Region:Global
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAA1012
Pages:97
Published On:August 2025
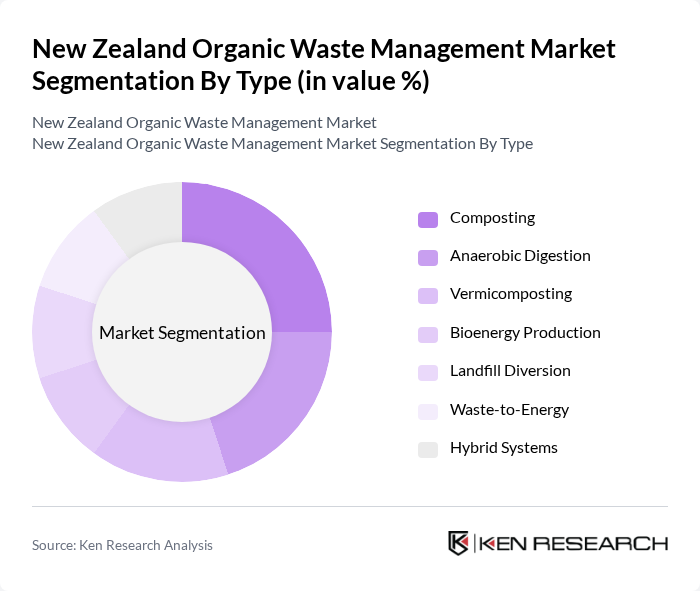
By Type:The market is segmented into various types of organic waste management methods, including composting, anaerobic digestion, vermicomposting, bioenergy production, landfill diversion, waste-to-energy, and hybrid systems. Composting is widely adopted in urban and rural settings for garden and food waste. Anaerobic digestion and bioenergy production are increasingly used for large-scale processing and renewable energy generation. Vermicomposting is popular among small-scale and community initiatives. Landfill diversion and waste-to-energy solutions are being promoted through government and municipal programs to reduce landfill dependency and recover resources .
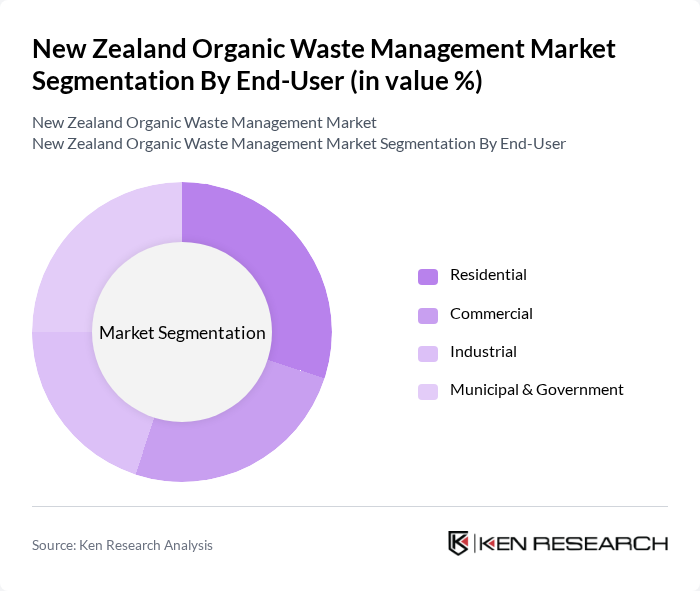
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes residential, commercial (e.g., restaurants, supermarkets, hotels), industrial (e.g., food processing, agriculture), and municipal & government sectors. The residential sector is driven by household composting and council-provided green waste collection. The commercial segment is characterized by food service and retail waste recycling initiatives. Industrial users, such as food processors and agricultural operations, focus on large-scale organic waste conversion. Municipal and government sectors are responsible for policy implementation, infrastructure development, and public education on organic waste management .
The New Zealand Organic Waste Management Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Waste Management NZ Limited, EnviroWaste Services Ltd, Composting New Zealand, Green Gorilla, Living Earth, Ecogas New Zealand, Smart Environmental Ltd, Clean Green NZ Ltd, Organic Waste Management Ltd, Recycle South, Waste Not Consulting, Bioenergy Association of New Zealand, Zero Waste Network, Sustainable Waste Management Ltd, Greenwaste to Zero contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the New Zealand organic waste management market appears promising, driven by increasing environmental regulations and a societal shift towards sustainability. As local governments enhance their waste management strategies, investments in innovative technologies are expected to rise. Additionally, community engagement initiatives will likely play a crucial role in educating the public about organic waste benefits, fostering greater participation in recycling programs and sustainable practices across the nation.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Composting Anaerobic Digestion Vermicomposting Bioenergy Production Landfill Diversion Waste-to-Energy Hybrid Systems |
| By End-User | Residential Commercial (e.g., restaurants, supermarkets, hotels) Industrial (e.g., food processing, agriculture) Municipal & Government |
| By Application | Agriculture & Horticulture Landscaping & Urban Greening Renewable Energy Generation Soil Amendment & Remediation |
| By Collection Method | Curbside Collection Drop-off Centers Commercial Collection Services Community-Based Collection Initiatives |
| By Processing Method | Mechanical Processing Biological Processing (e.g., composting, anaerobic digestion) Thermal Processing (e.g., incineration, pyrolysis) |
| By Material Type | Food Waste Green/Yard Waste Agricultural Residues Industrial Organic By-products |
| By Policy Support | Subsidies Tax Exemptions Grants Regulatory Mandates (e.g., landfill levies, waste diversion targets) |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Municipal Waste Management | 60 | City Waste Managers, Environmental Policy Advisors |
| Organic Waste Processing Facilities | 50 | Facility Operators, Plant Managers |
| Community Composting Initiatives | 40 | Community Leaders, Sustainability Coordinators |
| Food Industry Waste Management | 50 | Food Service Managers, Supply Chain Coordinators |
| Regulatory Bodies and NGOs | 40 | Policy Makers, Environmental Advocates |
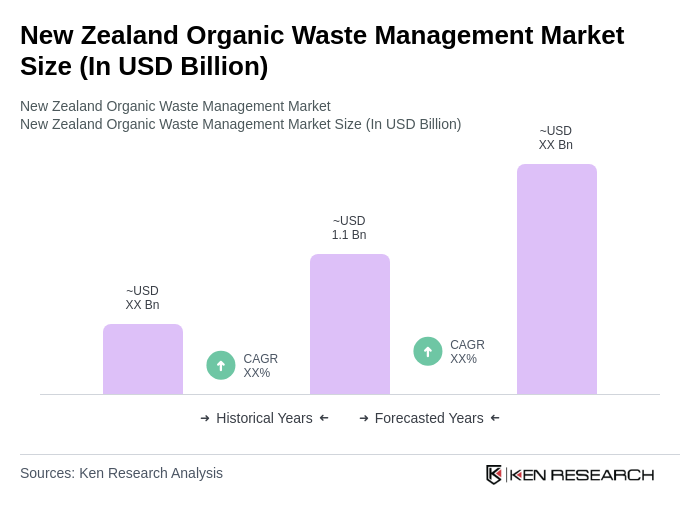
The New Zealand Organic Waste Management Market is valued at approximately USD 1.1 billion, reflecting a significant growth trend driven by increased environmental awareness and government initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable waste management practices.