Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAA1909
Pages:85
Published On:August 2025
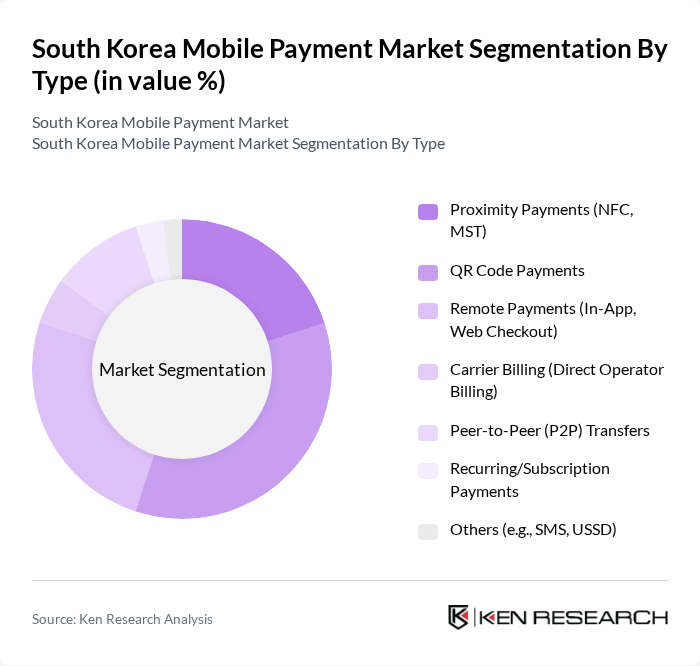
By Type:The mobile payment market can be segmented into various types, including Proximity Payments (NFC, MST), QR Code Payments, Remote Payments (In-App, Web Checkout), Carrier Billing (Direct Operator Billing), Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Transfers, Recurring/Subscription Payments, and Others (e.g., SMS, USSD). Among these, QR Code Payments have gained significant traction due to ease of use and widespread acceptance across retail and service sectors, alongside continued growth of NFC for contactless in-store payments.
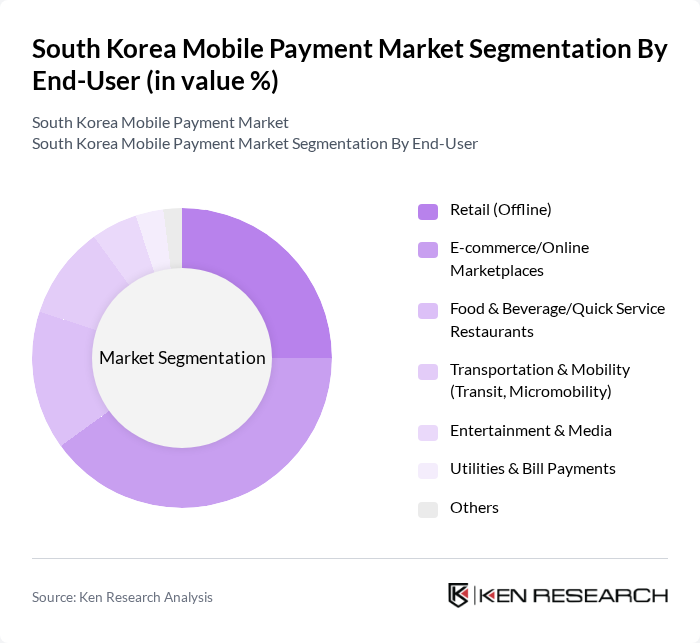
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Retail (Offline), E-commerce/Online Marketplaces, Food & Beverage/Quick Service Restaurants, Transportation & Mobility (Transit, Micromobility), Entertainment & Media, Utilities & Bill Payments, and Others. The E-commerce sector is the leading segment, propelled by high online shopping penetration and seamless mobile checkout via domestic wallets and card-on-file, while offline retail is sustained by ubiquitous contactless acceptance and wallet integrations.
