How Farm Mechanization mission is transforming Used Agricultural Equipment Business in India
India-Used-Agricultural-Equipment-Market
April 05, 2023
The agricultural sector is one of the few industries in India that witnessed a robust growth rate of ~3.4 % at constant prices during FY’21 despite the COVID lockdown. Also, there is an advent of farm mechanization in the agricultural industry due to the rising labor costs in the country. These agricultural equipment are helpful for farmers at many stages of farming. However, due to the high cost of new equipment, most farmers opt for used farm equipment which is pushing the demand for used agricultural equipment in India. Currently, the Used Agriculture equipment sector is growing at a CAGR of ~16% between 2016 and 2021.
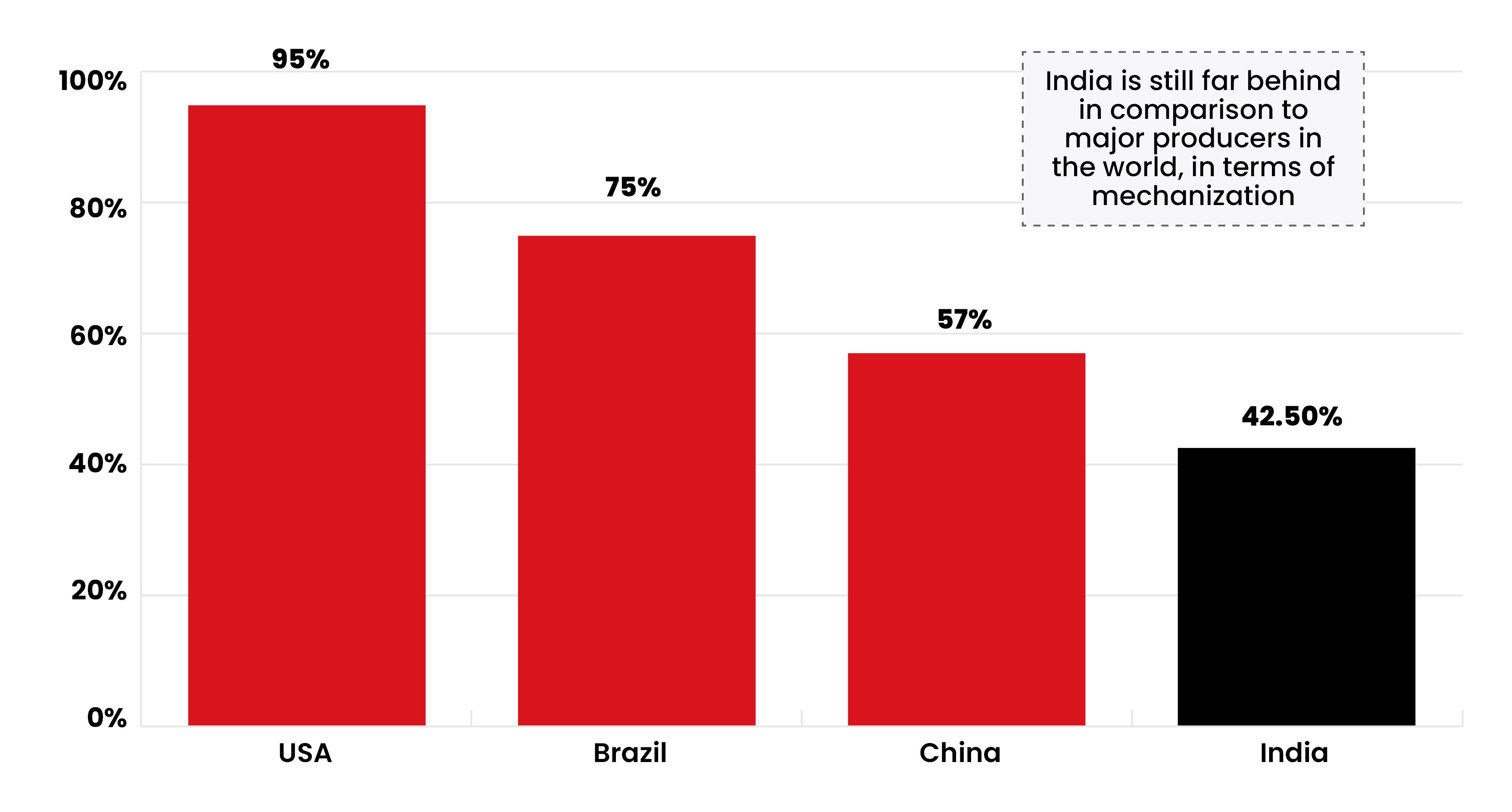
However, the adoption of farm mechanization is still low in the country as compared to other countries like China, Brazil, and more. But in the past years, several policies have been framed in order to improve farming infrastructure and focus on smaller land-holding farmers.
