Region:Middle East
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAD6021
Pages:95
Published On:December 2025
By Mining Method:
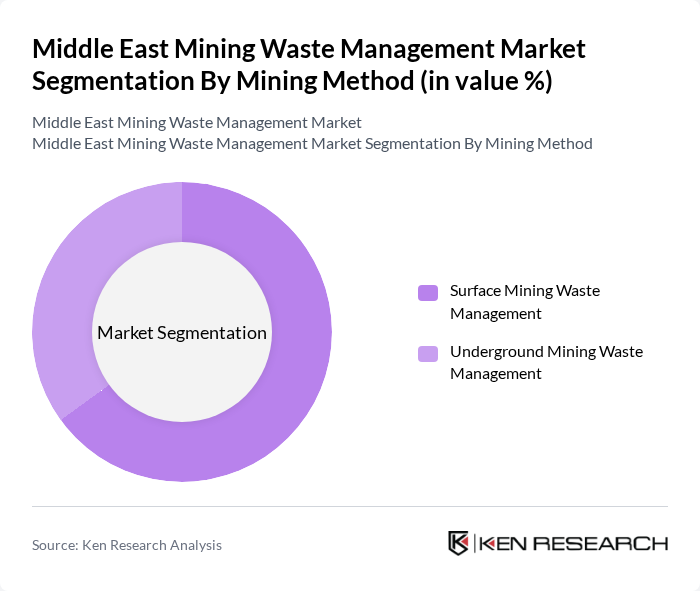
The mining method segmentation includes Surface Mining Waste Management and Underground Mining Waste Management. Surface mining, covering open-pit mines, quarries, and large-scale phosphate and industrial mineral operations, is currently the dominant method due to its cost-effectiveness, higher productivity, and suitability for the region’s near-surface ore bodies. This method generates substantial volumes of overburden, waste rock, and tailings, necessitating engineered storage facilities, water management systems, dust control, and progressive rehabilitation. Underground mining, while typically generating less waste per ton of ore, requires specialized waste management techniques such as backfilling, underground paste disposal, and careful ventilation and water treatment due to the complexities involved in subsurface waste handling and environmental protection. The increasing focus on sustainable practices is driving innovations in both segments, including filtered tailings, dry stacking, real-time monitoring, and closure planning, with surface mining leading the way in deployment of large-scale waste management solutions in the Middle East context.
By Mineral / Metal:
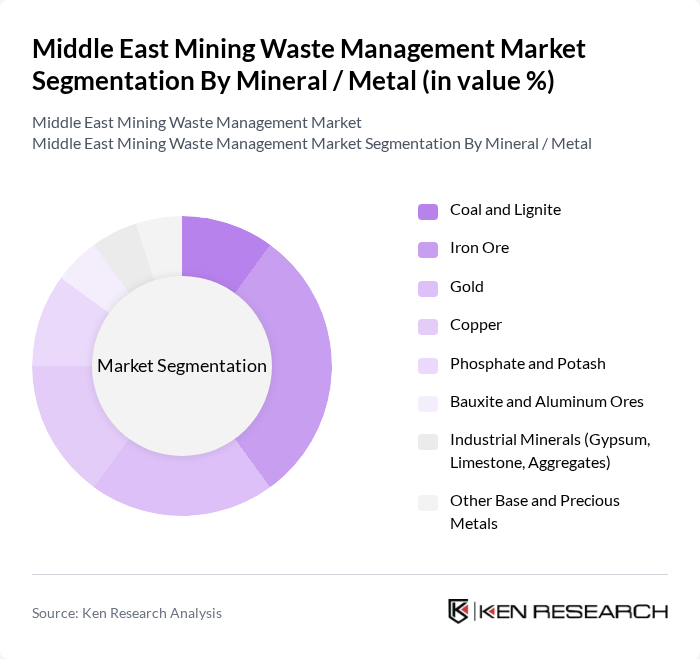
This segmentation includes Coal and Lignite, Iron Ore, Gold, Copper, Phosphate and Potash, Bauxite and Aluminum Ores, Industrial Minerals (Gypsum, Limestone, Aggregates), and Other Base and Precious Metals. In the Middle East, phosphate, gold, copper, and industrial minerals represent the most relevant mining segments, with Saudi Arabia and other Gulf countries focusing on phosphates, gold, copper, and large quarrying operations rather than iron ore and coal. Phosphate and associated fertilizers are in high demand for agriculture, while gold and copper are critical for electronics, infrastructure, and energy transition technologies, leading to significant tailings and process waste that must be carefully managed. The increasing extraction of industrial minerals such as gypsum, limestone, and aggregates for construction and infrastructure projects also contributes substantially to overburden and waste rock volumes, requiring robust overburden handling, reclamation, and dust mitigation measures. The focus on recycling, water reuse, and circular economy practices—including reprocessing tailings, using waste rock in construction, and recovering metals from legacy waste—is driving growth across all mineral segments, with phosphate, gold, copper, and industrial minerals playing a particularly important role in the Middle East mining waste management landscape.
