Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAD0622
Pages:85
Published On:August 2025
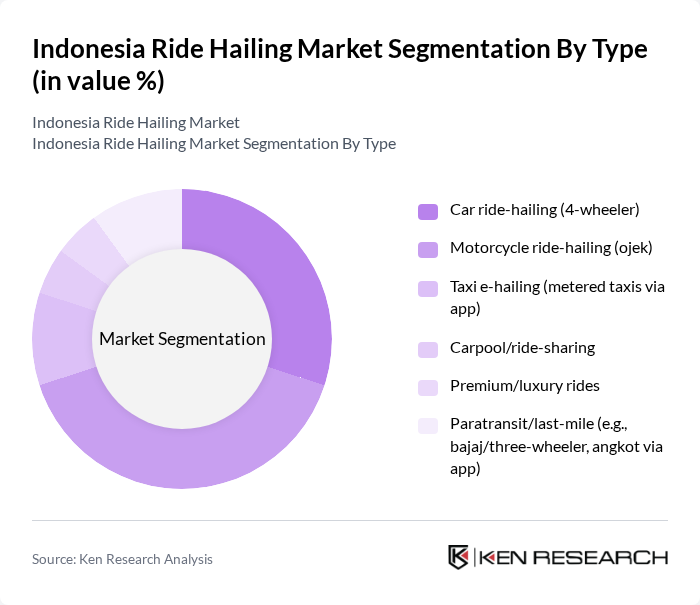
By Type:The ride-hailing market can be segmented into various types, including car ride-hailing (4-wheeler), motorcycle ride-hailing (ojek), taxi e-hailing (metered taxis via app), carpool/ride-sharing, premium/luxury rides, and paratransit/last-mile services. Each of these segments caters to different consumer needs and preferences, with motorcycle ride-hailing being particularly popular due to its affordability and ability to navigate through traffic efficiently. Industry sources consistently indicate two-wheelers account for the majority of trips due to congestion, lower fares, and faster pick-up in dense cities .
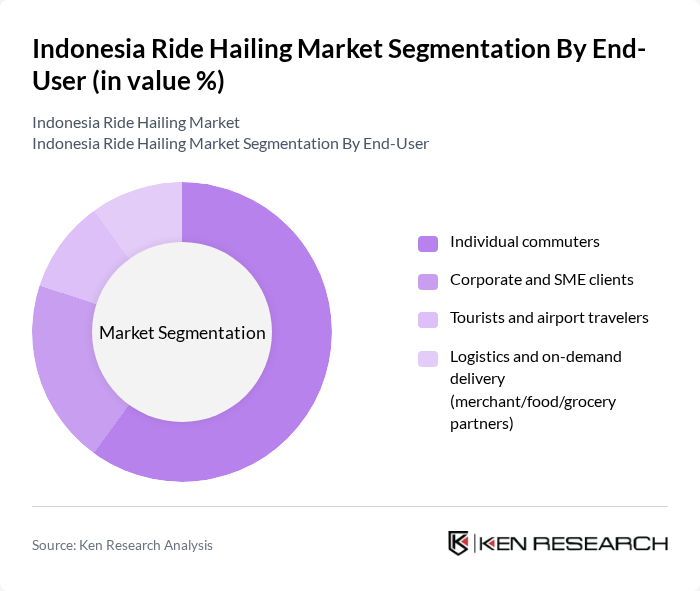
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes individual commuters, corporate and SME clients, tourists and airport travelers, and logistics and on-demand delivery services. Individual commuters represent the largest segment, driven by the convenience and cost-effectiveness of ride-hailing services for daily travel needs. Growth is reinforced by airport transfer demand, digital payment ubiquity, and integration with adjacent services (delivery and merchant ecosystems) .