Here we have thrown light on the major initiatives of the Indian government that will enable the used Agricultural Equipment Market in India to grow by a CAGR of ~23% in the next five years.
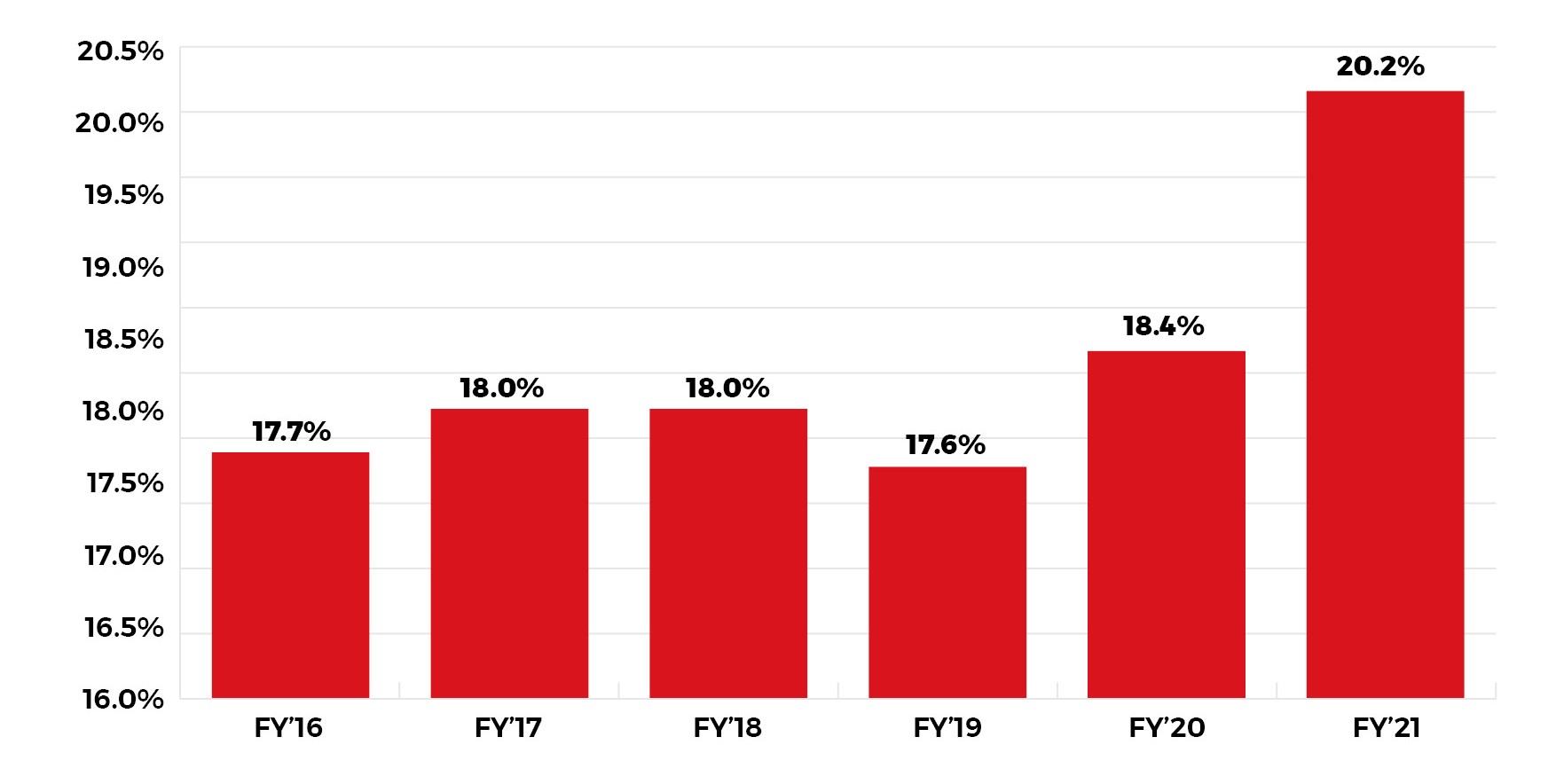
1. Agriculture and Allied Sectors are a major contributor to the Indian Economy, with a Gross Value Addition share of 20.2% in FY’21 to the Indian economy
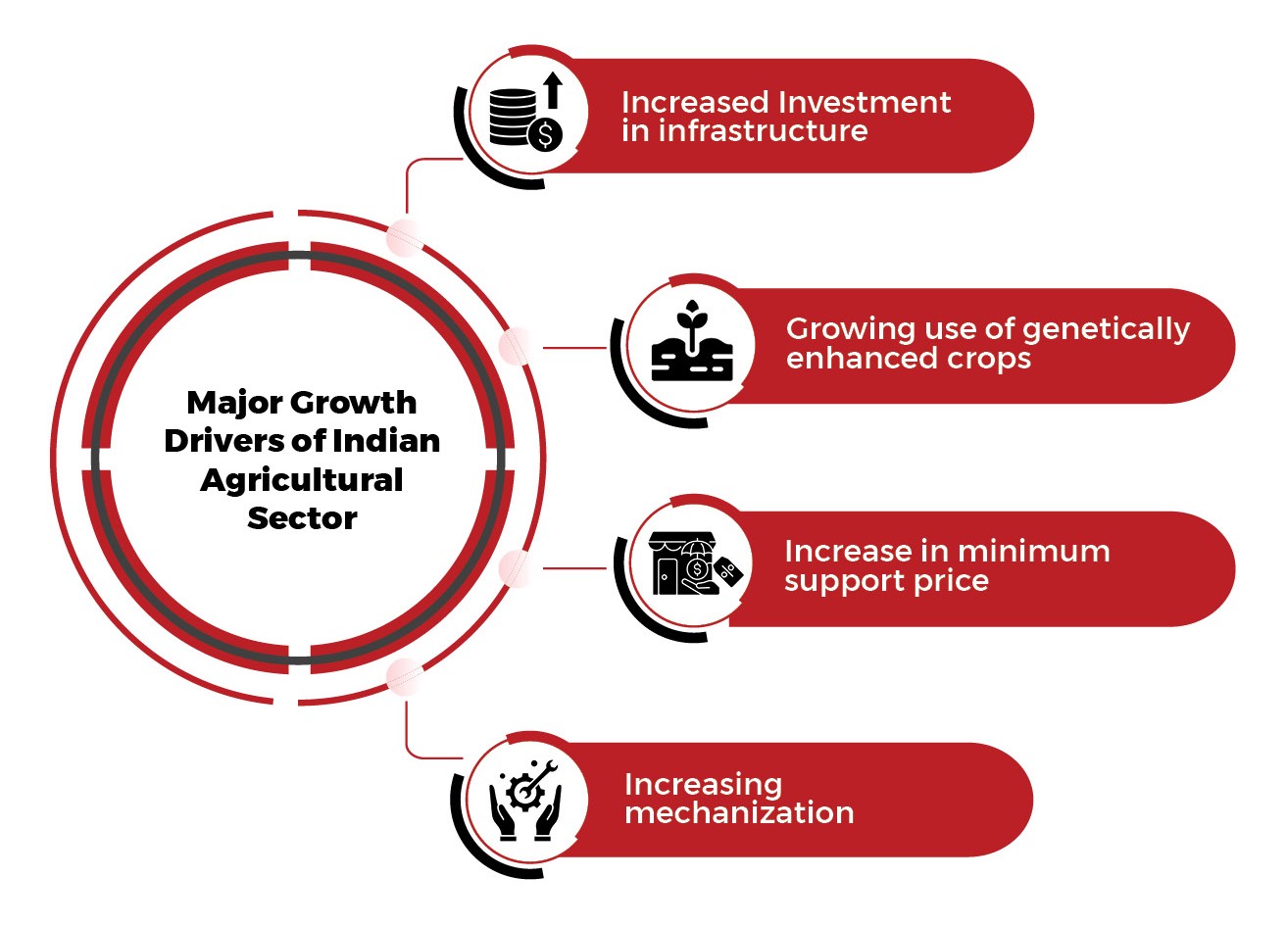
Key Growth Drivers of Indian Agricultural Industry
Share of Agriculture and Allied Sectors in Total GVA at current prices, In Percentage, FY’16-FY’21
Key Trends and Growth Drivers of Indian Agricultural Industry
- Agriculture is the primary source of livelihood for about 58% of India’s population.
- Gross Value Added by agriculture, forestry, and fishing was estimated at Rs. 19.48 lakh crore (US$ 276.37 billion) in FY’20.
