Region:Asia
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAB5540
Pages:99
Published On:October 2025
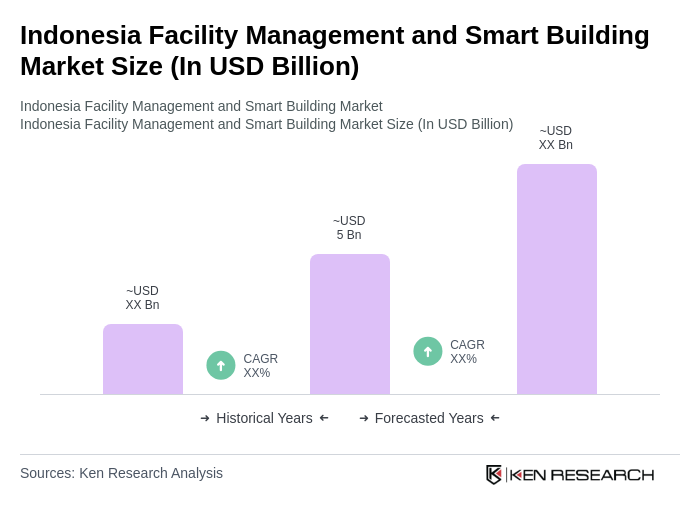
By Type:The market is segmented into Hard Services, Soft Services, Integrated Services, and Others. Hard Services include maintenance and repair of physical assets, while Soft Services encompass cleaning, security, and landscaping. Integrated Services combine both hard and soft services for a comprehensive management approach. The Others category includes specialized services that do not fit into the previous classifications.
The Hard Services segment is currently dominating the market due to the essential nature of maintenance and repair services in ensuring the operational efficiency of buildings. As urban infrastructure expands, the need for reliable hard services has increased, driven by both commercial and residential sectors. The Soft Services segment follows closely, as businesses increasingly prioritize cleanliness and security in their facilities, reflecting a growing consumer preference for well-maintained environments.
By End-User:The market is segmented into Residential, Commercial, Industrial, and Government & Utilities. The Residential segment includes services provided to residential buildings, while the Commercial segment covers office spaces and retail establishments. The Industrial segment pertains to manufacturing facilities, and Government & Utilities involve services for public sector buildings and infrastructure.
The Commercial segment is the largest end-user category, driven by the increasing number of office buildings and retail spaces in urban areas. As businesses focus on enhancing employee productivity and customer experience, the demand for facility management services in commercial properties has surged. The Residential segment is also significant, reflecting the growing trend of property management services in housing complexes.
The Indonesia Facility Management and Smart Building Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as ISS Indonesia, CBRE Indonesia, JLL Indonesia, Cushman & Wakefield Indonesia, Sodexo Indonesia, Knight Frank Indonesia, G4S Indonesia, Mitie Indonesia, Dalkia Indonesia, Apleona Indonesia, Serco Indonesia, Securitas Indonesia, AECOM Indonesia, Engie Indonesia, Veolia Indonesia contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the facility management and smart building market in Indonesia appears promising, driven by ongoing urbanization and government support for smart city initiatives. As the demand for energy-efficient solutions continues to rise, companies are likely to invest in innovative technologies that enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, the integration of IoT and AI in facility management will streamline processes, improve service delivery, and foster sustainable practices, positioning the market for significant growth in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Hard Services Soft Services Integrated Services Others |
| By End-User | Residential Commercial Industrial Government & Utilities |
| By Application | Office Buildings Retail Spaces Healthcare Facilities Educational Institutions |
| By Service Model | Outsourced Services In-House Services Hybrid Services |
| By Region | Java Sumatra Bali Others |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Investment Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Government Schemes |
| By Policy Support | Subsidies Tax Exemptions Regulatory Credits Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Building Management | 150 | Facility Managers, Building Owners |
| Residential Smart Building Solutions | 100 | Property Managers, Homeowners |
| Industrial Facility Operations | 80 | Operations Managers, Safety Officers |
| Energy Management Systems | 70 | Energy Managers, Sustainability Coordinators |
| Security and Surveillance Services | 90 | Security Managers, IT Directors |
The Indonesia Facility Management and Smart Building Market is valued at approximately USD 5 billion, driven by urbanization, energy efficiency demands, and the integration of smart technologies in building management.