Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAD6574
Pages:92
Published On:December 2025
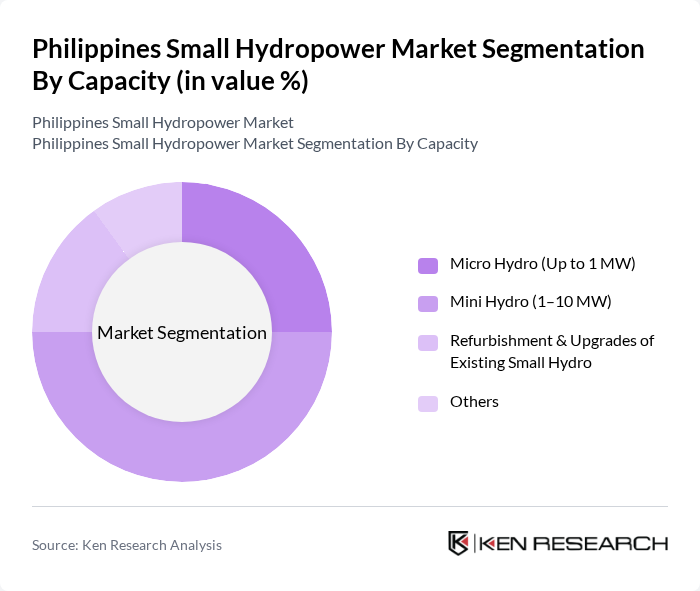
By Capacity:The capacity segmentation of the market includes various subsegments such as Micro Hydro (Up to 1 MW), Mini Hydro (1–10 MW), Refurbishment & Upgrades of Existing Small Hydro, and Others. This classification is aligned with common global practice, where small hydropower is typically defined as projects up to 10 MW and further divided into micro and mini categories. Among these, Mini Hydro systems are currently leading the market due to their scalability, grid?connected operation, and higher attractiveness for utilities and independent power producers, consistent with global trends where the 1–10 MW segment accounts for the largest revenue share. The increasing focus on sustainable energy solutions, hybridization with solar, and rural or peri?urban electrification has driven investments in this segment, making it a preferred choice for both private and public developers, especially in river basins suitable for run?of?river schemes.
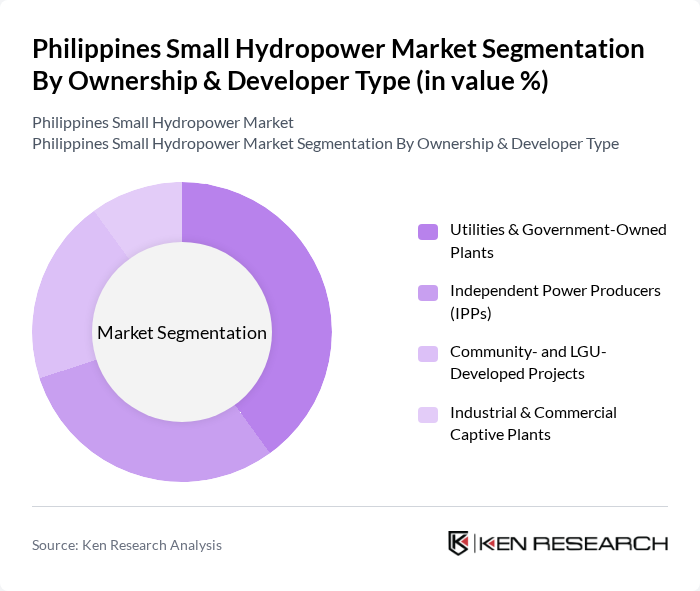
By Ownership & Developer Type:This segmentation includes Utilities & Government-Owned Plants, Independent Power Producers (IPPs), Community- and LGU-Developed Projects, and Industrial & Commercial Captive Plants. This ownership structure reflects the broader pattern observed in the Asia Pacific small hydropower sector, where public utilities, private developers, and community-based entities all participate in project development. The Utilities & Government-Owned Plants segment is currently the most dominant, as government initiatives, public–private partnerships, and utility?led investments have led to the establishment of numerous small hydropower projects that feed into the main grid. This segment benefits from regulatory support under the Renewable Energy Act and associated incentive schemes and is crucial in meeting the energy demands of rural and off-grid areas by providing stable baseload renewable power.
