Region:Global
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAC0873
Pages:87
Published On:August 2025
By Type:The smart factory market can be segmented into various types, including discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, batch manufacturing, continuous manufacturing, and hybrid manufacturing. Each of these segments plays a crucial role in the overall market dynamics, catering to different manufacturing needs and processes. Discrete manufacturing is distinguished by its application in industries producing distinct items such as automobiles and electronics, while process manufacturing focuses on the production of goods in bulk, such as chemicals and food. Batch manufacturing involves the production of goods in specific quantities, continuous manufacturing operates non-stop, and hybrid manufacturing combines multiple approaches to optimize efficiency and flexibility .
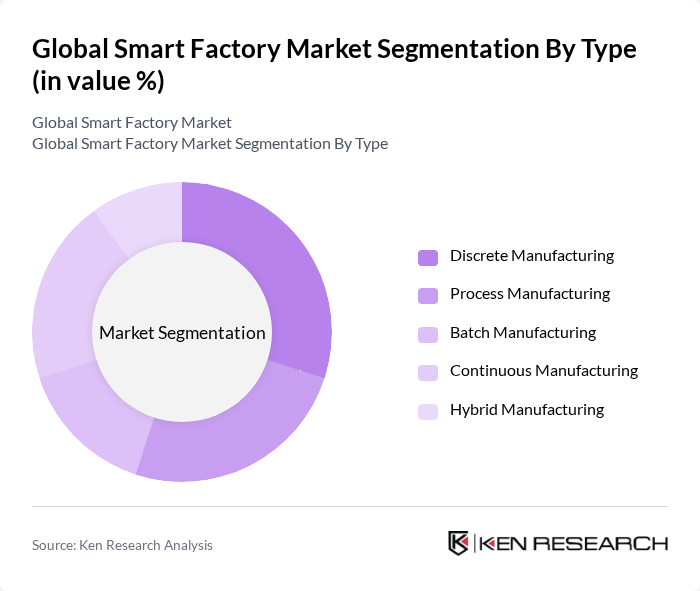
Thediscrete manufacturingsegment is currently dominating the market due to its widespread application in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. This segment benefits from the increasing demand for customized products and the need for efficient production processes. The trend towards automation and smart technologies in discrete manufacturing is driven by the need for flexibility, speed, and cost-effectiveness, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to enhance their operational capabilities. The adoption of digital twin technology, AI-driven analytics, and robotics is particularly strong in this segment, supporting rapid product innovation and customization .
By End-User:The smart factory market is also segmented by end-user industries, including automotive & transportation, electronics & semiconductors, aerospace & defense, food & beverage, pharmaceuticals & chemicals, energy & utilities, and others. Each of these sectors has unique requirements and applications for smart factory technologies. Automotive & transportation leverages smart factories for high-volume, precision manufacturing and supply chain optimization. Electronics & semiconductors utilize advanced automation for miniaturization and quality control. Aerospace & defense demand stringent standards and traceability, while food & beverage and pharmaceuticals focus on safety, compliance, and batch tracking. Energy & utilities use smart technologies for predictive maintenance and resource optimization .
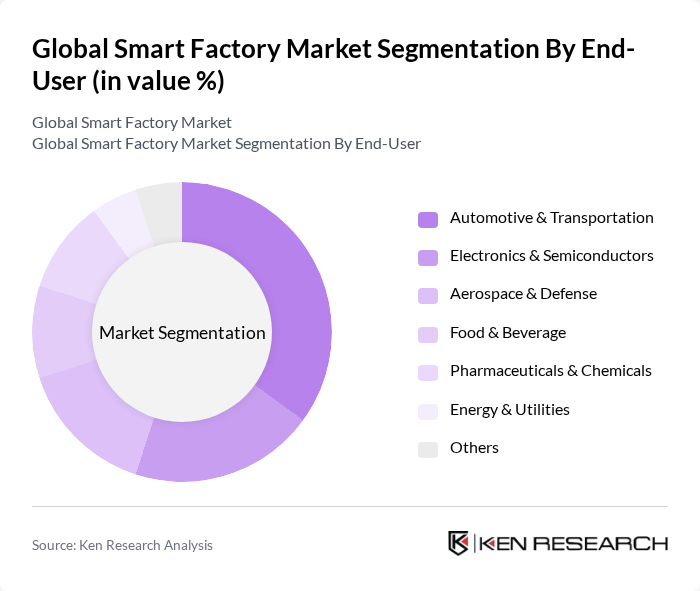
Theautomotive and transportationsector is leading the smart factory market due to the high demand for automation and smart technologies to enhance production efficiency and quality. The industry's focus on reducing production costs and improving supply chain management has led to significant investments in smart factory solutions. Additionally, the increasing complexity of automotive manufacturing processes necessitates the adoption of advanced technologies, further solidifying this sector's dominance in the market. The use of robotics, AI-based quality control, and connected supply chains is particularly prominent in automotive manufacturing, driving innovation and competitiveness .
