Kuwait Neobanking Market Overview
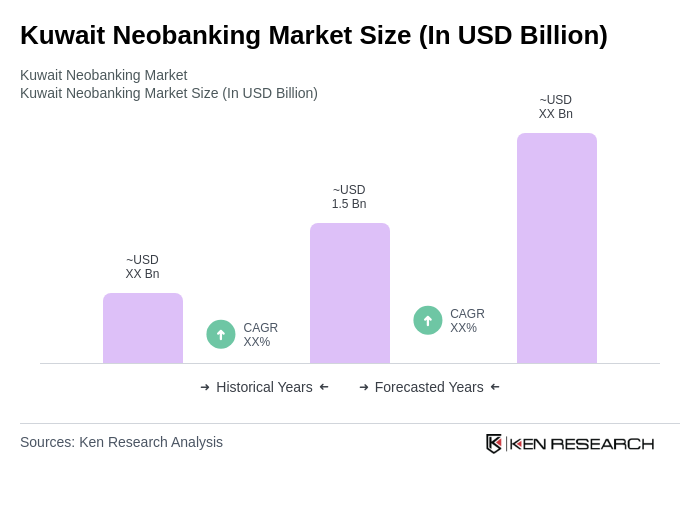
- The Kuwait Neobanking Market is valued at USD 1.5 billion, based on a five-year historical analysis. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing adoption of digital banking solutions, a surge in smartphone penetration, and a growing preference for cashless transactions among consumers. The rise of fintech innovations and the demand for personalized banking experiences have further propelled the market's expansion. Recent trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for hyper-personalized services, partnerships between neobanks and fintech or technology firms, and the rollout of virtual and contactless banking features that cater to a digitally native customer base.
- Kuwait City is the dominant hub in the neobanking market, attributed to its status as the financial center of the country. The concentration of banking institutions, coupled with a tech-savvy population, fosters an environment conducive to neobanking growth. Additionally, the presence of expatriate communities in urban areas contributes to the demand for digital banking services, enhancing the market's vibrancy.
- The Central Bank of Kuwait requires all financial institutions, including neobanks, to comply with the Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) Regulations, issued by the Central Bank of Kuwait and most recently updated to align with international standards. These regulations mandate rigorous customer due diligence, ongoing monitoring, and reporting of suspicious transactions, ensuring that neobanks operate within a secure and transparent framework that protects consumers and mitigates risks associated with digital transactions. Licensing for neobanks involves demonstrating robust AML/CFT controls, and non-compliance can result in supervisory action or revocation of authorization.
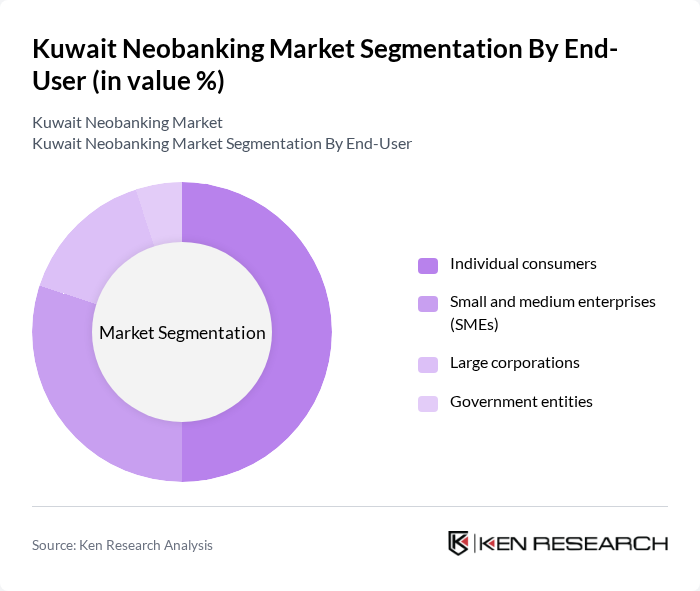
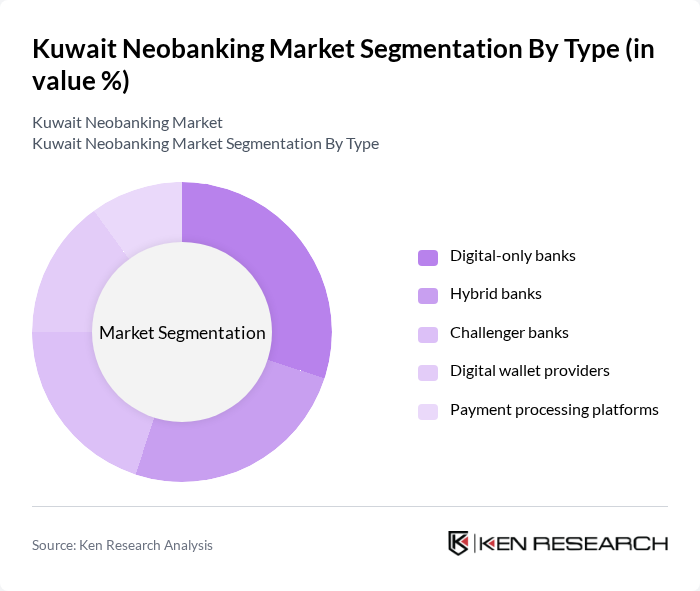
Kuwait Neobanking Market Segmentation
By Type:The neobanking market can be segmented into various types, including digital-only banks, hybrid banks, challenger banks, digital wallet providers, and payment processing platforms. Digital-only banks are gaining traction due to their low operational costs and customer-centric services. Hybrid banks combine traditional banking with digital services, appealing to a broader audience. Challenger banks focus on niche markets, while digital wallet providers and payment processing platforms cater to the growing demand for seamless transactions. The checking and bank account segment remains the most prevalent, as it forms the foundation for earning interest, executing transactions, and managing finances, while payment and money transfer services are rapidly expanding to serve digital nomads and underserved populations.
