Kuwait Coding Bootcamp Market Overview
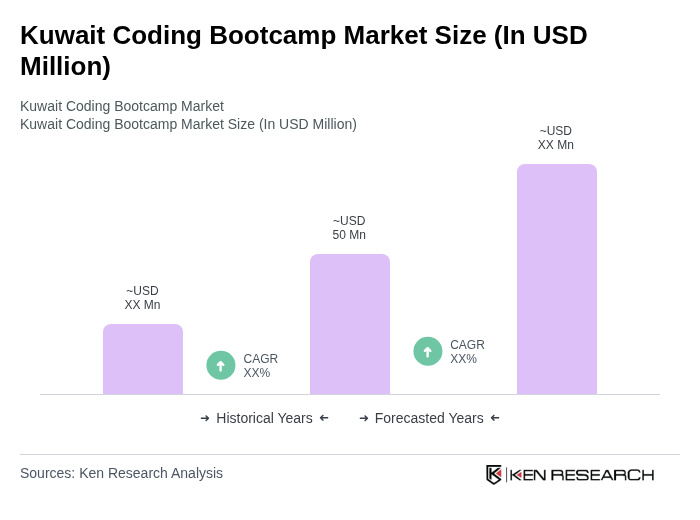
- The Kuwait Coding Bootcamp Market is valued at USD 50 million, based on a five-year historical analysis. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for skilled tech professionals, as Kuwait's economy diversifies and invests in digital transformation initiatives. The rise in technology adoption across various sectors has led to a surge in interest for coding bootcamps, which provide accelerated training for individuals seeking to enter the tech workforce.
- Kuwait City is the dominant hub for coding bootcamps, primarily due to its status as the capital and largest city, where most educational institutions and tech companies are located. The concentration of resources, including access to technology and a growing startup ecosystem, fosters an environment conducive to the growth of coding bootcamps. Additionally, the presence of expatriates seeking skill enhancement further drives demand in this region.
- In 2023, the Kuwaiti government implemented a new regulation aimed at enhancing the quality of vocational training programs, including coding bootcamps. This regulation mandates that all bootcamp providers must obtain accreditation from the Ministry of Education, ensuring that they meet specific educational standards and provide recognized certifications. This initiative is designed to improve the overall quality of training and increase the employability of graduates.
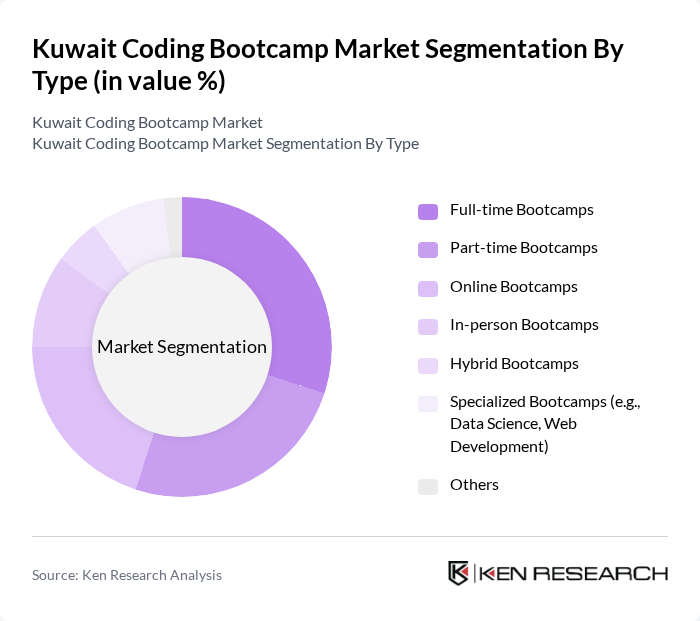
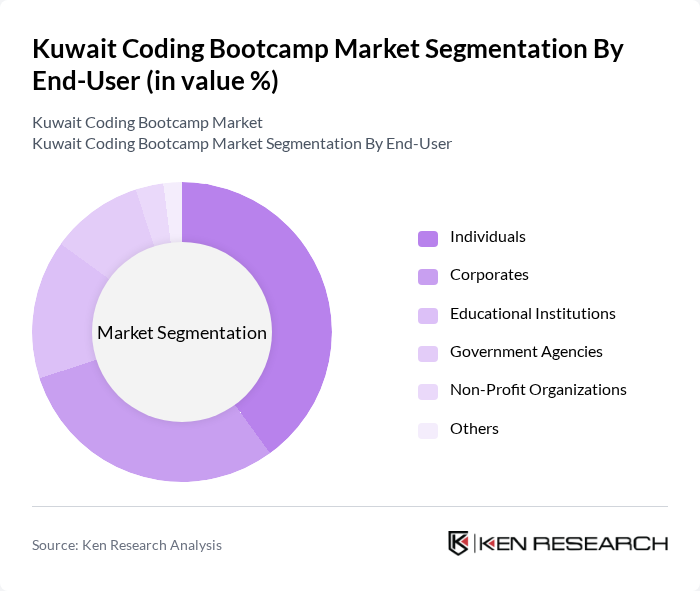
Kuwait Coding Bootcamp Market Segmentation
By Type:The coding bootcamp market can be segmented into various types, including Full-time Bootcamps, Part-time Bootcamps, Online Bootcamps, In-person Bootcamps, Hybrid Bootcamps, Specialized Bootcamps (e.g., Data Science, Web Development), and Others. Each type caters to different learning preferences and schedules, allowing a diverse range of participants to engage in coding education.