The Indonesia Ride Hailing Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Gojek (PT GoTo Gojek Tokopedia Tbk), Grab Indonesia, PT Blue Bird Tbk (MyBlueBird), Maxim Indonesia, Anterin, inDrive Indonesia, MyTrans (PT Transjakarta Integrasi Moda), DANA Indonesia, LinkAja (PT Fintek Karya Nusantara), Traveloka (Airport Rides & car rental partners), ShopeeFood & ShopeeExpress (mobility-adjacent), Xpress Indonesia (formerly Lalamove Indonesia), Karya Anak Bangsa (GrabKios is now Grab’s agent network; include GrabMerchant), Alfamart & Indomaret (top-up and agent ecosystem partners), Tiket.com (mobility integrations) contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Indonesian ride-hailing market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. As urbanization continues, the demand for efficient transportation solutions will likely increase. Additionally, the integration of AI and data analytics will enhance service delivery, improving user experiences. Companies that adapt to these trends and invest in sustainable practices, such as electric vehicle adoption, will be well-positioned to thrive in this competitive landscape, ensuring long-term growth and market relevance.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Car ride-hailing (4-wheeler) Motorcycle ride-hailing (ojek) Taxi e-hailing (metered taxis via app) Carpool/ride-sharing Premium/luxury rides Paratransit/last-mile (e.g., bajaj/three-wheeler, angkot via app) |
| By End-User | Individual commuters Corporate and SME clients Tourists and airport travelers Logistics and on-demand delivery (merchant/food/grocery partners) |
| By Pricing Model | Dynamic/surge pricing Metered/fixed fares (regulated taxi) Passes and subscriptions (ride passes, corporate plans) |
| By Service Area | Tier-1 metros (e.g., Jakarta, Surabaya, Bandung) Tier-2/3 cities Intercity and airport corridors |
| By Vehicle Type | Two-wheelers (motorcycles/scooters) Passenger cars (hatchback/sedan/MPV/SUV) Metered taxis Low-emission and electric vehicles (2W/4W/three-wheeler) |
| By Customer Demographics | Age cohorts Income tiers Occupation and student segment |
| By Payment Method | Bank cards E-wallets (GoPay, OVO, DANA, LinkAja) Cash Buy-now-pay-later and others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Urban Ride-Hailing Users | 150 | Frequent Users, Occasional Users |
| Ride-Hailing Drivers | 120 | Full-time Drivers, Part-time Drivers |
| Regulatory Stakeholders | 60 | Government Officials, Policy Makers |
| Industry Experts | 40 | Transportation Analysts, Market Researchers |
| Corporate Clients Using Ride-Hailing Services | 90 | Corporate Travel Managers, HR Representatives |
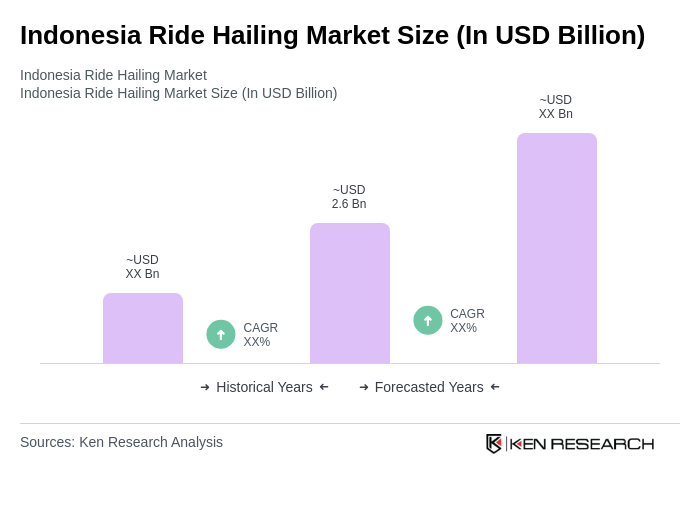
The Indonesia Ride Hailing Market is valued at approximately USD 2.6 billion, reflecting a five-year historical analysis. This valuation aligns with industry trackers that estimate the market value within the mid-USD 24 billion range, driven by urban congestion and digital payment adoption.