- Share of agriculture and allied sectors in gross value added (GVA) of India at current prices stood at 20.2% in FY21.
- While the difficulties created by COVID induced lockdowns adversely affected the performance of the non-agricultural sectors, the agriculture sector came up with a robust growth rate of 3.4 % at constant prices during FY’21.
Source: Interviews with Online Furniture & Home Décor Industry Experts, Industry Articles, Company Blogs, Ken Research Analysis
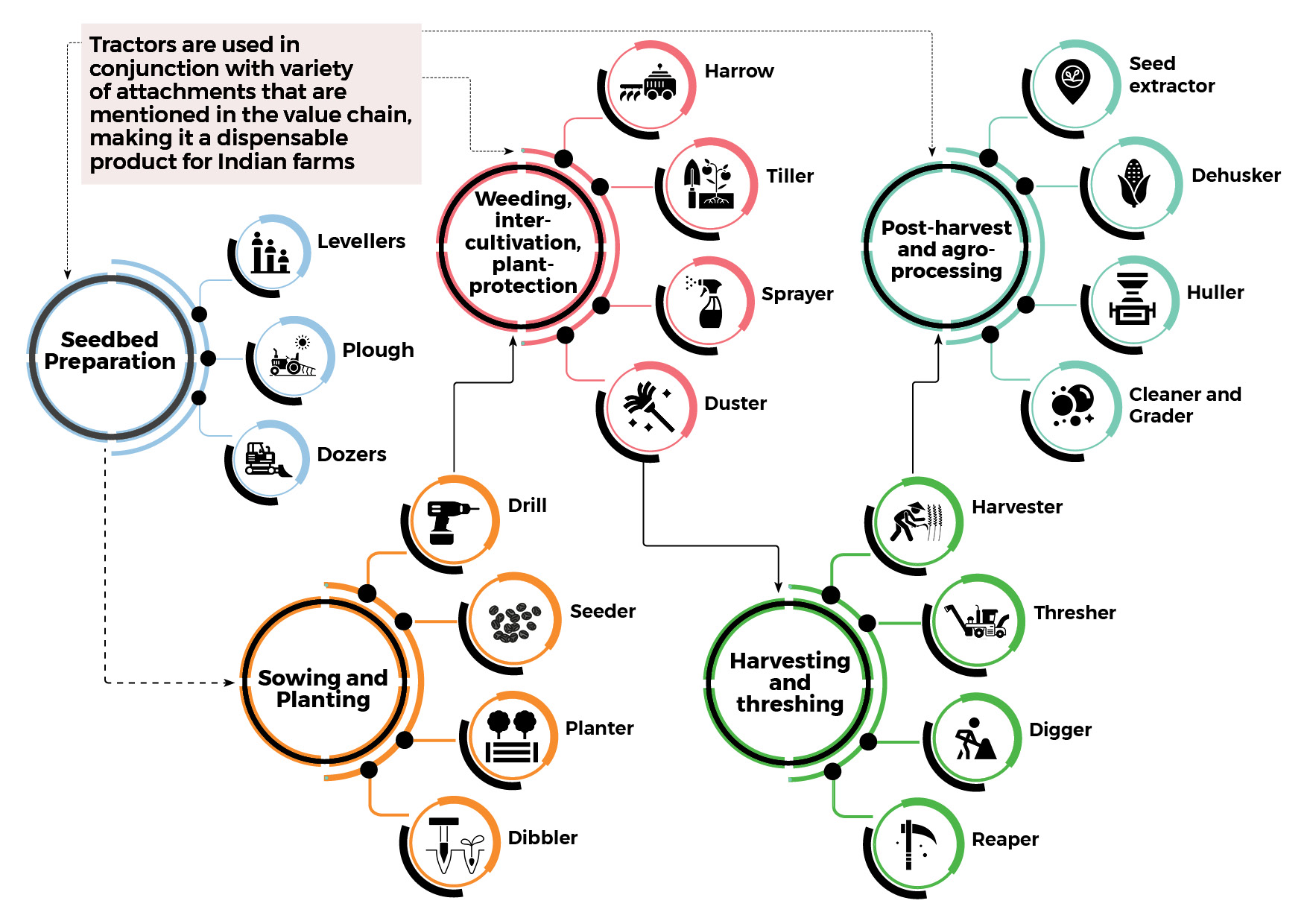
3. At each stage of the agricultural cycle, there are targeted requirements for farm equipment; tractors are the most versatile and are used to fulfil multiple requirements at every step
