Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAA4832
Pages:84
Published On:September 2025
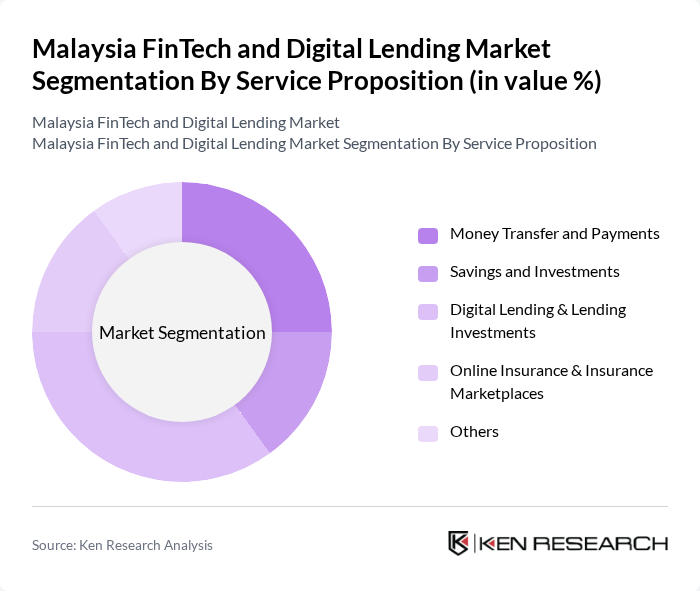
By Service Proposition:The service proposition segmentation includes various offerings such as Money Transfer and Payments, Savings and Investments, Digital Lending & Lending Investments, Online Insurance & Insurance Marketplaces, and Others. Among these, Digital Lending & Lending Investments is the leading sub-segment, driven by the increasing demand for quick and accessible credit solutions. Consumers are increasingly turning to digital platforms for loans due to their convenience and speed, which has significantly boosted this segment's growth. The adoption of AI-driven credit scoring and seamless onboarding processes are further propelling the popularity of digital lending services .
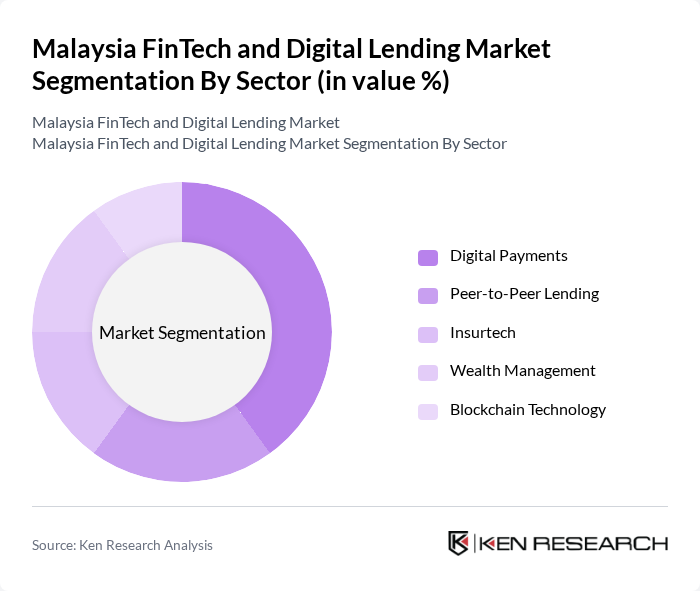
By Sector:The sector segmentation encompasses Digital Payments, Peer-to-Peer Lending, Insurtech, Wealth Management, and Blockchain Technology. Digital Payments is the dominant sector, fueled by the rapid adoption of cashless transactions and the increasing use of e-wallets among consumers. The convenience and security offered by digital payment solutions have made them a preferred choice, leading to substantial growth in this sector. The sector is further supported by government initiatives promoting cashless societies and the integration of advanced security features in payment platforms .
The Malaysia FinTech and Digital Lending Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Grab Financial Group, Funding Societies, CapBay, BigPay, Razer Fintech, Axiata Digital (Aspirasi), Touch ‘n Go Digital, Jirnexu (RinggitPlus), Maybank (Maybank Fintech), CIMB Bank (CIMB Fintech), Hong Leong Bank, UOB Malaysia, Standard Chartered Bank Malaysia, Affin Bank, AmBank, OCBC Bank Malaysia contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Malaysia FinTech and digital lending market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and increasing consumer acceptance. As artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies become more integrated into lending processes, efficiency and personalization will improve. Additionally, the ongoing push for financial inclusion will likely lead to innovative solutions tailored for underserved populations, enhancing market penetration and fostering sustainable growth in the sector.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Service Proposition | Money Transfer and Payments Savings and Investments Digital Lending & Lending Investments Online Insurance & Insurance Marketplaces Others |
| By Sector | Digital Payments Peer-to-Peer Lending Insurtech Wealth Management Blockchain Technology |
| By Customer Type | Retail Consumers Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Corporates |
| By Distribution Channel | Online Platforms Mobile Applications Direct Sales Partnerships with Financial Institutions |
| By Loan Amount | Small Loans (up to RM 10,000) Medium Loans (RM 10,001 - RM 50,000) Large Loans (above RM 50,000) |
| By Repayment Period | Short-term (up to 1 year) Medium-term (1 to 3 years) Long-term (above 3 years) |
| By Risk Profile | Low Risk Medium Risk High Risk |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Digital Lending Usage | 120 | Individual Borrowers, Financial Literacy Advocates |
| SME Financing Needs | 90 | Business Owners, Financial Managers |
| Fintech Service Providers | 50 | Product Managers, Business Development Executives |
| Regulatory Perspectives | 40 | Regulatory Officials, Compliance Officers |
| Consumer Attitudes Towards Digital Lending | 100 | General Public, Financial Advisors |
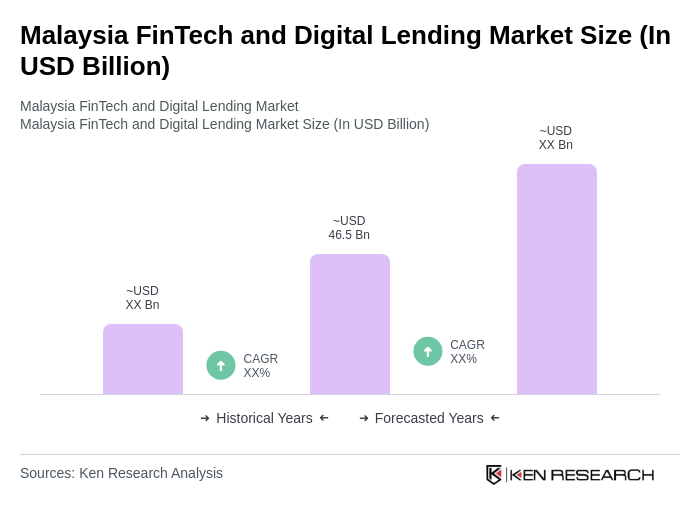
The Malaysia FinTech and Digital Lending Market is valued at approximately USD 46.5 billion, driven by the increasing adoption of digital financial services and a growing preference for online transactions among consumers.