The Middle East Mining Waste Management Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Veolia Environnement SA, SUEZ Group (including SUEZ Recycling and Recovery), Averda, Bee’ah (Sharjah Environmental Company), Tadweer Group (Abu Dhabi Waste Management Company), Dulsco, EnviroServe, Imdaad, Saudi Investment Recycling Company (SIRC), Al Dhafra Waste Management Company, Al Dhow Environmental Services, Gulf Environment & Waste FZE (GEW), Al Haya Enviro, SRK Consulting, and Worley contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space, including hazardous and industrial waste streams that are relevant to mining activities in the region.
The future of the Middle East mining waste management market appears promising, driven by increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures. As countries in the region continue to prioritize sustainable practices, investments in innovative waste management technologies are expected to rise significantly. The integration of AI and IoT will enhance operational efficiencies, while public and private partnerships will likely foster collaborative efforts to address waste management challenges, paving the way for a more sustainable mining industry in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Mining Method | Surface Mining Waste Management Underground Mining Waste Management |
| By Mineral / Metal | Coal and Lignite Iron Ore Gold Copper Phosphate and Potash Bauxite and Aluminum Ores Industrial Minerals (Gypsum, Limestone, Aggregates) Other Base and Precious Metals |
| By Waste Type | Overburden and Waste Rock Tailings Mine Water and Process Effluents Sludges and Filter Cakes Acid Mine Drainage and Metal?contaminated Waste |
| By Management / Treatment Solution | Tailings Storage Facilities and Dams Waste Rock and Overburden Management Mine Water Treatment and Recycling Backfilling and Paste Fill Waste?to?Resource / Recycling and Valorization Mine Closure, Remediation and Rehabilitation Services |
| By Service Provider Type | Integrated Environmental Service Companies Specialized Mining Waste Management Contractors Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) Firms Environmental Consulting and Design Firms In?house Mining Company Operations |
| By Country | Saudi Arabia United Arab Emirates Qatar Oman Kuwait Bahrain Egypt Jordan Rest of Middle East |
| By Ownership & Project Stage | State?owned Mining Projects Private / International Mining Operators Exploration and Early?stage Projects Operating Mines Closure and Post?closure Sites |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Mining Waste Management Practices | 100 | Environmental Managers, Compliance Officers |
| Recycling and Reuse of Mining Waste | 80 | Waste Management Specialists, Sustainability Officers |
| Regulatory Compliance in Mining | 70 | Legal Advisors, Regulatory Affairs Managers |
| Technological Innovations in Waste Management | 60 | R&D Managers, Technology Officers |
| Market Trends and Future Outlook | 90 | Industry Analysts, Market Researchers |
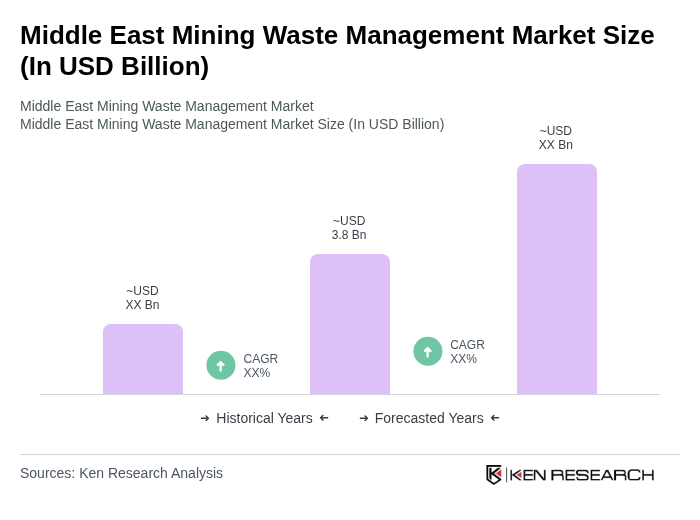
The Middle East Mining Waste Management Market is valued at approximately USD 3.8 billion, driven by increasing mining activities and stringent environmental regulations in countries like Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Oman, and Qatar.