The Global Smart Factory Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, Inc., Honeywell International Inc., ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric SE, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Bosch Rexroth AG, Emerson Electric Co., General Electric Company, Fanuc Corporation, Yokogawa Electric Corporation, Omron Corporation, PTC Inc., Dassault Systèmes SE, Siemens Digital Industries Software, SAP SE, Schneider Electric Industrial Software, ABB Ability™, Honeywell Process Solutions, Yokogawa Electric Industrial Automation contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the smart factory market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for efficiency. As manufacturers continue to embrace automation and IoT technologies, the landscape will evolve significantly. In future, the focus will shift towards enhancing cybersecurity measures and workforce training to address existing skill gaps. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning will further optimize production processes, leading to smarter, more efficient factories that can adapt to changing market demands.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Discrete Manufacturing Process Manufacturing Batch Manufacturing Continuous Manufacturing Hybrid Manufacturing |
| By End-User | Automotive & Transportation Electronics & Semiconductors Aerospace & Defense Food & Beverage Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals Energy & Utilities Others |
| By Component | Industrial Hardware (Sensors, Controllers, Robots) Software (MES, SCADA, PLM, ERP) Services (Consulting, Integration, Maintenance) |
| By Application | Predictive Maintenance Quality Control & Inspection Supply Chain & Inventory Management Production Planning & Scheduling Asset Management |
| By Sales Channel | Direct Sales Distributors & System Integrators Online Sales |
| By Distribution Mode | Offline Distribution Online Distribution |
| By Price Range | Low Price Mid Price High Price |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Smart Manufacturing | 100 | Production Managers, Automation Engineers |
| Electronics Smart Factory Solutions | 80 | Operations Directors, IT Managers |
| Consumer Goods Automation | 70 | Supply Chain Managers, Quality Control Officers |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Technologies | 60 | Regulatory Affairs Managers, Production Supervisors |
| Textile Industry Automation | 40 | Process Engineers, Sustainability Managers |
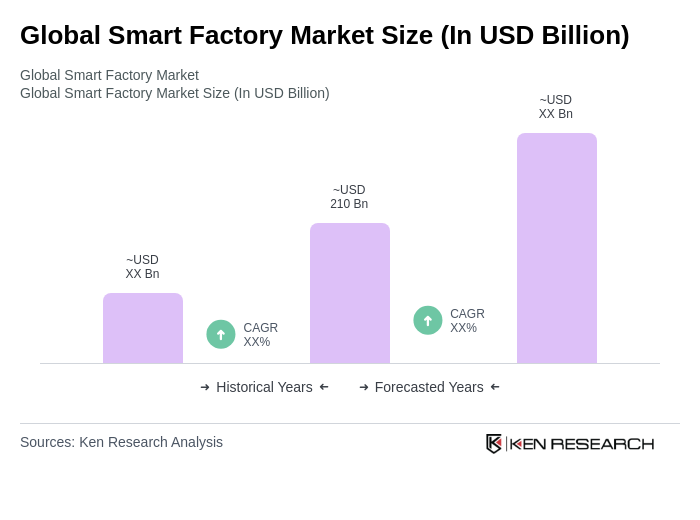
The Global Smart Factory Market is valued at approximately USD 210 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by the adoption of automation technologies, IoT, and the need for operational efficiency in manufacturing processes.