Region:Asia
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAA0257
Pages:97
Published On:August 2025
By Type:The cold chain industry can be segmented into refrigerated transport, temperature-controlled warehousing, cold storage equipment, and last-mile delivery solutions. Each of these segments plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of temperature-sensitive products throughout the supply chain. Refrigerated transport and temperature-controlled warehousing are particularly vital for supporting the distribution of perishable foods and pharmaceuticals, while cold storage equipment and last-mile delivery solutions address the need for specialized storage and timely delivery in urban and rural areas .
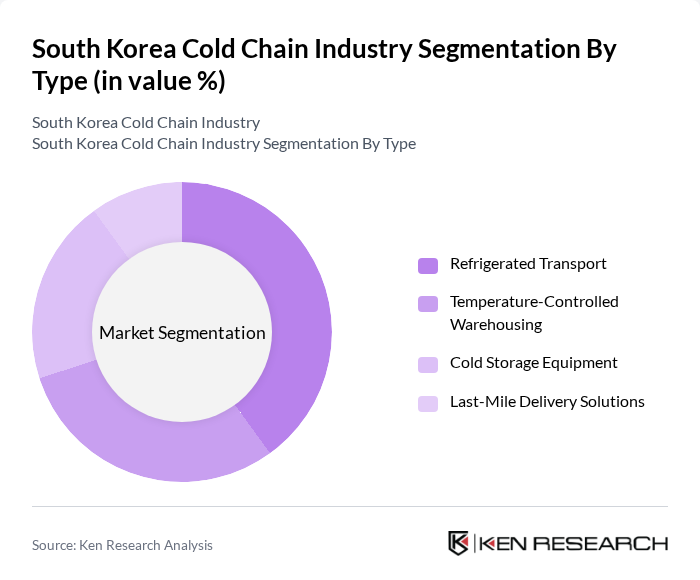
The refrigerated transport segment is currently dominating the market due to the increasing demand for fresh food and pharmaceuticals that require strict temperature control during transit. This segment benefits from advancements in logistics technology, such as real-time tracking and automated temperature monitoring, which enhance operational efficiency and reliability. The growing trend of e-commerce in food delivery further propels the need for efficient refrigerated transport solutions, making it the leading subsegment in the cold chain industry .
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes food and beverage, pharmaceuticals and healthcare, fruits and vegetables, agriculture, and chemicals and cosmetics. Each of these sectors has unique requirements for cold chain logistics, influencing the overall market dynamics. The food and beverage sector, for example, requires extensive cold storage and transport for seafood, meat, dairy, and processed foods, while the pharmaceutical sector demands precise temperature control for vaccines and biologics .
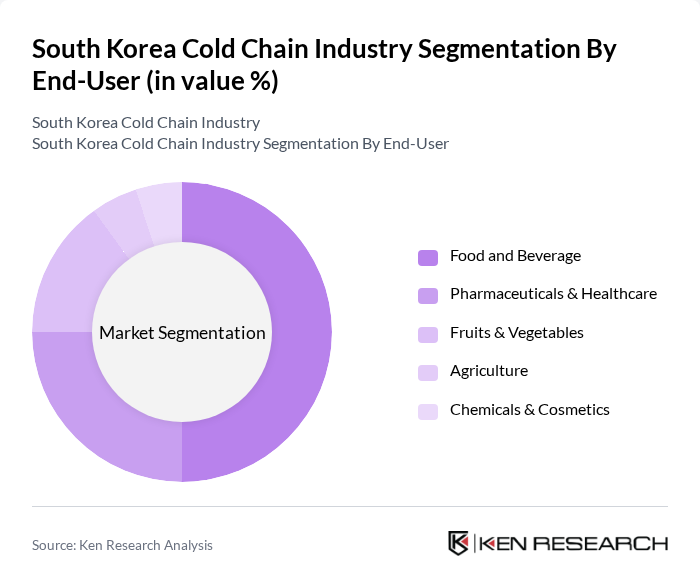
The food and beverage sector is the largest end-user of cold chain services, driven by the rising consumer demand for fresh and perishable goods. This segment encompasses a wide range of products, including seafood, meat, dairy, and processed foods, all of which require stringent temperature control to maintain quality and safety. The increasing trend of online grocery shopping and meal kit deliveries has further amplified the need for robust cold chain solutions in this sector, solidifying its position as the leading end-user .
The South Korea Cold Chain Industry market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as CJ Logistics, Lotte Global Logistics, Hanjin Transportation, Hyundai Glovis, SK Networks, Daewoo Logistics, GS Global, Samsung C&T, KCTC (Korea Container Terminal Co.), Dongbu Express, Hanil Express, Logen Logistics, Kwangdong Pharmaceutical, Dongyang Logis, SML (Seoul Multi Logistics), Korea Express, Pantos Logistics (LG Group), SF Express Korea, Hankook Samgong, Dongwon Loex contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korean cold chain industry is poised for substantial growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing consumer demand for fresh and safe products. As the market adapts to evolving consumer preferences, companies are expected to invest in innovative solutions that enhance efficiency and reduce waste. Additionally, government support for infrastructure improvements will play a critical role in shaping the industry's landscape, ensuring that it meets the challenges of a dynamic market environment while maintaining high standards of quality and safety.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Refrigerated Transport Temperature-Controlled Warehousing Cold Storage Equipment Last-Mile Delivery Solutions |
| By End-User | Food and Beverage (including seafood, meat, dairy, processed foods, meal kits) Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare (including vaccines, biologics, clinical trial logistics) Fruits & Vegetables Agriculture (including seeds, flowers, and agri-exports) Chemicals & Cosmetics |
| By Distribution Channel | Direct Sales Third-Party Logistics (3PL) E-commerce & Online Grocery Platforms Retail Chains |
| By Temperature Range | Chilled (0°C to 5°C) Frozen (-18°C and below) Controlled Ambient (Above 5°C up to 25°C) |
| By Technology | Active Systems (mechanical refrigeration, reefer trucks) Passive Systems (insulated containers, gel packs) Hybrid Systems |
| By Service Type | Transportation Services Warehousing Services Packaging & Labelling Services Value-Added Services (e.g., real-time monitoring, customs clearance) |
| By Policy Support | Subsidies for Cold Chain Infrastructure Tax Incentives for Cold Storage Facilities Grants for Technology Adoption Regulatory Compliance Support |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage Cold Storage | 100 | Warehouse Managers, Supply Chain Coordinators |
| Pharmaceutical Cold Chain Logistics | 60 | Quality Assurance Managers, Logistics Directors |
| Retail Cold Chain Operations | 50 | Operations Managers, Inventory Control Specialists |
| Cold Chain Technology Providers | 40 | Product Development Managers, Technical Sales Representatives |
| Government Regulatory Bodies | 40 | Policy Makers, Regulatory Compliance Officers |
The South Korea Cold Chain Industry is valued at approximately USD 1.3 billion, driven by the increasing demand for temperature-sensitive products in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, along with advancements in logistics technology and infrastructure.