Region:Europe
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAA1780
Pages:90
Published On:August 2025
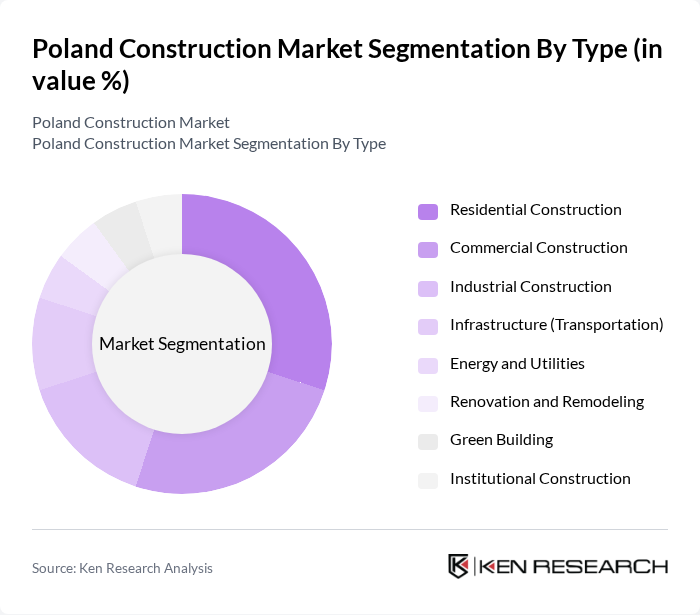
By Type:The construction market can be segmented into various types, including Residential Construction, Commercial Construction, Industrial Construction, Infrastructure (Transportation), Energy and Utilities, Renovation and Remodeling, Green Building, and Institutional Construction. Each of these segments plays a crucial role in the overall market dynamics, driven by specific consumer needs and regulatory frameworks.
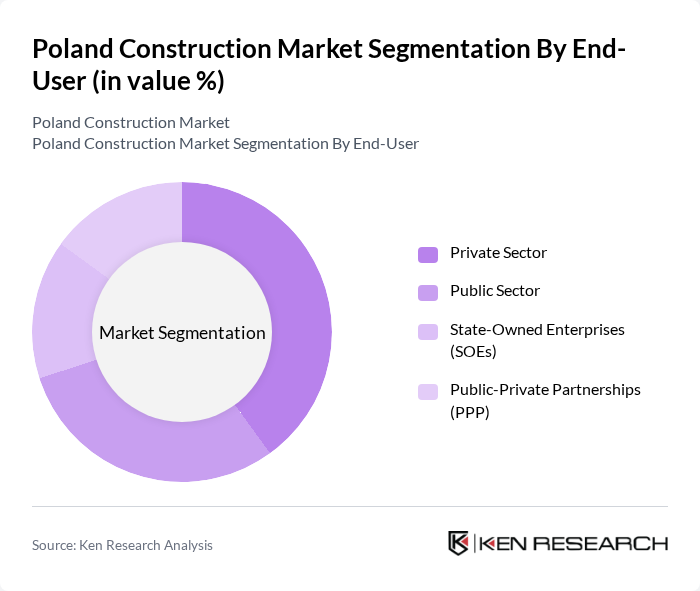
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes the Private Sector, Public Sector, State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs), and Public-Private Partnerships (PPP). Each of these segments has distinct characteristics and influences on the construction market, reflecting the varying demands and funding sources for construction projects. Public sector and EU-backed investments continue to underpin civil works, while private capital supports commercial and select residential development.
The Poland Construction Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Budimex S.A., Strabag Sp. z o.o., Skanska S.A., Polimex-Mostostal S.A., Mostostal Warszawa S.A., Warbud S.A., Erbud S.A., Unibep S.A., PORR S.A., ZUE S.A., Alstal Grupa Budowlana Sp. z o.o. Sp.k., Mota-Engil Central Europe S.A., Karmar S.A. (Bouygues Construction Polska), Gülermak A??r Sanayi ?n?aat ve Taahhüt A.?., Porr Polska Infrastructure S.A. contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Poland construction market appears promising, driven by substantial government investments and EU funding aimed at infrastructure development. As urbanization accelerates, the demand for sustainable and smart construction practices will likely increase. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as digitalization and automation, are expected to enhance efficiency and safety in construction processes. These trends will create a dynamic environment for growth, fostering innovation and attracting investment in the sector.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Residential Construction Commercial Construction Industrial Construction Infrastructure (Transportation) Energy and Utilities Renovation and Remodeling Green Building Institutional Construction |
| By End-User | Private Sector Public Sector State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) |
| By Application | Residential Buildings Commercial Spaces (Office, Retail, Hospitality) Infrastructure Development (Road, Rail, Airports, Ports) Industrial Facilities (Manufacturing, Logistics, Warehousing) Energy Projects (Power Generation, Grid, Renewables) |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Private Investment Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) EU Funds and Cohesion Policy Financing Government Budget and Development Bank Loans |
| By Policy Support | Subsidies and Grants for Green Projects Tax Incentives (CIT relief, Depreciation, VAT preferences) Regulatory Support for Innovation (BIM, Digital Permitting) Housing and Infrastructure Programs (e.g., social/affordable housing) |
| By Construction Method | Traditional On-site Construction Modular Construction Prefabricated/Off-site Construction Design-Build/EPC Contracts |
| By Project Size | Small Scale Projects Medium Scale Projects Large/Mega Projects |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Construction Projects | 120 | Project Managers, Site Engineers |
| Commercial Building Developments | 100 | Architects, Construction Supervisors |
| Infrastructure Projects (Roads, Bridges) | 80 | Government Officials, Civil Engineers |
| Construction Material Suppliers | 70 | Sales Managers, Product Development Leads |
| Regulatory Compliance in Construction | 60 | Compliance Officers, Legal Advisors |
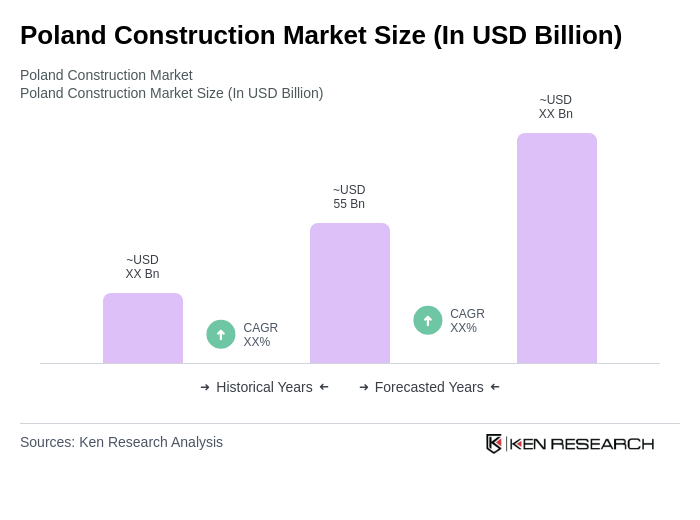
The Poland construction market is valued at approximately USD 55 billion, reflecting a robust growth trajectory driven by urbanization, government investments, and EU-funded infrastructure programs. This valuation is based on a comprehensive five-year historical analysis of construction output.