Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAB0209
Pages:83
Published On:August 2025
By Service Provider:
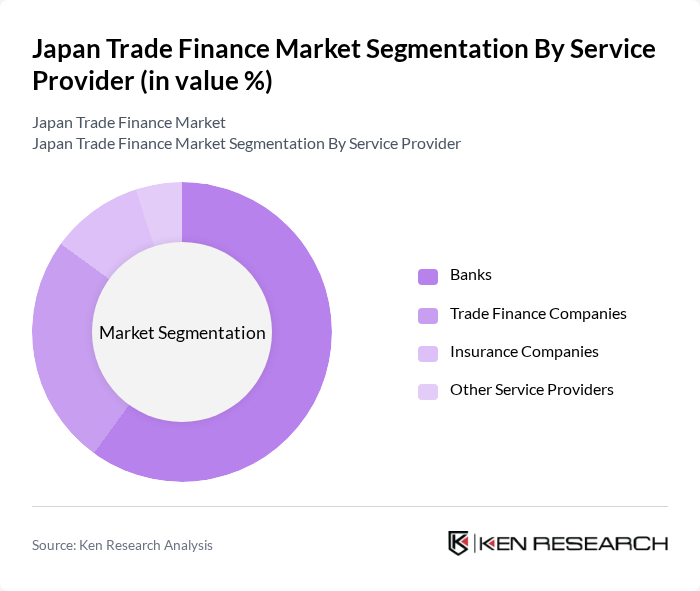
The service provider segment is crucial in the Japan Trade Finance Market, comprising banks, trade finance companies, insurance companies, and other service providers. Banks dominate this segment due to their extensive networks, established relationships with businesses, and comprehensive product offerings such as letters of credit, supply chain financing, and export credit. Trade finance companies are also significant players, providing specialized services tailored to the needs of businesses engaged in cross-border transactions. Insurance companies contribute by offering risk mitigation solutions, including trade credit insurance, while other service providers, including fintech firms, enhance the overall service ecosystem through digital innovation .
By Application:
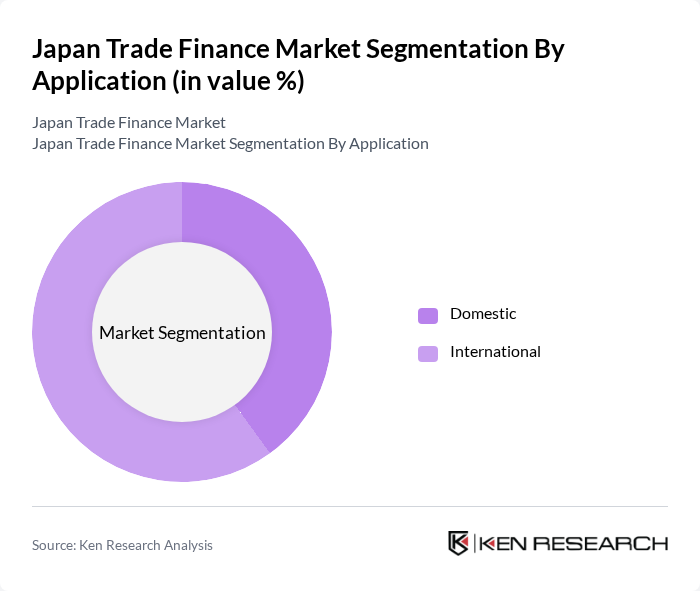
The application segment of the Japan Trade Finance Market is divided into domestic and international applications. The international application segment is the leading sub-segment, driven by Japan's strong export-oriented economy and the need for sophisticated financing solutions to manage cross-border transactions. Domestic applications remain significant, supporting local businesses in their trade activities within Japan. The increasing globalization of trade and the adoption of digital trade finance solutions have further accelerated demand for international trade finance services .
The Japan Trade Finance Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as MUFG Bank, Ltd., Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation, Mizuho Bank, Ltd., Resona Bank, Ltd., Japan Finance Corporation, SBI Holdings, Inc., Nomura Holdings, Inc., Dai-ichi Life Holdings, Inc., ORIX Corporation, Aozora Bank, Ltd., Shizuoka Bank, Ltd., Chiba Bank, Ltd., Fukuoka Financial Group, Inc., Hokuhoku Financial Group, Inc., The Shiga Bank, Ltd. contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of Japan's trade finance market appears promising, driven by increasing digitalization and a focus on sustainability. As businesses seek to streamline operations, the integration of automated processes and data analytics will enhance risk assessment and decision-making. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainable trade practices will likely lead to the development of innovative financing solutions that align with environmental goals, positioning Japan as a leader in responsible trade finance.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Service Provider | Banks Trade Finance Companies Insurance Companies Other Service Providers |
| By Application | Domestic International |
| By End-User | Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Large Corporations Government Entities Financial Institutions |
| By Industry | Manufacturing Retail Agriculture Technology Others |
| By Transaction Size | Small Transactions Medium Transactions Large Transactions |
| By Geographic Focus | Domestic Trade International Trade |
| By Policy Support | Government Subsidies Tax Incentives Regulatory Support Programs Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Export Financing in Manufacturing | 100 | Export Managers, Financial Analysts |
| Import Financing in Technology Sector | 60 | Procurement Officers, Supply Chain Managers |
| Letters of Credit Utilization | 50 | Trade Finance Specialists, Risk Managers |
| Supply Chain Financing Solutions | 70 | Logistics Coordinators, Chief Financial Officers |
| Impact of Trade Agreements on Financing | 40 | Policy Analysts, Trade Compliance Officers |
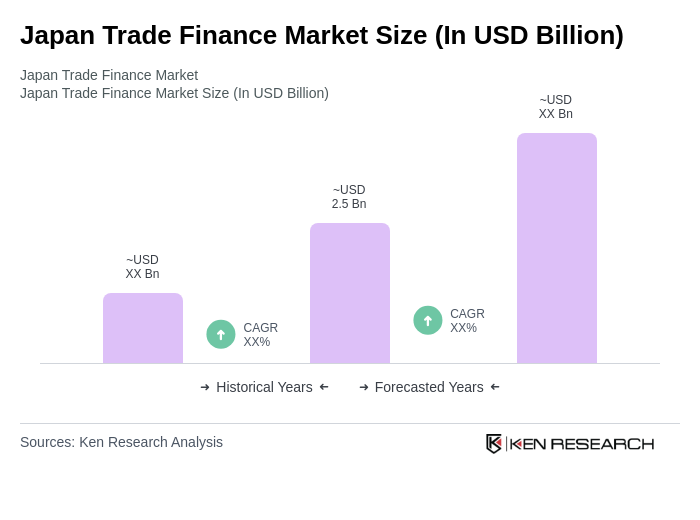
The Japan Trade Finance Market is valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion, reflecting a robust growth driven by increasing international trade, globalization of Japanese businesses, and advancements in technology such as blockchain and artificial intelligence.