Region:Global
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAB0434
Pages:83
Published On:August 2025
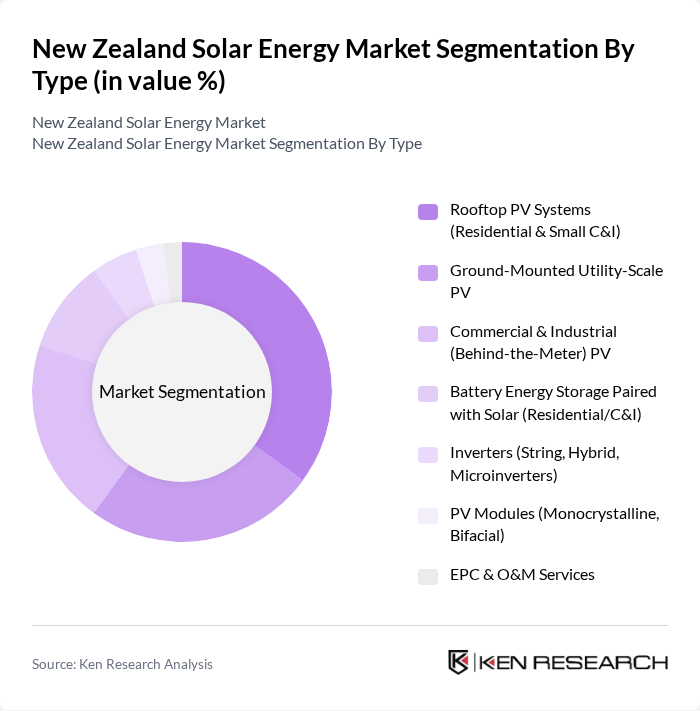
By Type:The market is segmented into various types, including Rooftop PV Systems (Residential & Small C&I), Ground-Mounted Utility-Scale PV, Commercial & Industrial (Behind-the-Meter) PV, Battery Energy Storage Paired with Solar (Residential/C&I), Inverters (String, Hybrid, Microinverters), PV Modules (Monocrystalline, Bifacial), and EPC & O&M Services. Among these, Rooftop PV Systems are gaining traction due to their suitability for residential and small commercial applications, driven by decreasing installation costs and increasing consumer awareness of energy independence.
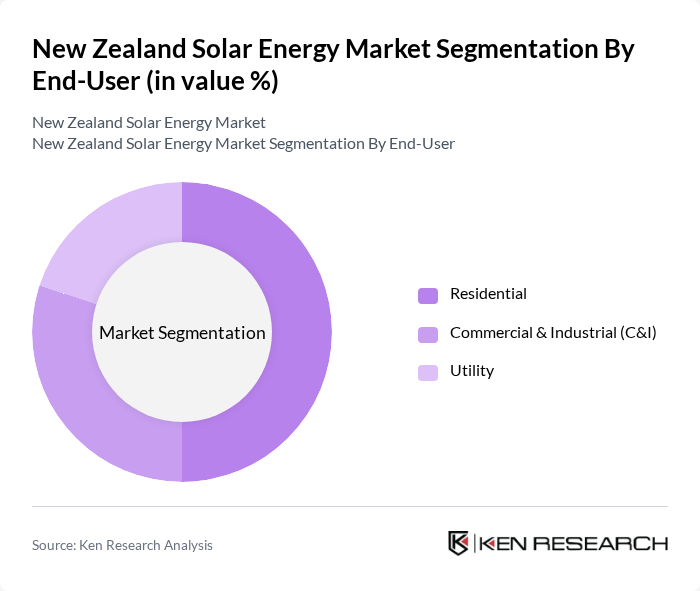
By End-User:The market is segmented by end-user into Residential, Commercial & Industrial (C&I), and Utility. The Residential segment is currently leading the market due to the increasing adoption of solar energy systems among homeowners, driven by rising electricity costs and the desire for energy independence. The trend towards sustainable living is also contributing to the growth of this segment.
The New Zealand Solar Energy Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Meridian Energy Limited, Contact Energy Limited, Genesis Energy Limited, Vector Limited, Lodestone Energy Limited, Lightyears Solar Limited, SolarZero Limited, Infratec Limited, Todd Generation (Todd Corporation), EECA – Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority, Flick Electric Co., Manawa Energy Limited, Vector Powersmart (Powersmart Solar), JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd., Trina Solar Co., Ltd. contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the New Zealand solar energy market appears promising, driven by ongoing investments in renewable technologies and policy commitments to decarbonisation. Integration of solar with smart grids and distributed energy resource management is expected to enhance efficiency and reliability in future, in line with electricity sector reforms and flexibility initiatives . Community and distributed generation frameworks enable wider participation in future, supporting a more resilient energy landscape .
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Rooftop PV Systems (Residential & Small C&I) Ground-Mounted Utility-Scale PV Commercial & Industrial (Behind-the-Meter) PV Battery Energy Storage Paired with Solar (Residential/C&I) Inverters (String, Hybrid, Microinverters) PV Modules (Monocrystalline, Bifacial) EPC & O&M Services |
| By End-User | Residential Commercial & Industrial (C&I) Utility |
| By Application | Grid-Connected Systems Off-Grid and Remote/Islanded Systems Rooftop Installations Utility-Scale Solar Farms |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Investment Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) / Corporate PPA Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) |
| By Policy Support | Distributed Generation Buy-Back/Export Tariffs Tax Depreciation and Accelerated Asset Write-Offs Renewable Energy Certificates / Emissions Trading Scheme Alignment |
| By Distribution Mode | Direct (EPC/Developer) Sales Installer Networks and Solar Retailers Online Sales Channels |
| By Price Range | Entry-Level Systems Mid-Range Systems Premium Systems |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Solar Users | 120 | Homeowners, Energy Managers |
| Commercial Solar Installations | 100 | Facility Managers, Sustainability Officers |
| Utility-Scale Solar Projects | 80 | Project Developers, Energy Analysts |
| Government Policy Makers | 50 | Regulatory Officials, Energy Policy Advisors |
| Solar Technology Providers | 70 | Product Managers, R&D Engineers |
The New Zealand solar energy market is valued at approximately USD 1.1 billion, reflecting significant growth in installed capacity and grid-scale developments, driven by decreasing photovoltaic (PV) costs and increased adoption among residential and commercial users.