Region:Middle East
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAC3019
Pages:80
Published On:October 2025
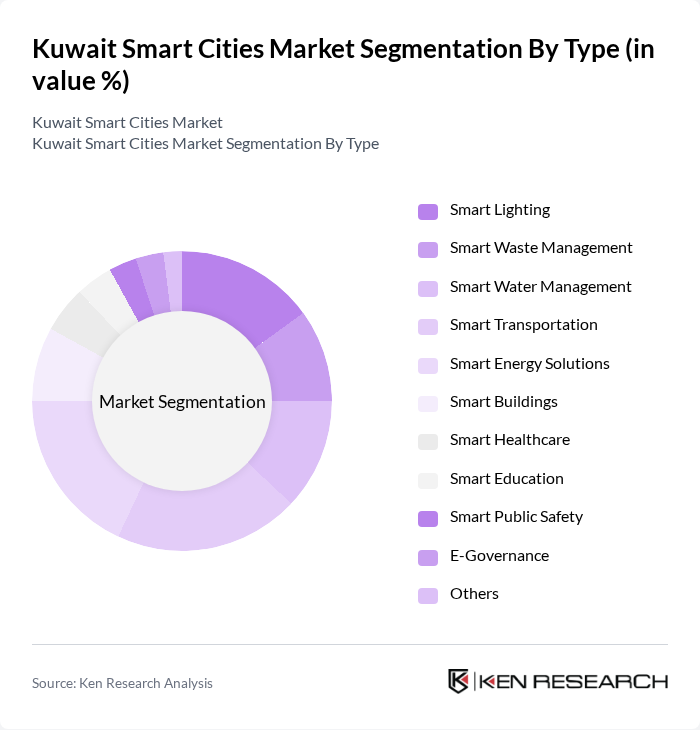
By Type:The market is segmented into a broad range of smart solutions tailored to diverse urban needs. Key segments include Smart Lighting, Smart Waste Management, Smart Water Management, Smart Transportation, Smart Energy Solutions, Smart Buildings, Smart Healthcare, Smart Education, Smart Public Safety, E-Governance, and Others. Each segment plays a vital role in driving efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life improvements in Kuwait’s urban environments, with a notable emphasis on digital transformation, mobility, and resource optimization .
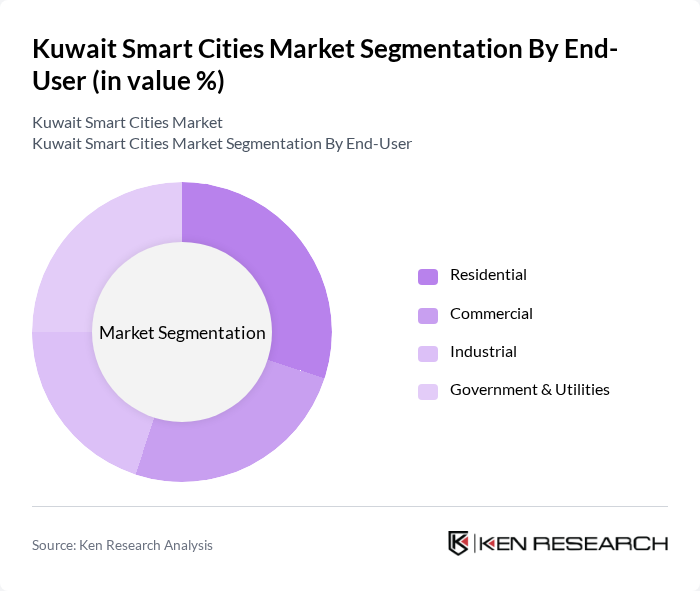
By End-User:The market is also segmented by end-user, including Residential, Commercial, Industrial, and Government & Utilities. Each end-user segment has distinct requirements and adoption patterns, with government and utilities driving large-scale infrastructure projects, commercial and industrial users focusing on operational efficiency, and residential adoption rising due to smart home and community initiatives .
The Kuwait Smart Cities Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Kuwait Integrated Petroleum Industries Company (KIPIC), Zain Group, stc Kuwait (formerly VIVA), Boubyan Bank, National Bank of Kuwait (NBK), Kuwait Oil Company (KOC), Kuwait Municipality, Gulf Bank, Kuwait National Petroleum Company (KNPC), Kuwait Investment Authority (KIA), Agility Public Warehousing Company, Kuwait Projects Company (Holding) – KIPCO, Alghanim Industries, Al-Mazaya Holding Company, Al-Futtaim Group, Honeywell Kuwait, Siemens Kuwait, Huawei Kuwait, IBM Kuwait, Schneider Electric Kuwait contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space .
The future of the Kuwait smart cities market is poised for significant transformation, driven by ongoing urbanization and technological advancements. In future, the integration of smart technologies is expected to enhance urban living, improve resource management, and foster economic growth. Increased collaboration among government entities, private sectors, and technology providers will be crucial in overcoming existing challenges. As sustainability becomes a priority, innovative solutions will emerge, paving the way for a more connected and efficient urban environment in Kuwait.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Smart Lighting Smart Waste Management Smart Water Management Smart Transportation Smart Energy Solutions Smart Buildings Smart Healthcare Smart Education Smart Public Safety E-Governance Others |
| By End-User | Residential Commercial Industrial Government & Utilities |
| By Application | Urban Mobility Energy Management Public Safety Environmental Monitoring Smart Governance Smart Healthcare Smart Education Others |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Investment Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Government Schemes |
| By Policy Support | Subsidies Tax Exemptions Regulatory Support Incentives for Green Technologies |
| By Technology | IoT Solutions Cloud Computing Artificial Intelligence Big Data Analytics Mobility Solutions Cybersecurity |
| By Distribution Mode | Direct Sales Online Platforms Distributors Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Transportation Solutions | 60 | City Transport Officials, Urban Mobility Experts |
| Smart Energy Management | 50 | Energy Sector Managers, Sustainability Coordinators |
| Public Safety and Security Systems | 40 | Law Enforcement Officials, Security Technology Providers |
| Smart Waste Management | 40 | Environmental Managers, Waste Management Directors |
| Smart Healthcare Initiatives | 50 | Healthcare Administrators, Telehealth Coordinators |
The Kuwait Smart Cities Market is valued at approximately USD 1.1 billion, driven by urbanization, government initiatives, and the adoption of advanced technologies like IoT and AI, aimed at improving urban living standards.