemic accelerated this trend, leading to increased demand for warehousing solutions that can handle high volumes of inventory and rapid delivery requirements. The Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare sector is also expanding, necessitating specialized warehousing for temperature-sensitive products .
The South Korea Warehousing Outsourcing Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as CJ Logistics, Hyundai Glovis, Lotte Global Logistics, Pantos Logistics (LG CNS), DB Schenker Korea, LS Networks, Samsung SDS, DSV Korea, Yusen Logistics Korea, Nippon Express Korea, Kuehne + Nagel Korea, Toll Group Korea, Agility Korea, Geodis Korea, Sinotrans Korea contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korean warehousing outsourcing market is poised for transformative growth, driven by the integration of advanced technologies and evolving consumer expectations. As businesses increasingly adopt automation and AI, operational efficiencies will improve, enabling faster response times and enhanced service levels. Additionally, the expansion of e-commerce and the need for sustainable practices will further shape the market landscape, encouraging innovative solutions that meet both consumer demands and regulatory requirements in future.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | General Warehousing Temperature-Controlled Warehousing Hazardous Material Warehousing Automated Warehousing Bonded Warehousing Cross-Docking Warehousing Others |
| By End-User | Retail & E-commerce Manufacturing Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare Food and Beverage Automotive Electronics & Technology Others |
| By Service Type | Storage Services Inventory Management Order Fulfillment Transportation & Distribution Services Value-Added Services (Packaging, Labeling, Kitting) Reverse Logistics Others |
| By Technology | Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) Internet of Things (IoT) Solutions Robotics Process Automation (RPA) Artificial Intelligence & Analytics Others |
| By Region | Seoul Busan Incheon Daegu Gyeonggi Province Others |
| By Customer Type | B2B B2C E-commerce Platforms Government & Public Sector SMEs Others |
| By Contract Type | Long-term Contracts Short-term Contracts Spot Contracts Project-Based Contracts Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Warehousing Operations | 60 | Warehouse Managers, Logistics Coordinators |
| Manufacturing Supply Chain Management | 50 | Operations Directors, Supply Chain Analysts |
| E-commerce Fulfillment Strategies | 50 | eCommerce Operations Managers, Inventory Control Specialists |
| Cold Chain Logistics | 40 | Cold Storage Managers, Quality Assurance Officers |
| Third-Party Logistics Providers | 40 | Business Development Managers, Client Relationship Managers |
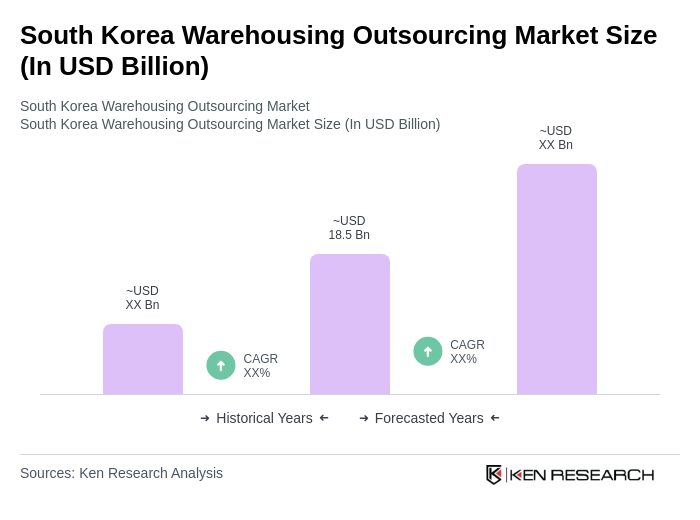
The South Korea Warehousing Outsourcing Market is valued at approximately USD 18.5 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by the expansion of e-commerce, demand for efficient supply chain solutions, and globalization in trade.