Source: FICCI- PwC Report, Interviews with Indian Agriculture Equipment Industry Experts, Industry Articles, Company Websites & Ken Research Analysis
4. Farm mechanization in India is still in its nascent stages due to the high cost of farm machinery and equipment, insufficient policy framework
Farm Mechanization in India is low due to high costs involved
- Lack of access to farm power is one of the primary reasons for slow uptake of farm mechanization and hence non-intensification of farm productivity, particularly among small and marginal farmers.
- The sector faces critical challenges in terms of large share of small and marginal farmers, declining land holding sizes, high cost of farm machinery and equipment, inappropriate technology, undeveloped markets, complex operations, maze of legislation and insufficient policy framework.
- Land size, cropping pattern, market price of crops including Minimum Support Price (MSP), availability of labor and cost of labor are the major factors deciding the growth of agricultural mechanization in India.
- Unlike other agricultural sectors, farm mechanization sector in India has a far more complex structural composition.
Stages of Mechanization in a farm
Farm operations requiring high power inputs and low skill and/or control such as tillage, transport, water pumping, milling, threshing, etc.
1
Farm operations requiring medium levels of power and skill/control such as seeding, spraying, inter-row operations, etc.
2
Farm operations requiring a high degree of skill/control and varying levels of power inputs such as transplanting, planting of vegetables, harvesting and grading of fruits and vegetables, etc.
