Region:Global
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAA6489
Pages:85
Published On:January 2026
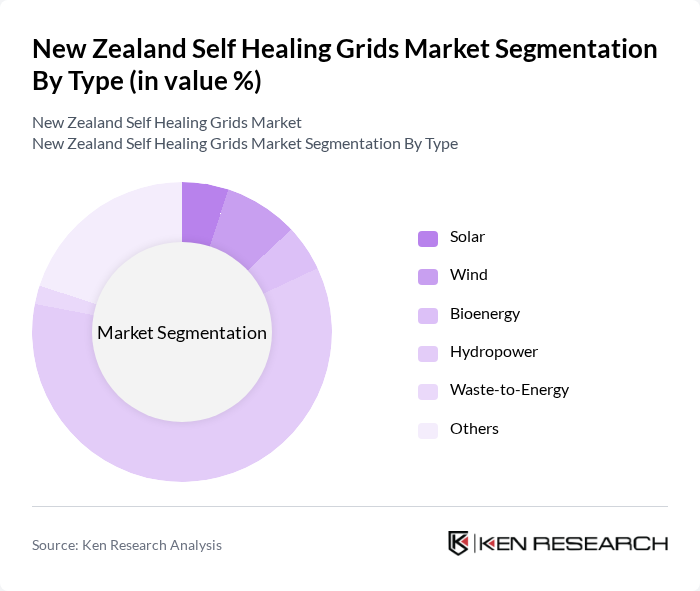
By Type:The market is segmented into various types, including Solar, Wind, Bioenergy, Hydropower, Waste-to-Energy, and Others. Each type plays a significant role in the overall energy mix and contributes to the self-healing capabilities of the grid.
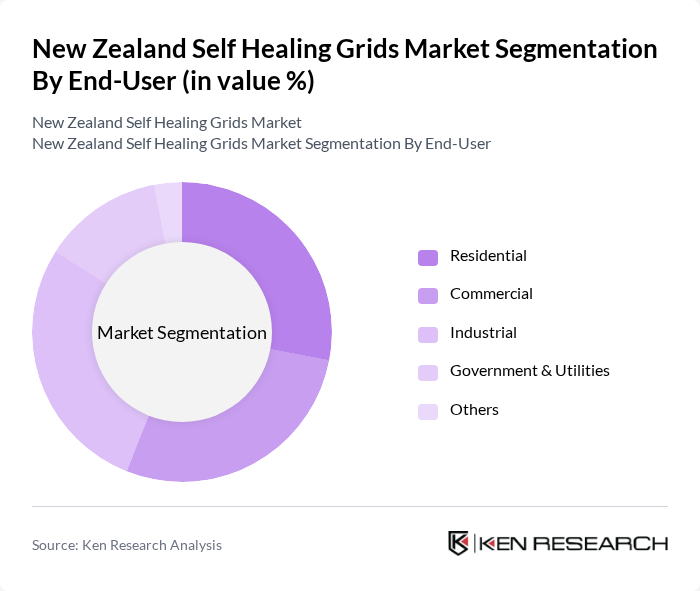
By End-User:The market is further segmented by end-user categories, including Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Government & Utilities, and Others. Each segment has unique requirements and contributes differently to the self-healing grid ecosystem.
The New Zealand Self Healing Grids Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Meridian Energy, Contact Energy, Genesis Energy, Trustpower, Vector Limited, Powerco, Transpower, Flick Electric Co., Nova Energy, Z Energy, Mercury NZ Limited, Infratil, Trustpower, Energy Online, Powershop contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the New Zealand self-healing grids market appears promising, driven by a combination of technological advancements and increasing government support. As the country moves towards its renewable energy goals, the integration of smart grid technologies will likely enhance grid reliability and efficiency. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability and carbon neutrality will encourage further investments in innovative energy solutions. The market is expected to evolve rapidly, with a focus on decentralized energy systems and community-based projects gaining traction in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type (e.g., Solar, Wind, Bioenergy, Hydropower, Waste-to-Energy) | Solar Wind Bioenergy Hydropower Waste-to-Energy Others |
| By End-User (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Government & Utilities) | Residential Commercial Industrial Government & Utilities Others |
| By Region (North Island, South Island) | North Island South Island |
| By Technology (Photovoltaic, CSP, Onshore/Offshore Wind, Biomass Gasification) | Photovoltaic CSP Onshore Wind Offshore Wind Biomass Gasification Others |
| By Application (Grid-Connected, Off-Grid, Rooftop Installations, Utility-Scale Projects) | Grid-Connected Off-Grid Rooftop Installations Utility-Scale Projects Others |
| By Investment Source (Domestic, FDI, PPP, Government Schemes) | Domestic FDI PPP Government Schemes Others |
| By Policy Support (Subsidies, Tax Exemptions, RECs) | Subsidies Tax Exemptions RECs Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Self-Healing Product Usage | 120 | Wellness Enthusiasts, Regular Users of Self-Healing Products |
| Retailer Insights on Self-Healing Products | 80 | Store Managers, Product Buyers |
| Practitioner Perspectives on Self-Healing | 60 | Holistic Health Coaches, Wellness Practitioners |
| Market Trends in Wellness Apps | 50 | App Developers, Digital Health Experts |
| Consumer Attitudes Towards Self-Care | 100 | General Consumers, Health-Conscious Individuals |
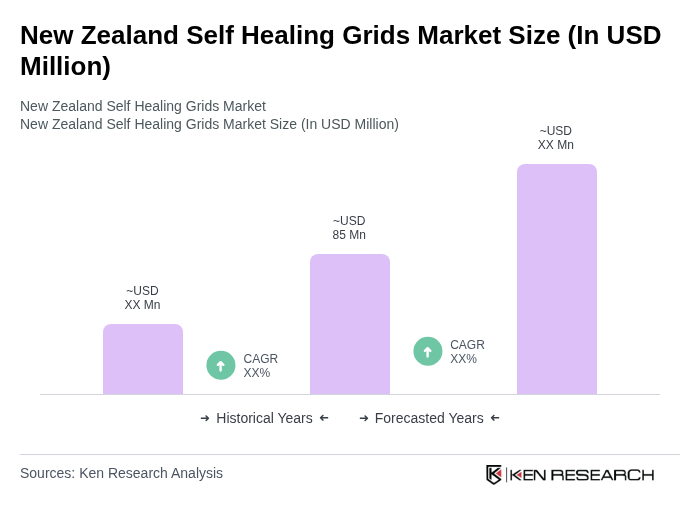
The New Zealand Self Healing Grids Market is valued at approximately USD 85 million, reflecting a five-year historical analysis. This growth is driven by the demand for resilient energy systems and advancements in smart grid technologies.