Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAB0796
Pages:93
Published On:August 2025
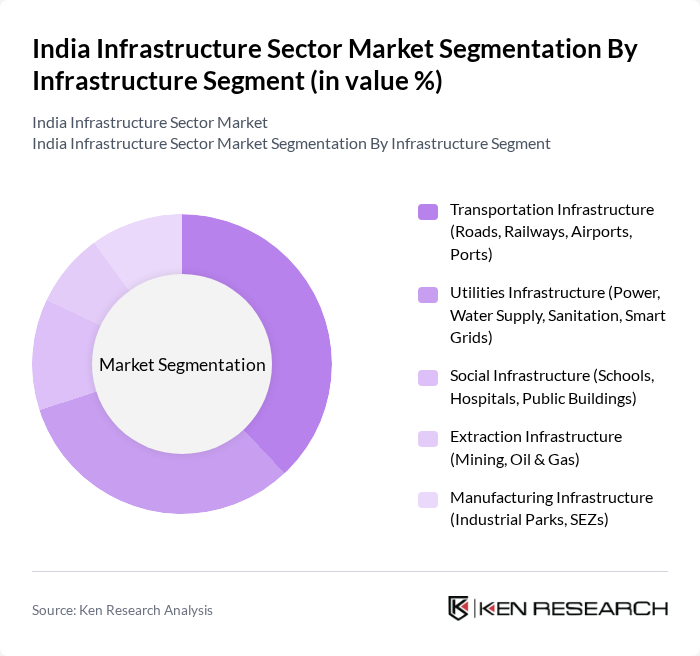
By Infrastructure Segment:The infrastructure segment encompasses various categories, including transportation, utilities, social, extraction, and manufacturing infrastructure. Each of these segments plays a crucial role in supporting the overall development of the country. Thetransportation infrastructuresegment, which includes roads, railways, airports, and ports, holds the largest share, driven by the increasing demand for efficient logistics and connectivity.Utilities infrastructure, focusing on power, water supply, and sanitation, is also vital as it underpins the functioning of urban and rural areas. The sector is further supported by ongoing digitalization, adoption of smart grids, and sustainability initiatives .
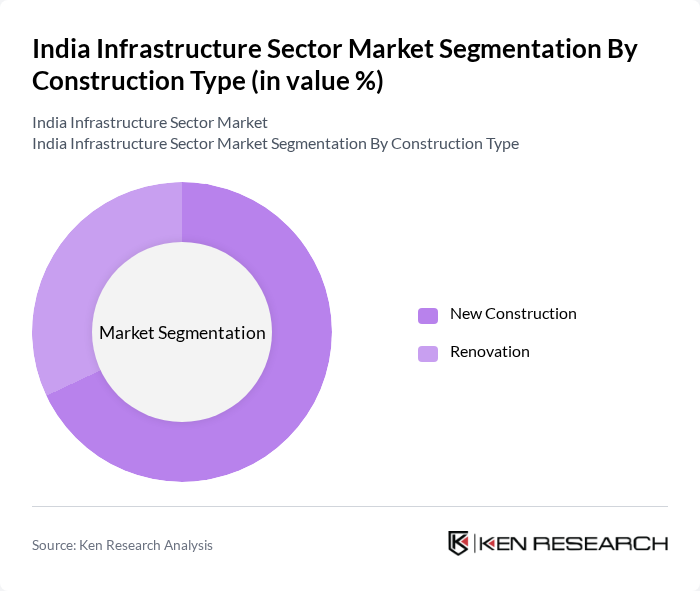
By Construction Type:The construction type segment is divided into new construction and renovation.New constructionis the leading sub-segment, driven by the need for modern infrastructure to support urbanization, industrialization, and economic growth. Renovation projects are also significant, focusing on upgrading existing facilities to meet contemporary standards, improve resilience, and achieve sustainability goals .
The India Infrastructure Sector Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Larsen & Toubro Limited, Tata Projects Limited, GMR Group, Hindustan Construction Company Limited (HCC), IRB Infrastructure Developers Limited, Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (Adani Ports & SEZ), NCC Limited, J Kumar Infraprojects Limited, Shapoorji Pallonji Group, Gammon India Limited, Simplex Infrastructures Limited, PNC Infratech Limited, Ashoka Buildcon Limited, KNR Constructions Limited, Dilip Buildcon Limited, Afcons Infrastructure Limited, GVK Group, Lanco Infratech Limited, DLF Limited, Reliance Infrastructure Limited contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Indian infrastructure sector appears promising, driven by ongoing urbanization and government initiatives. With the National Infrastructure Pipeline in full swing, investments in smart cities and sustainable practices are expected to gain momentum. Additionally, the integration of digital technologies will enhance project efficiency and transparency. As the government continues to prioritize infrastructure development, the sector is poised for significant growth, attracting both domestic and foreign investments in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Infrastructure Segment | Transportation Infrastructure (Roads, Railways, Airports, Ports) Utilities Infrastructure (Power, Water Supply, Sanitation, Smart Grids) Social Infrastructure (Schools, Hospitals, Public Buildings) Extraction Infrastructure (Mining, Oil & Gas) Manufacturing Infrastructure (Industrial Parks, SEZs) |
| By Construction Type | New Construction Renovation |
| By Investment Source | Public Private Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) |
| By Region/State | Maharashtra Karnataka Delhi NCR Telangana Other States |
| By Key Cities | Mumbai Metropolitan Region Pune Bengaluru Hyderabad Chennai Kolkata Ahmedabad Rest of India |
| By Technology | Smart Infrastructure Technologies Green Building Technologies Construction Automation |
| By Application | Residential Construction Commercial Construction Industrial Construction |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Transportation Infrastructure Projects | 120 | Project Managers, Civil Engineers |
| Energy Sector Developments | 60 | Energy Analysts, Project Developers |
| Urban Development Initiatives | 50 | Urban Planners, Local Government Officials |
| Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Projects | 40 | PPP Coordinators, Financial Advisors |
| Infrastructure Financing and Investment | 45 | Investment Bankers, Financial Analysts |
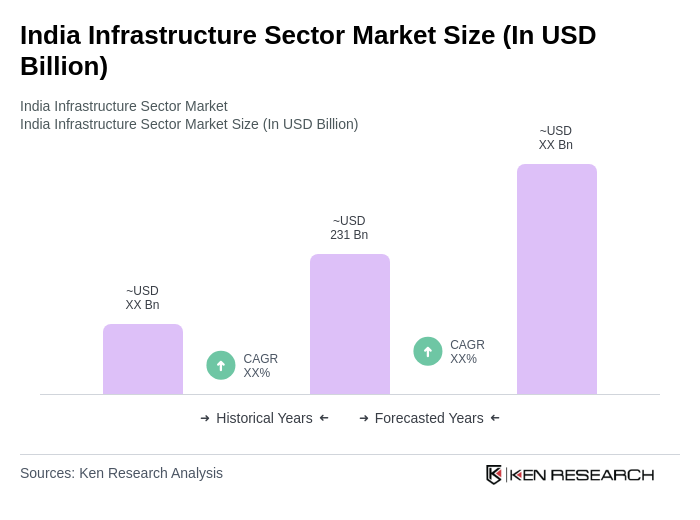
The India Infrastructure Sector Market is valued at approximately USD 231 billion, driven by rapid urbanization, government initiatives, and increased investments in infrastructure development. This valuation reflects a comprehensive analysis over the past five years.