3
Share of farming entities employing mechanical support in 2018, In percentage
Source: NABARD, Interviews with Indian Agriculture Equipment Industry Experts, Industry Articles, Company Websites & Ken Research Analysis
*Note: Level of mechanization is the extent of use of mechanical power sources and equipment on a farm.
4. However, recent years have seen the greatest amount of policies and reforms aiming at improving farming infrastructure and focusing on smaller land-holding farmers.
2018
2018 policies strengthened exports and Public-Private Partnerships
- Agriculture Export Policy was framed with a focus on agriculture export-oriented production, export promotion, better farmer realization, and synchronization within policies and programs of the Government of India.
- Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay SanraksHan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA) under which states can decide the compensation scheme and can also partner with private agencies to ensure fair prices for farmers in the country
2019
A move towards solidifying online platform-e-NAM and expanding it’s reach
- Amendment of the Essential Commodities Act (ECA) & Agricultural Produce Market Committee Act, which aimed to help farmers get better prices for their produce and more discretion over who and where to sell. The proposed changes will allow Indian farmers to sell their products to anyone outside the Agricultural Product Market Committee (APMC) mandis. mendments to ECA will allow farmers to engage in inter-state trade, which was not allowed earlier.
- Expansion of federal eCommerce platform e-NAM app through addition of 415 more mandis raising the total wholesale market connected on e-NAM to over 1000
- Investment of Rs 1 lakh crore for strengthening agriculture infrastructure.
2020
Coverage provided for small and marginal farmers
