Region:Asia
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAA1535
Pages:84
Published On:August 2025
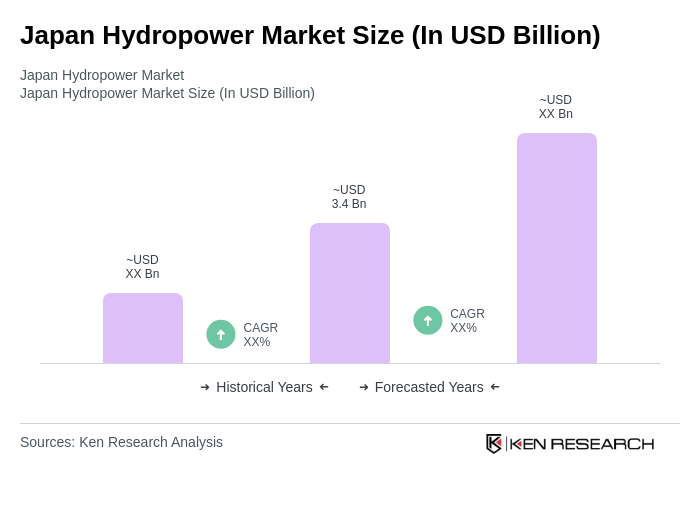
By Type:The hydropower market can be segmented into various types, including Run-of-River Hydropower, Pumped Storage Hydropower, Reservoir (Storage) Hydropower, Small Hydropower (?10 MW), and Micro & Pico Hydropower (?100 kW). Among these, Run-of-River Hydropower continues to gain traction where feasible due to lower reservoir impacts, while most of Japan’s installed base is conventional reservoir and pumped-storage assets located in mountainous regions. Pumped Storage Hydropower remains critical for grid balancing, load shifting, and integrating solar and wind, given Japan’s growing variable renewables and peak demand needs.
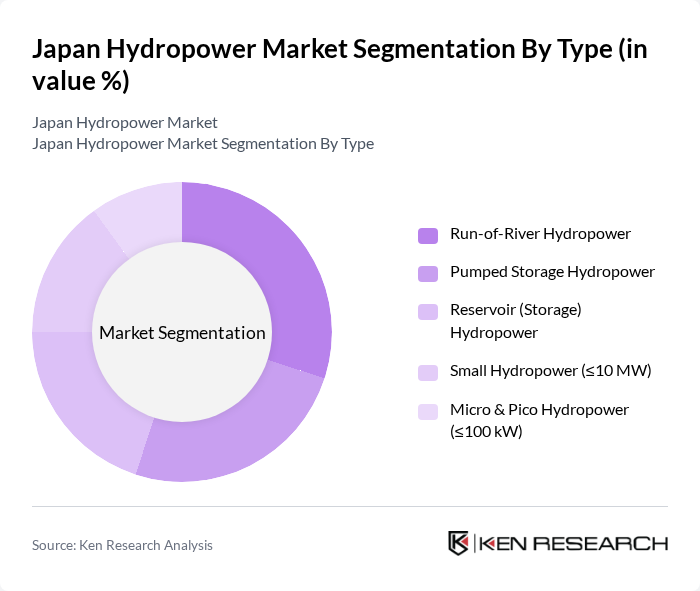
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Utility (General Electric Utilities and EPCOs), Industrial & Commercial, Residential & Community Energy Cooperatives, and Government & Municipalities. The Utility segment is the largest because EPCOs own and operate most hydropower and pumped-storage assets and lead refurbishment and capacity uprating. Industrial and commercial users participate mainly through small hydro and on-site/community projects, while municipalities support distributed small hydro and river improvements tied to local energy goals.
The Japan Hydropower Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO), Chubu Electric Power Co., Inc. (Chubu Electric Power Company), The Kansai Electric Power Co., Inc. (Kansai Electric Power Company), Tohoku Electric Power Co., Inc. (Tohoku Electric Power Company), Kyushu Electric Power Co., Inc. (Kyushu Electric Power Company), J-POWER (Electric Power Development Co., Ltd.), Shikoku Electric Power Co., Inc. (Shikoku Electric Power Company), Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Inc. (Hokkaido Electric Power Company), Renewable Japan Co., Ltd. (Renewable Japan), Hitachi Mitsubishi Hydro Corporation (HM Hydro), Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation, Hitachi, Ltd., IHI Corporation, Marubeni Corporation, and Sumitomo Corporation contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of Japan's hydropower market appears promising, driven by a combination of technological advancements and increasing government support. As the country aims to achieve its renewable energy targets, investments in small-scale hydropower projects are expected to rise significantly. Furthermore, the integration of smart grid technologies will enhance energy distribution efficiency, allowing for better management of renewable resources. This evolving landscape will likely attract both domestic and international investments, fostering innovation and sustainability in the hydropower sector.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Run-of-River Hydropower Pumped Storage Hydropower Reservoir (Storage) Hydropower Small Hydropower (?10 MW) Micro & Pico Hydropower (?100 kW) |
| By End-User | Utility (General Electric Utilities and EPCOs) Industrial & Commercial Residential & Community Energy Cooperatives Government & Municipalities |
| By Application | Grid-Connected Systems Off-Grid and Remote Area Supply Pumped-Storage for Grid Balancing Rehabilitation & Repowering of Existing Plants |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Investment Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Government Programs & FIT Schemes |
| By Policy Support | Feed-in Tariffs (FIT) & Feed-in Premiums (FIP) Tax Incentives & Accelerated Depreciation Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) Environmental Permitting & Water Rights Frameworks |
| By Technology | Turbines (Francis, Kaplan, Pelton) Balance of Plant & Control Systems (SCADA, IIoT) Energy Storage (Pumped-Storage Integration) Civil Works & Dam Safety Upgrades |
| By Distribution Mode | Direct EPC/IPP Contracts OEM to Utility Procurement Engineering Consultants & Integrators Distributors & Local Agents |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Hydropower Plant Operators | 100 | Plant Managers, Operations Directors |
| Energy Policy Experts | 75 | Government Officials, Regulatory Analysts |
| Environmental Consultants | 50 | Sustainability Advisors, Environmental Engineers |
| Investors in Renewable Energy | 60 | Investment Analysts, Portfolio Managers |
| Technology Providers for Hydropower | 40 | Product Managers, R&D Engineers |
The Japan Hydropower Market is valued at approximately USD 3.4 billion, reflecting a significant investment in renewable energy driven by government policies and modernization efforts in existing hydro assets.