Region:Middle East
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAD0431
Pages:97
Published On:August 2025
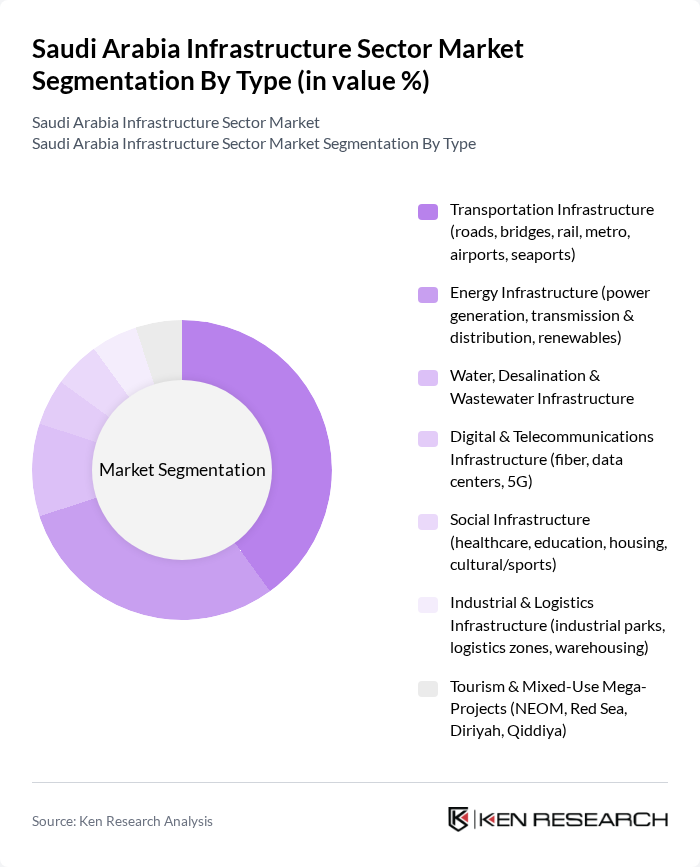
By Type:The infrastructure sector in Saudi Arabia can be segmented into various types, including transportation, energy, water, digital, social, industrial, and tourism infrastructure. Each of these segments plays a crucial role in the overall development of the country's infrastructure landscape. The transportation infrastructure segment, which includes roads, bridges, rail, metro, airports, and seaports, is particularly significant due to multimodal logistics plans and urban mobility programs such as metros and rail expansions. Energy infrastructure, focusing on power generation, transmission and distribution, and renewables, remains vital given large-scale grid, IPP, and renewable additions aligned with Vision 2030 and utility-led investments.
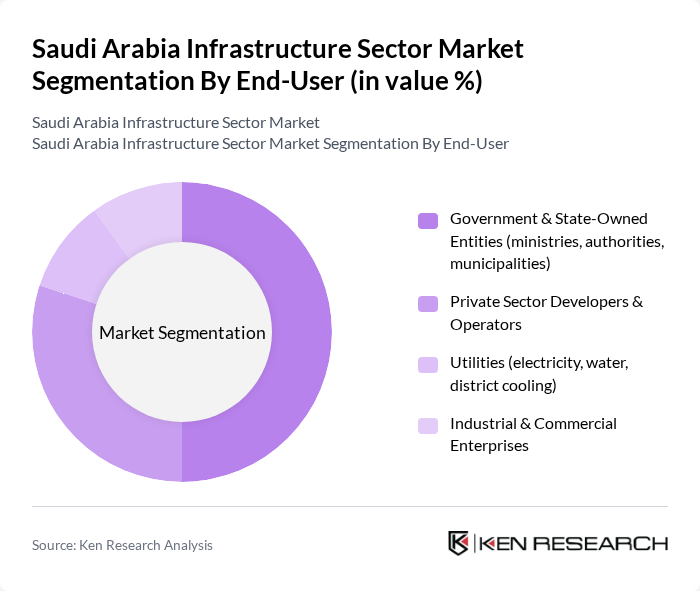
By End-User:The end-user segmentation of the infrastructure sector includes government entities, private sector developers, utilities, and industrial enterprises. Government and state-owned entities are the primary drivers of infrastructure projects, as they initiate and fund most large-scale developments. Private sector developers are increasingly participating in public-private partnerships, while utilities play a crucial role in energy and water infrastructure.
The Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Saudi Binladin Group, El Seif Engineering Contracting Company, Nesma & Partners Contracting Company Ltd., Al-Mabani General Contractors, Al Rashid Trading & Contracting Company (RTCC), Al Bawani Co. Ltd., Al Rajhi Construction (Abdulrahman Saad Al-Rashid & Sons Co.), China Railway Construction Corporation Limited (CRCC) – Saudi Operations, Bechtel Corporation – Saudi Arabia, Hyundai Engineering & Construction Co., Ltd. – KSA, Samsung C&T Corporation – KSA, Larsen & Toubro (L&T) – KSA, ACWA Power, National Water Company (NWC), Public Investment Fund (PIF) – Giga Projects Delivery Entities contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The Saudi infrastructure sector is poised for significant transformation, driven by government initiatives and urbanization trends. As the population grows and urban areas expand, the demand for modern infrastructure will intensify. The focus on sustainable practices and digital transformation will shape future projects, ensuring resilience against environmental challenges. Additionally, the integration of advanced technologies will enhance operational efficiency, making the sector more competitive and attractive for foreign investments, ultimately supporting the nation’s economic diversification goals.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Transportation Infrastructure (roads, bridges, rail, metro, airports, seaports) Energy Infrastructure (power generation, transmission & distribution, renewables) Water, Desalination & Wastewater Infrastructure Digital & Telecommunications Infrastructure (fiber, data centers, 5G) Social Infrastructure (healthcare, education, housing, cultural/sports) Industrial & Logistics Infrastructure (industrial parks, logistics zones, warehousing) Tourism & Mixed-Use Mega-Projects (NEOM, Red Sea, Diriyah, Qiddiya) |
| By End-User | Government & State-Owned Entities (ministries, authorities, municipalities) Private Sector Developers & Operators Utilities (electricity, water, district cooling) Industrial & Commercial Enterprises |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Public Expenditure Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP/PFI) Sovereign Funds & Government-Related Entities (e.g., PIF) |
| By Application | Urban Development & Smart Cities Regional & Rural Development Asset Rehabilitation & Maintenance Capacity Expansion & Greenfield Projects |
| By Policy Support | Subsidies & Tariff Mechanisms Tax & Customs Incentives Regulatory & Permitting Support Grants & Concessional Financing |
| By Financing Model | EPC (Public Procurement) Project Finance (non-recourse/limited recourse) Equity & Joint Ventures Debt Financing (bonds, sukuk, bank loans) |
| By Project Size | Mega/Giga Projects (SAR 10B+) Large Projects (SAR 1B–10B) Medium & Small Projects (below SAR 1B) |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Transportation Infrastructure Projects | 140 | Project Managers, Civil Engineers |
| Utility Infrastructure Development | 100 | Operations Managers, Utility Executives |
| Social Infrastructure Initiatives | 80 | Government Officials, Urban Planners |
| Construction Material Suppliers | 70 | Supply Chain Managers, Procurement Officers |
| Infrastructure Financing and Investment | 90 | Financial Analysts, Investment Managers |
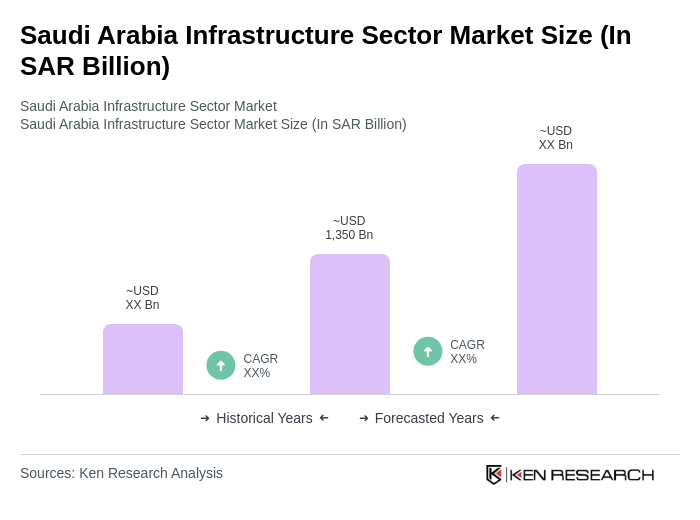
The Saudi Arabia Infrastructure Sector Market is valued at approximately SAR 1,350 billion. This valuation is based on a five-year historical analysis and reflects significant growth driven by government initiatives, particularly the Vision 2030 program aimed at economic diversification.