The Philippines Small Hydropower Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Aboitiz Power Corporation (AboitizPower), SN Aboitiz Power Group, Hedcor, Inc., First Gen Corporation, Energy Development Corporation (EDC), Alternergy Holdings Corporation, PhilNewEnergy, Inc., PhilHydro Power Corporation, Alsons Renewable Energy Corporation, Sta. Clara International Corporation, CleanTech Global Renewables, Inc., APC Group, Inc., München Energy Company, Inc. (MECO), Magis Energy Holdings Corporation, Green Power Panay Philippines, Inc. contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the small hydropower market in the Philippines appears promising, driven by increasing investments in renewable energy and supportive government policies. As the country continues to prioritize energy security and sustainability, small hydropower is expected to play a crucial role in diversifying the energy mix. The integration of smart grid technologies and energy storage solutions will further enhance the efficiency and reliability of small hydropower systems, making them more competitive against other renewable sources in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Capacity | Micro Hydro (Up to 1 MW) Mini Hydro (1–10 MW) Refurbishment & Upgrades of Existing Small Hydro Others |
| By Ownership & Developer Type | Utilities & Government-Owned Plants Independent Power Producers (IPPs) Community- and LGU-Developed Projects Industrial & Commercial Captive Plants |
| By Region | Luzon Visayas Mindanao |
| By Component / Technology | Turbines Generators & Inverters Control & Protection Systems Civil Works & Balance of Plant |
| By Connection & Application | Grid-Connected Off-Grid / Islanded Mini?Grids Hybrid Systems (Hydro + Solar / Other RE) Others |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Private Investment Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Government & Multilateral Financing |
| By Policy & Revenue Mechanism | Feed-in Tariff (FIT) Projects Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) & Green Energy Auction Projects Net Metering / Embedded Generation Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Small Hydropower Project Developers | 100 | Project Managers, Business Development Executives |
| Regulatory Authorities | 50 | Policy Makers, Energy Regulators |
| Energy Sector Consultants | 80 | Consultants, Analysts |
| Local Community Stakeholders | 60 | Community Leaders, Local Government Officials |
| Environmental NGOs | 40 | Environmental Advocates, Project Coordinators |
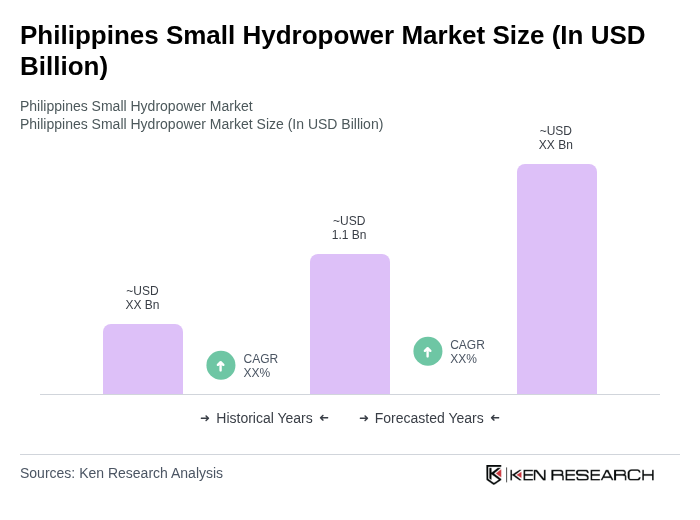
The Philippines Small Hydropower Market is valued at approximately USD 1.1 billion. This valuation reflects a significant share within the global small hydropower market, driven by increasing investments and the demand for renewable energy sources.