Region:Middle East
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAC1126
Pages:82
Published On:October 2025
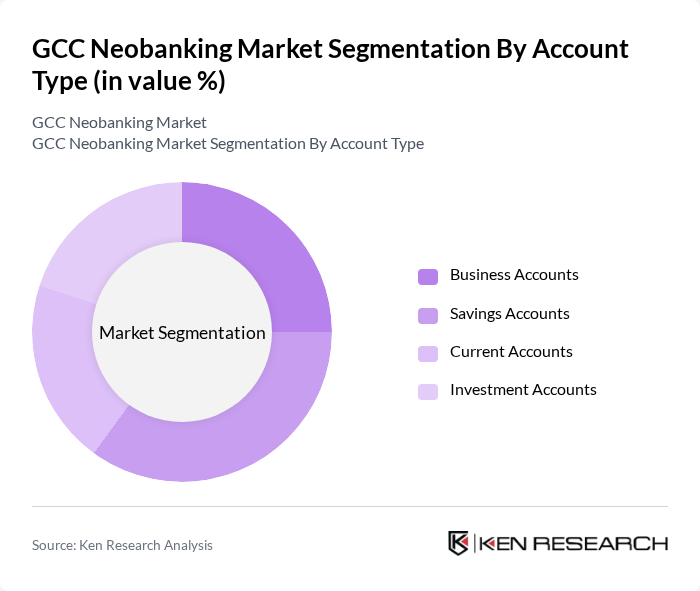
By Account Type:The account type segmentation includes various categories such as Business Accounts, Savings Accounts, Current Accounts, and Investment Accounts. Each of these account types serves different customer needs, with Business Accounts catering to enterprises, Savings Accounts focusing on individual savings, Current Accounts for daily transactions, and Investment Accounts for wealth management. The Savings Accounts segment is currently leading the market due to the growing emphasis on personal savings and investment opportunities among consumers, supported by high-yield digital savings products and automated investment tools.
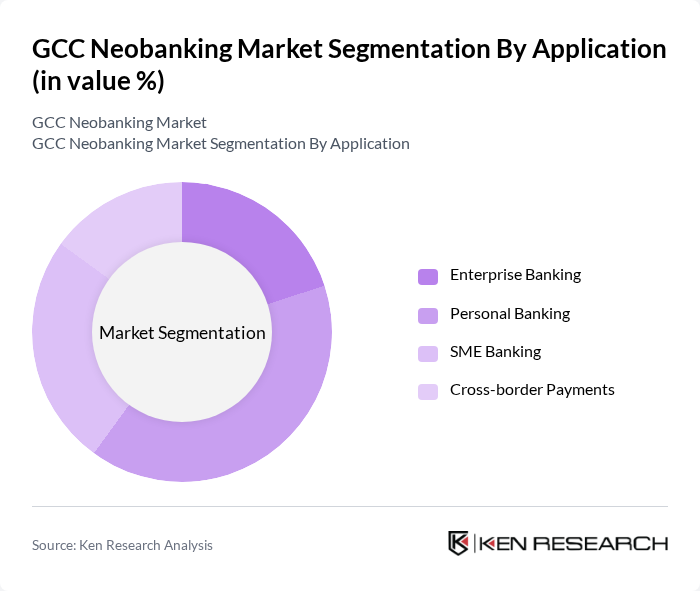
By Application:The application segmentation encompasses Enterprise Banking, Personal Banking, SME Banking, and Cross-border Payments. Each application type addresses specific banking needs, with Personal Banking being the most prominent due to the increasing number of individuals seeking digital banking solutions for personal finance management. The rise of mobile banking apps has significantly contributed to the growth of Personal Banking applications. Emerging trends include the expansion of SME-focused digital lending platforms and the integration of cross-border payment solutions with real-time FX capabilities.
The GCC Neobanking Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Liv. (Emirates NBD), STC Bank (Saudi Telecom Company), Zand, YAP, Mashreq Neo, ADIB (Abu Dhabi Islamic Bank) Digital, Meem (Gulf International Bank), Alinma Bank Digital, Wio Bank, NOW Money, Nymcard, PayTabs, STC Pay, Tarabut Gateway, Rasan Information Technology contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the GCC neobanking market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. As digital transformation accelerates, neobanks are likely to enhance their service offerings through innovative financial products and improved customer experiences. The integration of AI and machine learning will enable personalized banking solutions, fostering customer loyalty. Additionally, partnerships with fintech companies will facilitate the development of new services, positioning neobanks as key players in the region's financial landscape, ultimately reshaping the banking experience for consumers.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Account Type | Business Accounts Savings Accounts Current Accounts Investment Accounts |
| By Application | Enterprise Banking Personal Banking SME Banking Cross-border Payments |
| By Service Offering | Digital Payment Solutions Money Transfer and Remittances Loans and Credit Facilities Savings and Investment Products Islamic Banking Services (Sharia-compliant) |
| By Customer Segment | Tech-savvy Millennials and Gen Z Expatriate Communities Unbanked and Underbanked Population High-net-worth Individuals (HNWIs) |
| By Country | United Arab Emirates Saudi Arabia Qatar Kuwait Bahrain Oman |
| By Distribution Channel | Mobile Applications Web Platforms API Integrations and Open Banking Telecom Super-apps |
| By Business Model | Standalone Digital Banks Bank-sponsored Digital Brands Telecom-led Financial Services Fintech Partnerships |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Adoption of Neobanking | 120 | Millennials, Gen Z, Tech-savvy Users |
| Small Business Banking Solutions | 60 | Small Business Owners, Finance Managers |
| Investment and Wealth Management Services | 50 | High Net Worth Individuals, Financial Advisors |
| Regulatory Impact on Neobanking | 40 | Regulatory Officials, Compliance Officers |
| Technological Innovations in Neobanking | 45 | IT Managers, Product Development Leads |
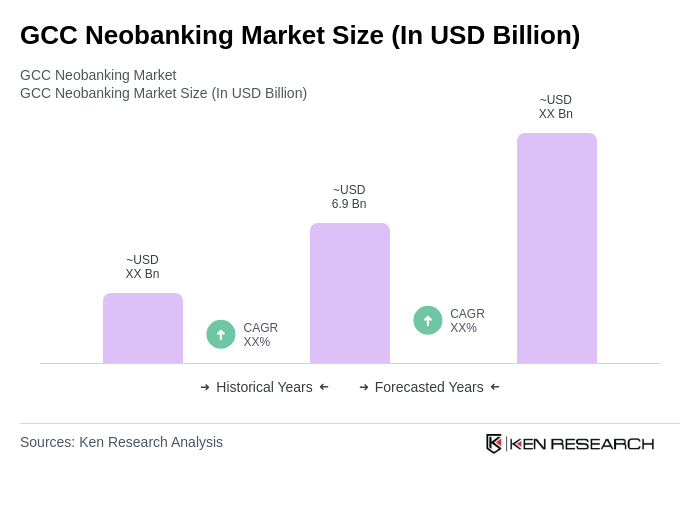
The GCC Neobanking Market is valued at approximately USD 6.9 billion, driven by the increasing adoption of digital banking solutions, smartphone penetration, and consumer preference for online banking services.