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes individual consumers, small and medium enterprises (SMEs), large corporations, and government entities. Individual consumers are the largest segment, driven by the increasing preference for digital banking solutions. SMEs are also adopting neobanking services to streamline their financial operations, while large corporations and government entities leverage these services for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Globally, SMEs adopting neobanking solutions report improved operational effectiveness and cash flow management, a trend likely reflected in Kuwait’s market as well.
Kuwait Neobanking Market Competitive Landscape
The Kuwait Neobanking Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Kuwait Finance House, Boubyan Bank, Gulf Bank, Al Ahli Bank of Kuwait, Warba Bank, National Bank of Kuwait, Kuwait International Bank, Ahli United Bank, Bank of Bahrain and Kuwait, Burgan Bank, Arab Bank, HSBC Bank Middle East, Citibank Kuwait, Emirates NBD, Mashreq Bank, Standard Chartered Bank contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
Kuwait Neobanking Market Industry Analysis
Growth Drivers
- Increasing Smartphone Penetration:As of future, Kuwait's smartphone penetration rate is projected to reach 95%, with approximately 4.3 million smartphone users. This surge facilitates access to neobanking services, enabling users to manage finances conveniently. The World Bank reports that mobile internet subscriptions in Kuwait have increased by 5% annually, indicating a growing digital landscape. This trend supports the adoption of neobanking, as consumers increasingly rely on mobile devices for financial transactions and services.
- Demand for Digital Financial Services:The demand for digital financial services in Kuwait is expected to grow significantly, with an estimated 70% of the population seeking online banking solutions in future. The Central Bank of Kuwait has noted a 30% increase in digital transactions over the past year, reflecting a shift in consumer preferences. This growing demand is driven by the convenience and efficiency of digital platforms, encouraging neobanks to innovate and expand their service offerings to meet customer needs.
- Supportive Regulatory Environment:Kuwait's regulatory framework is increasingly favorable for neobanks, with the Central Bank of Kuwait implementing new guidelines to promote digital banking. In future, the government plans to introduce initiatives aimed at reducing compliance costs by 15%, encouraging more startups to enter the market. This supportive environment fosters innovation and competition, allowing neobanks to thrive and offer diverse financial products tailored to consumer demands, thus enhancing market growth.
Market Challenges
- High Competition from Traditional Banks:Traditional banks in Kuwait hold a significant market share, with over 75% of the population still relying on established institutions for their banking needs. This dominance poses a challenge for neobanks, which must differentiate themselves through innovative services and competitive pricing. The competition is intensified by the loyalty of consumers to traditional banks, making it difficult for neobanks to capture market share and establish a strong customer base.
- Cybersecurity Concerns:Cybersecurity remains a critical challenge for neobanks, with a reported 25% increase in cyberattacks targeting financial institutions in the region. As neobanks rely heavily on digital platforms, the risk of data breaches and fraud poses significant threats to consumer trust. The Central Bank of Kuwait has mandated stricter cybersecurity measures, which could increase operational costs for neobanks, impacting their profitability and ability to scale effectively in a competitive market.
Kuwait Neobanking Market Future Outlook
The future of the Kuwait neobanking market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. As digital literacy improves, more consumers are expected to embrace neobanking solutions, leading to increased competition and innovation. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning will enhance customer experiences, allowing for personalized services. The regulatory landscape will continue to evolve, fostering a conducive environment for neobanks to thrive while addressing security concerns and compliance challenges effectively.
Market Opportunities
- Expansion of Financial Inclusion:Neobanks have a unique opportunity to enhance financial inclusion in Kuwait, targeting underserved populations. With approximately 1 million individuals lacking access to traditional banking services, neobanks can offer tailored solutions that cater to these demographics, potentially increasing their customer base and driving growth in the sector.
- Partnerships with Fintech Companies:Collaborating with fintech firms can provide neobanks access to innovative technologies and expertise. By forming strategic partnerships, neobanks can enhance their service offerings, streamline operations, and improve customer engagement, positioning themselves competitively in the rapidly evolving financial landscape of Kuwait.