- Launch of Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maan-Dhan Yojana (PM-KMDY) under which a minimum fixed pension of Rs 3000 to be provided to eligible small and marginal farmers on attaining the age of 60 years.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana (PM-KISAN) saw a transfer of Rs 2,021 crore to bank accounts of more than 10 million beneficiaries on February 24, 2019
- Launch of Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha Utthan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM) Scheme for farmers for the installation of solar pumps and grid-connected solar and other renewable power plants in the country.
2021
Budget focused on expansion of existing initiatives and agri-research
Plans Under Union Budget 2020-21
- The Government announced plans to launch Krishi Udaan on international and national routes. Fish production is expected to increase to 200 lakh tonnes by 2022-23.
- PM-KUSUM scheme has expanded to support 20 lakh farmers for setting up stand-alone solar pumps and will help another 15 lakh farmers to set up their grid-connected solar pumps.
- Rs 1.34 lakh crore allocated to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare.
- Rs 8,363 crore allocated to the Department of Agricultural Research and Education.
Source: Interviews with Indian Agriculture Equipment Industry Experts, Industry Articles, Company Websites & Ken Research Analysis
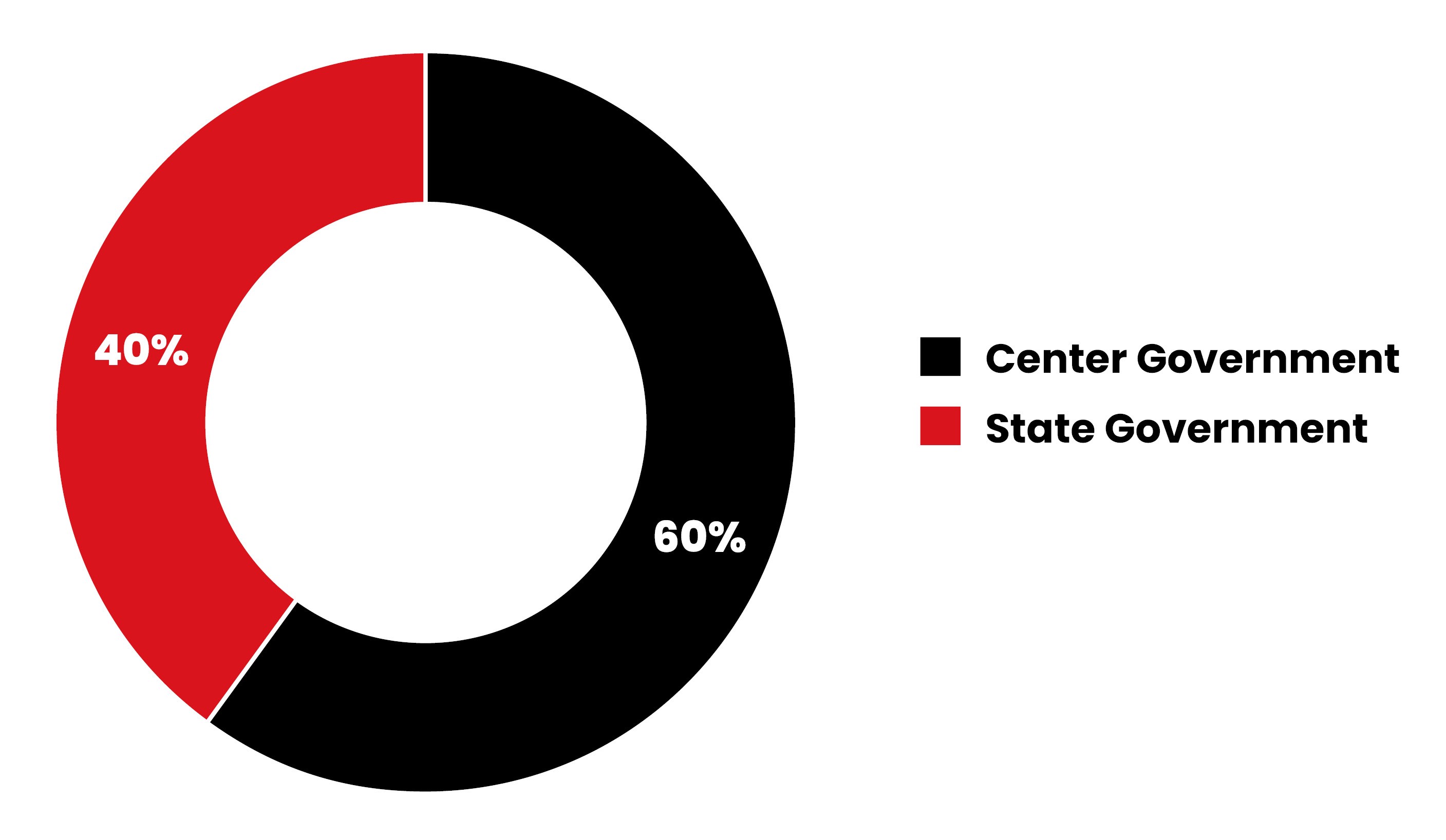
5. The Sub-mission on agricultural mechanization aims to provide subsidies of 40%-60% to small and marginal farmers, to enable mechanization at a granular level.
Mission Objectives
- Increasing the reach of farm mechanization to small and marginal farmers and to the regions where availability of farm power is low.
- Promoting ‘Custom Hiring Centres’ to offset the adverse economies of scale arising due to small landholding and high cost of individual ownership.
- Creating hubs for hi-tech & high value farm equipment.
- Creating awareness among stakeholders through demonstration and capacity building activities.