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Individuals, Corporates, Educational Institutions, Government Agencies, Non-Profit Organizations, and Others. This segmentation highlights the diverse clientele that coding bootcamps serve, from individuals seeking career changes to organizations looking to upskill their workforce.
Kuwait Coding Bootcamp Market Competitive Landscape
The Kuwait Coding Bootcamp Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Code Academy, Le Wagon, General Assembly, Ironhack, Thinkful, Flatiron School, Springboard, Coding Dojo, Nucamp, CareerFoundry, KodeKloud, Tech Elevator, Bloc, App Academy, Udacity contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
Kuwait Coding Bootcamp Market Industry Analysis
Growth Drivers
- Increasing Demand for Tech Skills:The demand for tech skills in Kuwait is surging, with the World Bank reporting a 30% increase in job postings for tech-related roles from 2022 to 2023. This trend is driven by the digital transformation across various sectors, including finance and healthcare, which are projected to require over 16,000 new tech professionals in the future. As businesses seek to innovate, coding bootcamps are positioned to fill this skills gap effectively.
- Government Initiatives Promoting Digital Education:The Kuwaiti government has allocated approximately $55 million for digital education initiatives in the future, aiming to enhance the tech workforce. This funding supports coding bootcamps and other educational programs, fostering a culture of innovation. Additionally, the Ministry of Education is integrating coding into school curricula, which is expected to increase enrollment in bootcamps by 25% over the next year, further driving market growth.
- Rise of the Startup Ecosystem in Kuwait:Kuwait's startup ecosystem is thriving, with over 220 startups launched in 2023 alone, according to the Kuwait National Fund for Small and Medium Enterprises. This growth is creating a robust demand for skilled tech workers, as startups often require agile and adaptable talent. Coding bootcamps are increasingly collaborating with these startups to provide tailored training, enhancing job placement rates and attracting more students to enroll.
Market Challenges
- Limited Awareness of Coding Bootcamps:Despite the growing demand for tech skills, awareness of coding bootcamps remains low in Kuwait. A recent survey indicated that only 30% of potential students are familiar with bootcamp offerings. This lack of awareness hinders enrollment, as many individuals still prefer traditional educational pathways. Increasing marketing efforts and outreach programs are essential to bridge this knowledge gap and attract more participants.
- Competition from Traditional Educational Institutions:Traditional universities in Kuwait are expanding their technology programs, posing significant competition to coding bootcamps. In 2023, universities reported a 20% increase in enrollment in computer science degrees. This trend may deter prospective students from considering bootcamps, which are often perceived as less credible. To remain competitive, bootcamps must emphasize their unique advantages, such as shorter duration and practical training.
Kuwait Coding Bootcamp Market Future Outlook
The future of the Kuwait coding bootcamp market appears promising, driven by increasing government support and a burgeoning tech ecosystem. As digital transformation accelerates, bootcamps are likely to adapt their curricula to meet evolving industry needs, focusing on emerging technologies. Furthermore, partnerships with local businesses will enhance job placement opportunities, making bootcamps an attractive option for aspiring tech professionals. The emphasis on practical skills and rapid training will continue to resonate with students seeking immediate employment in the tech sector.
Market Opportunities
- Expansion of Online Coding Bootcamp Offerings:The shift towards online education presents a significant opportunity for coding bootcamps in Kuwait. With internet penetration reaching 100% in the future, bootcamps can expand their reach and attract students from diverse backgrounds. This flexibility allows for tailored learning experiences, catering to the needs of working professionals and those in remote areas, potentially increasing enrollment by 35%.
- Collaboration with International Tech Companies:Collaborating with international tech firms can enhance the credibility and appeal of coding bootcamps. Such partnerships can provide access to global resources, mentorship, and internship opportunities, which are crucial for student success. By aligning with established companies, bootcamps can attract more students and improve job placement rates, fostering a stronger tech workforce in Kuwait.