Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAD0210
Pages:88
Published On:August 2025

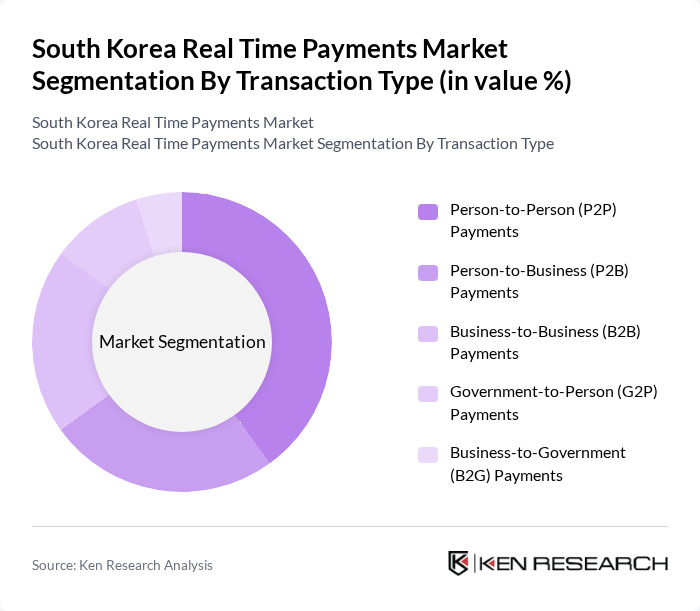
By Transaction Type:The transaction type segmentation includes various methods through which payments are made. The subsegments are Person-to-Person (P2P) Payments, Person-to-Business (P2B) Payments, Business-to-Business (B2B) Payments, Government-to-Person (G2P) Payments, and Business-to-Government (B2G) Payments. Among these, P2P Payments currently hold a larger market share due to early adoption and the increasing popularity of mobile payment applications and social media platforms that facilitate easy money transfers between individuals. The convenience and speed of these transactions have led to a surge in user adoption, making P2P Payments a significant contributor to the overall market growth. However, P2B Payments are experiencing accelerated growth as businesses seek efficient and cost-effective payment solutions .
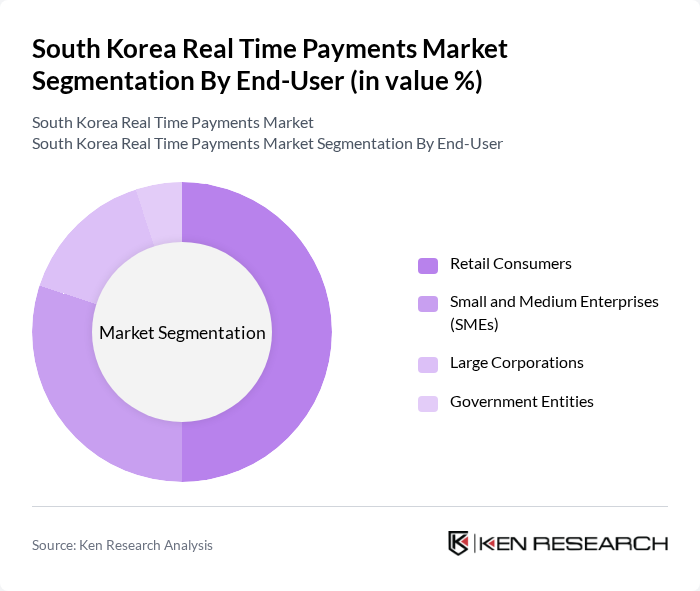
By End-User:The end-user segmentation encompasses various categories of users engaging in real-time payments. This includes Retail Consumers, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Large Corporations, and Government Entities. Retail Consumers are leading this segment, driven by the increasing adoption of mobile wallets and digital payment platforms. The convenience of making instant payments for everyday purchases has significantly influenced consumer behavior, leading to a higher market share for this subsegment. SMEs are also increasingly utilizing real-time payment solutions to streamline their operations and enhance cash flow management .
The South Korea Real Time Payments Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Kakao Pay, Naver Pay, Viva Republica (Toss), Samsung Pay, LG Uplus, Shinhan Bank, KB Kookmin Bank, NH Nonghyup Bank, Hana Bank, Woori Bank, Payco (NHN Corp.), Citibank Korea, Standard Chartered Bank Korea, KEB Hana Bank, Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK), BC Card, Lotte Card, Visa Korea, and Mastercard Korea contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korea real-time payments market is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. By future, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in payment systems is expected to enhance transaction security and user experience. Additionally, the shift towards open banking frameworks will facilitate greater collaboration between banks and fintech companies, fostering innovation and expanding the range of payment solutions available to consumers and businesses alike.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Transaction Type | Person-to-Person (P2P) Payments Person-to-Business (P2B) Payments Business-to-Business (B2B) Payments Government-to-Person (G2P) Payments Business-to-Government (B2G) Payments |
| By End-User | Retail Consumers Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Large Corporations Government Entities |
| By Application | E-commerce Transactions Utility Payments Remittances Subscription Services Payroll & Wage Disbursements |
| By Payment Method | Bank Transfers (including Open Banking) Mobile Wallets QR Code Payments Contactless Payments (NFC, RFID) |
| By Transaction Size | Micro Transactions (< KRW 10,000) Small Transactions (KRW 10,000 - KRW 100,000) Medium Transactions (KRW 100,000 - KRW 1,000,000) Large Transactions (> KRW 1,000,000) |
| By Industry | Retail & E-commerce Healthcare Transportation & Mobility Hospitality & Leisure Utilities & Telecom |
| By Technology Deployment | Cloud-based Solutions On-premise Solutions Hybrid Models |
| By Policy Support | Government Subsidies Tax Incentives Regulatory Support Programs Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Adoption of Real-Time Payments | 150 | Retail Customers, Digital Payment Users |
| Merchant Perspectives on Payment Solutions | 100 | Small Business Owners, E-commerce Managers |
| Banking Sector Insights on Payment Innovations | 70 | Bank Executives, Payment Product Managers |
| Regulatory Impact on Payment Systems | 60 | Regulatory Officials, Compliance Officers |
| Fintech Startups and Market Trends | 50 | Startup Founders, Product Development Leads |
The South Korea Real Time Payments Market is valued at approximately USD 1.7 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by the increasing adoption of digital payment solutions and the rise of e-commerce, alongside a growing demand for instant payment services.