Region:Asia
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAA0410
Pages:92
Published On:August 2025
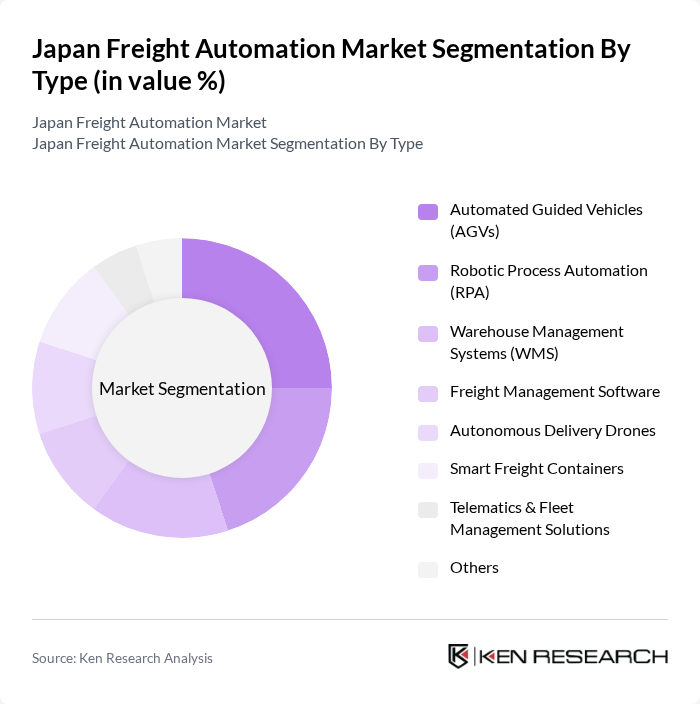
By Type:The market is segmented into Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Freight Management Software, Autonomous Delivery Drones, Smart Freight Containers, Telematics & Fleet Management Solutions, and Others. These segments represent key automation technologies that drive operational efficiency, cost reduction, and improved accuracy in freight operations. AGVs and WMS are particularly prominent due to their widespread adoption in warehouses and distribution centers, while RPA and telematics solutions are increasingly used for process optimization and real-time fleet management .
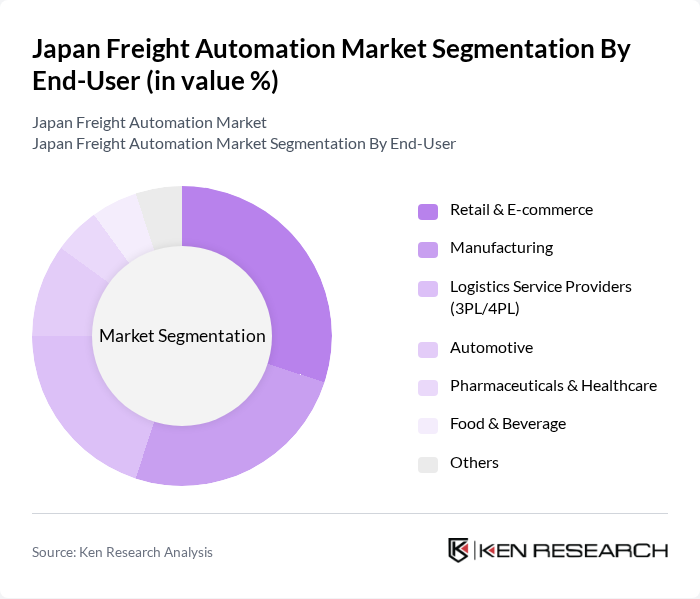
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Retail & E-commerce, Manufacturing, Logistics Service Providers (3PL/4PL), Automotive, Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare, Food & Beverage, and Others. Each sector has distinct operational requirements that drive the adoption of freight automation. Retail & e-commerce and manufacturing are the largest adopters, leveraging automation to improve supply chain responsiveness and reduce delivery times. Logistics service providers are also significant users, integrating automation to manage complex, multi-modal operations efficiently .
The Japan Freight Automation Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Nippon Express, Yamato Holdings, Kintetsu World Express, Sagawa Express, Hitachi Transport System, Seino Holdings, Mitsui-Soko Holdings, Japan Post Holdings, Fujitsu, Panasonic, Daifuku, Toyota Industries, NEC Corporation, SoftBank Robotics, Murata Machinery, Okamura Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric, and Toshiba Logistics contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Japan freight automation market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and increasing e-commerce activities. As companies invest in smart logistics solutions, the integration of AI and IoT technologies will enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, the push for sustainability will lead to the development of eco-friendly freight solutions. These trends indicate a transformative shift in the logistics landscape, positioning Japan as a leader in freight automation in future.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) Freight Management Software Autonomous Delivery Drones Smart Freight Containers Telematics & Fleet Management Solutions Others |
| By End-User | Retail & E-commerce Manufacturing Logistics Service Providers (3PL/4PL) Automotive Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare Food & Beverage Others |
| By Industry Vertical | Automotive Consumer Goods Electronics & Electricals Food & Beverage Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals Chemicals Others |
| By Deployment Mode | On-Premises Cloud-Based Hybrid Others |
| By Region | Kanto Kansai Chubu Kyushu Hokkaido Shikoku Others |
| By Technology | Artificial Intelligence (AI) Machine Learning (ML) Internet of Things (IoT) Blockchain Big Data Analytics Computer Vision Others |
| By Policy Support | Government Subsidies Tax Incentives Grants for Technology Development Regulatory Sandboxes for Automation Pilots Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Sector Automation | 100 | Operations Managers, Logistics Coordinators |
| Retail Freight Automation | 80 | Supply Chain Directors, E-commerce Managers |
| Automotive Logistics Solutions | 70 | Procurement Managers, Warehouse Supervisors |
| Technology Providers in Freight Automation | 60 | Product Managers, Sales Executives |
| Government and Regulatory Bodies | 40 | Policy Makers, Industry Analysts |
The Japan Freight Automation Market is valued at approximately USD 5 billion, driven by the increasing demand for efficient logistics solutions, advancements in automation technologies, and the growth of the e-commerce sector, which requires faster delivery systems.