Subsidies proposed for the purchase of following Agricultural Equipment under SMAM
50%-60% Assistance (upto INR 1.6-5 Lakhs based on the model and HP)
Tractors
40%-50% Assistance (upto INR 0.5-0.85 Lakhs based on the model and HP)
Power Tillers
40%-50% Assistance (upto INR 0.16-0.5 Lakhs based on the model and HP)
Cultivators
40%-50% Assistance (upto INR 0.34-0.50 Lakhs based on the model and HP)
Rotavators
40%-50% Assistance (upto INR 0.28-1.25 Lakhs based on the model and HP)
Sprayers
40%-50% Assistance (upto INR 2.4-11 Lakhs based on the model and HP)
Harvesters (Includes combine harvester)
40%-50% Assistance (upto INR 0.16-0.5 Lakhs based on the model and HP)
Ploughs
40%-50% Assistance (upto INR 0.16-0. 5 Lakhs based on the model and HP)
Harrows
Key Takeaways
The scheme of SMAM (Sub mission of Agricultural mechanization), revised for 2020-2021, will be implemented in all the states, to promote the usage of farm mechanization and increase the ratio of farm power to cultivable unit area up to 2.5 kW/ha
The financial assistance being provided is upto 40% of the total value of implement, with added 10% aid to SC, ST, Small & Marginal farmers, Women and NE States beneficiary
Objectives of SMAM
Conduct performance testing for various farm machineries and equipment at the major institutions
Promote farm mechanization among stakeholders by way of on-field and off-field training and demonstrations.
Provide financial assistance to farmers for procurement of farm machinery and implements.
Establish custom hiring centres for renting location and crop specific farm machinery and implements.
Source: Interviews with Indian Agriculture Equipment Industry Experts, Industry Articles, Company Websites & Ken Research Analysis
6. Other initiatives such as National Food Security mission and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojna have announced substantial subsidies for purchase of farm equipment.
| Scheme |
Support for Farm Mechanization |
Financing Patterm |
National Food Security Mission (NFSM)
 |
- Assistance (up to 50% the cost of machinery) to be provided for machinery such as pump sets, tractor mounted sprayers, seed drills, zero till seed drills to varying degrees.
|
|
Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
 |
- Farm mechanization comes under production growth stream of RKVY – with 35% of the outlay.
- Assistance for large equipment (tractors, combine harvesters, sugarcane harvesters, cotton pickers, etc.) is available for establishing custom hiring centers (CHCs)
|

|
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)
 |
- One of the key interventions under the scheme is ‘horticulture mechanization’.
- Assistance is provided for procurement of power-operated machines and tools, besides for import of new machines.
- Assistance is also available for grower associations, farmer groups, SHGs, women farmer groups (with more than 10 members), etc., that are engaged in cultivation of horticulture crops.
|

|
Source: Interviews with Indian Agriculture Equipment Industry Experts, Industry Articles, Company Websites & Ken Research Analysis
7. Trickle effect of the growing new farm equipment market and the rise of contract farming among small & marginal farmers will further support the growth of the Used Agri-Equipment Market in India
Agricultural
Increasing cropping intensity
- Demand for more crops being cultivated in the same field is increasing due to finite arable land, thus requiring mechanization for enhancing income per unit of land.
Rise of contract farming
- Increasing participation of corporates that are entering into farming through contract farming agreements will lead to increased use of used agri-equipment on the fields, especially for those contracts including small and marginal farmers
- In turn these farmers will be incentivized to purchase farm implement. Used implementation will be cheaper, and hence, a viable option for this segment.
Social
Increased participation of women
- Increased migration of men for better prospects in non-farm opportunities has rendered farming a responsibility for women, especially in poorer states.
- This coupled with physically demanding work on farms will make mechanization a necessity
Drudgery of farm activities
- Hard labor on animate and farm labourers in the field coupled with timely performance and the small window available for conducting these operations calls for mechanising farm operations.
Status issues
- The successive generations of a farming family refrain from agriculture because of the manual handling of operations. Farm mechanization can acts as a stop to this important ‘labor drain’ from the farm to the non- farm sector.
Economic
Cost and time efficiency
- Mechanizing operations results in time and cost savings, thus making farming activity more profitable.
Government Interventions
- The effects of recent initiatives such as SMAM and NFSM, will be first seen in the new agri-equipment market and subsequently to the used agri-equipment market, through the trickle effect of increased equipment sale.
Source: Interviews with Indian Agriculture Equipment Industry Experts, Industry Articles, Company Websites & Ken Research Analysis