Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAB5304
Pages:85
Published On:October 2025
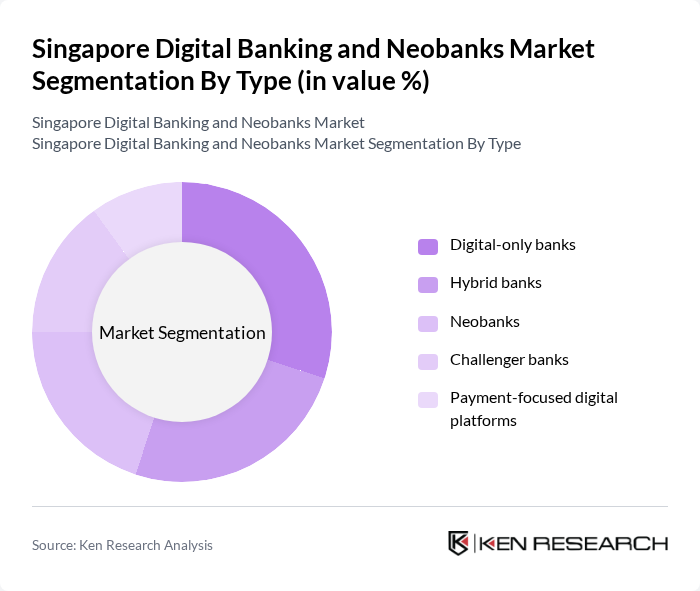
By Type:The market is segmented into various types, including digital-only banks, hybrid banks, neobanks, challenger banks, and payment-focused digital platforms. Digital-only banks are gaining traction due to their low operational costs and customer-centric services, often unencumbered by legacy IT systems which allows them to innovate products and enhance banking experiences more rapidly. Hybrid banks combine traditional banking with digital services, appealing to a broader audience. Neobanks focus on providing streamlined banking experiences, while challenger banks aim to disrupt traditional banking models. Payment-focused platforms are also emerging as significant players, catering to the growing demand for digital payment solutions.
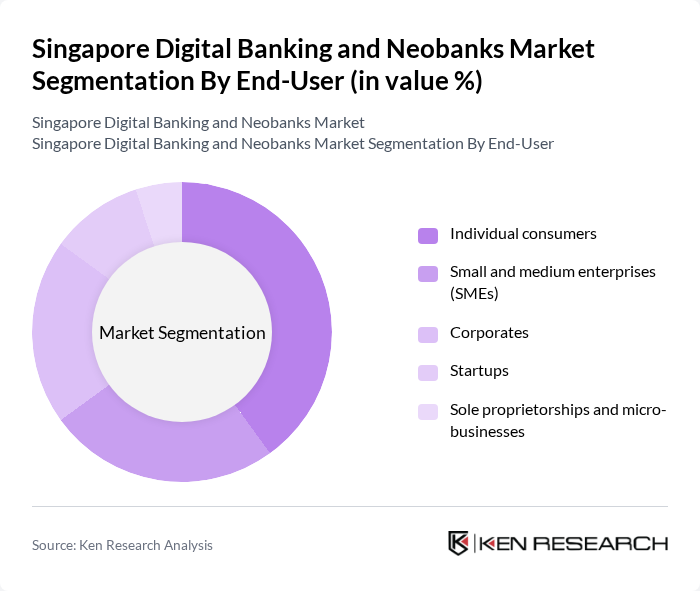
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes individual consumers, small and medium enterprises (SMEs), corporates, startups, and sole proprietorships and micro-businesses. Individual consumers are the largest segment, driven by the increasing preference for digital banking solutions and the shift from traditional banking to online banking. SMEs are also adopting digital banking services to streamline operations and enhance financial management. Corporates leverage these services for efficient cash management, while startups and micro-businesses benefit from tailored financial products that cater to their unique needs.
The Singapore Digital Banking and Neobanks Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as DBS Bank, OCBC Bank, UOB, Trust Bank, GXS Bank, MariBank, Grab Financial Group, Singtel Dash, Revolut, Standard Chartered Bank, CIMB Bank, Maybank, HSBC, N26, and Monzo contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of Singapore's digital banking and neobanks market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. As the digital economy expands, banks are likely to invest in innovative solutions that enhance customer engagement and streamline operations. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will further personalize banking experiences, while regulatory support will foster a competitive environment. Overall, the market is poised for significant transformation, with a focus on customer-centric services and enhanced digital capabilities.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Digital-only banks Hybrid banks Neobanks Challenger banks Payment-focused digital platforms |
| By End-User | Individual consumers Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) Corporates Startups Sole proprietorships and micro-businesses |
| By Service Offering | Savings accounts Loans and credit facilities Investment services Payment solutions Ancillary business services (e.g., invoicing, payment terminals) |
| By Customer Segment | Millennials Gen Z Professionals Retirees Newly affluent segments |
| By Distribution Channel | Mobile applications Web platforms Third-party integrations Ecosystem partnerships (e.g., e-commerce, ride-hailing) Others |
| By Pricing Model | Subscription-based Transaction-based Freemium Others |
| By Geographic Focus | Urban areas Suburban areas Rural areas Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Banking Customers | 120 | Individuals aged 18-65, using digital banking services |
| Small Business Owners | 80 | Owners of SMEs utilizing neobanking solutions |
| Fintech Industry Experts | 45 | Consultants, analysts, and academics specializing in fintech |
| Regulatory Bodies | 25 | Officials from the Monetary Authority of Singapore |
| Digital Banking Executives | 40 | Senior management from neobanks and digital banking divisions |
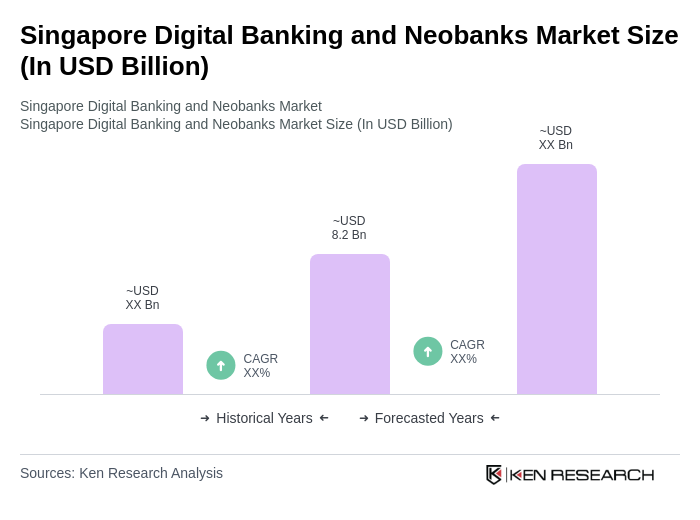
The Singapore Digital Banking and Neobanks Market is valued at approximately USD 8.2 billion, driven by the increasing adoption of digital financial services and technological advancements, reflecting a significant shift in consumer preferences towards online banking solutions.