The South Korea Mobile Payment Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Samsung Pay (Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.), Kakao Pay (Kakao Pay Corp.), Naver Pay (NAVER Financial Corp.), Toss (Viva Republica Co., Ltd.), PAYCO (NHN Payco Corp.), LG Uplus (LG Uplus Corp.), SK Telecom (SK Telecom Co., Ltd.), Shinhan SOL Pay (Shinhan Bank), KB Pay (KB Kookmin Bank), Hana OneQ Pay (Hana Bank), Woori WON Pay (Woori Bank), NH NongHyup Bank (NH Pay/Allone Pay), BC Card Co., Ltd., Lotte Card Co., Ltd. (L.Pay), Coupang Pay Corp. contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korean mobile payment market is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. The integration of AI and machine learning will enhance personalized services, while the rise of contactless payments will further streamline transactions. Additionally, the increasing collaboration between fintech companies and traditional banks is expected to create a more integrated financial ecosystem. These trends indicate a dynamic future for mobile payments, with continued growth and innovation on the horizon.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Proximity Payments (NFC, MST) QR Code Payments Remote Payments (In-App, Web Checkout) Carrier Billing (Direct Operator Billing) Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Transfers Recurring/Subscription Payments Others (e.g., SMS, USSD) |
| By End-User | Retail (Offline) E-commerce/Online Marketplaces Food & Beverage/Quick Service Restaurants Transportation & Mobility (Transit, Micromobility) Entertainment & Media Utilities & Bill Payments Others |
| By Payment Method Funding Source | Card-on-File (Credit/Debit) Bank Account (Account-to-Account, Open Banking) Prepaid/Stored-Value Balance Mobile Carrier Billing Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Others |
| By User Demographics | Gen Z (Under 25) Millennials (25–40) Gen X (41–56) Seniors (57+) Others |
| By Transaction Size | Micro & Small Transactions (? KRW 50,000) Medium Transactions (KRW 50,001–300,000) Large Transactions (? KRW 300,001) Others |
| By Geographic Distribution | Seoul Capital Area Metropolitan Cities (Busan, Incheon, Daegu, Daejeon, Gwangju, Ulsan) Provincial Cities & Counties Others |
| By Industry Vertical | Retail & Commerce Hospitality & Travel Healthcare Education Public Services & Government Payments Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Mobile Payment Usage | 150 | Regular mobile payment users, aged 18-60 |
| Merchant Adoption of Mobile Payments | 100 | Small to medium-sized business owners |
| Fintech Industry Insights | 80 | Executives from fintech startups and established firms |
| Regulatory Impact Assessment | 50 | Policy makers and regulatory body representatives |
| Consumer Attitudes Towards Security | 120 | General consumers with varying levels of tech-savviness |
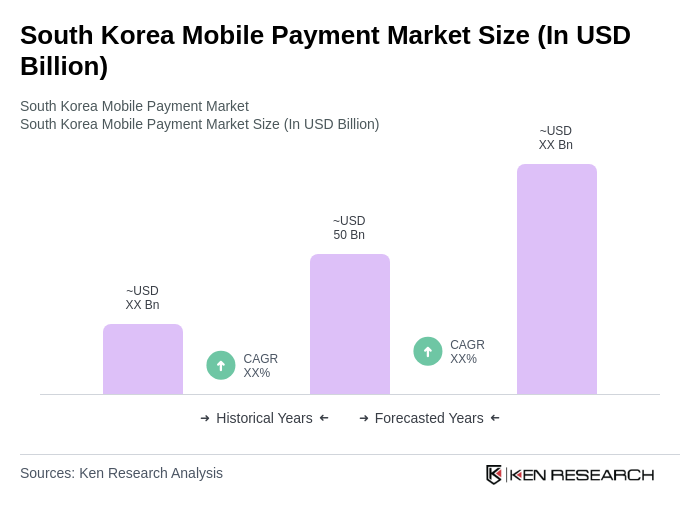
The South Korea mobile payment market is valued at approximately USD 50 billion, reflecting strong smartphone adoption, widespread internet usage, and a shift towards cashless transactions among consumers. This market size is supported by various industry trackers indicating a range of USD 4551 billion.