Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAB4498
Pages:82
Published On:October 2025
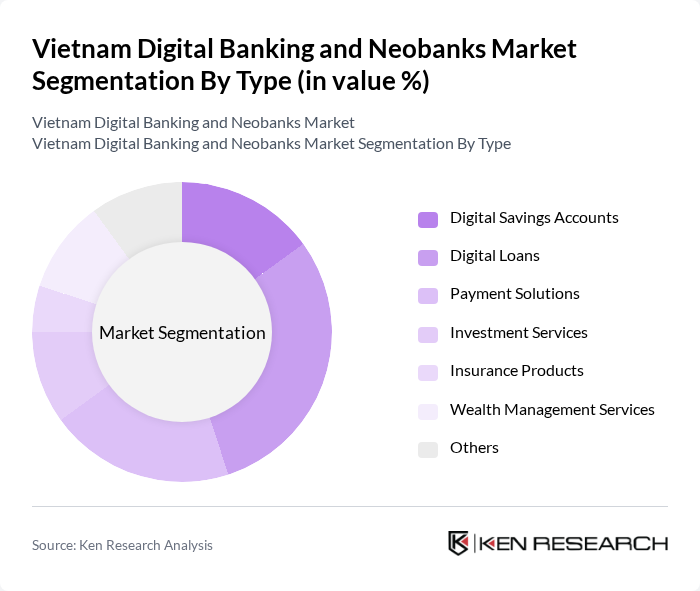
By Type:The market is segmented into various types of digital banking services, including Digital Savings Accounts, Digital Loans, Payment Solutions, Investment Services, Insurance Products, Wealth Management Services, and Others. Among these, Digital Loans have emerged as a leading segment due to the increasing demand for quick and accessible credit solutions, particularly among young consumers and small businesses. The convenience of applying for loans through mobile applications has significantly contributed to this trend.
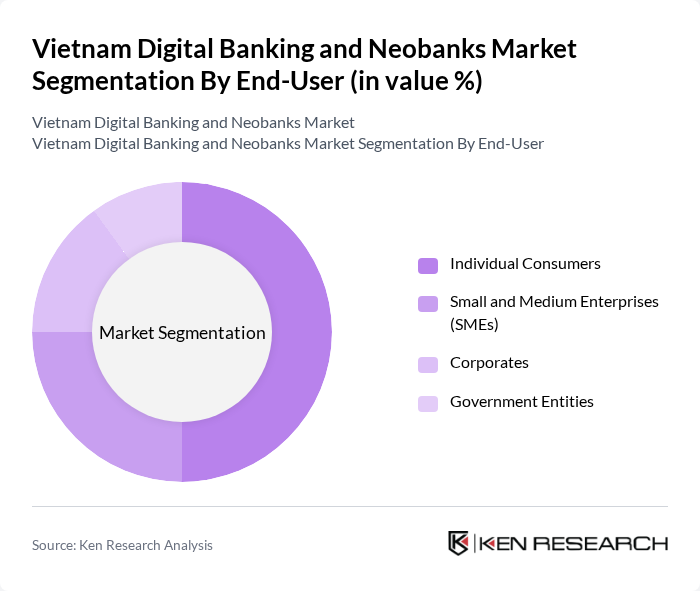
By End-User:This segmentation includes Individual Consumers, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Corporates, and Government Entities. Individual Consumers represent the largest segment, driven by the increasing number of young adults entering the workforce and their preference for digital banking solutions. The ease of access and user-friendly interfaces of digital banking platforms have made them particularly appealing to this demographic.
The Vietnam Digital Banking and Neobanks Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Timo, MoMo, VNPay, ZaloPay, TPBank, VietCapital Bank, Sacombank, BIDV, Techcombank, ACB, VPBank, Agribank, Maritime Bank, Shinhan Bank, HSBC Vietnam contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of Vietnam's digital banking and neobanks market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. As the government continues to support digital finance initiatives, the integration of AI and machine learning will enhance customer experiences and operational efficiencies. Additionally, the rise of open banking will foster innovation, allowing neobanks to offer tailored financial solutions, thereby attracting a broader customer base and driving market growth.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Digital Savings Accounts Digital Loans Payment Solutions Investment Services Insurance Products Wealth Management Services Others |
| By End-User | Individual Consumers Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Corporates Government Entities |
| By Customer Segment | Millennials Gen Z Professionals Retirees |
| By Service Channel | Mobile Applications Web Platforms Customer Support Centers |
| By Geographic Presence | Urban Areas Rural Areas |
| By Pricing Model | Subscription-Based Transaction-Based Freemium |
| By Regulatory Compliance Level | Fully Compliant Partially Compliant Non-Compliant |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Digital Banking Users | 150 | Consumers aged 18-45 using digital banking services |
| Small Business Neobank Clients | 100 | Owners and financial managers of SMEs utilizing neobanking |
| Fintech Industry Experts | 50 | Consultants and analysts specializing in fintech and digital banking |
| Regulatory Stakeholders | 30 | Officials from the State Bank of Vietnam and financial regulators |
| Digital Banking Product Managers | 70 | Product development leads from digital banks and neobanks |
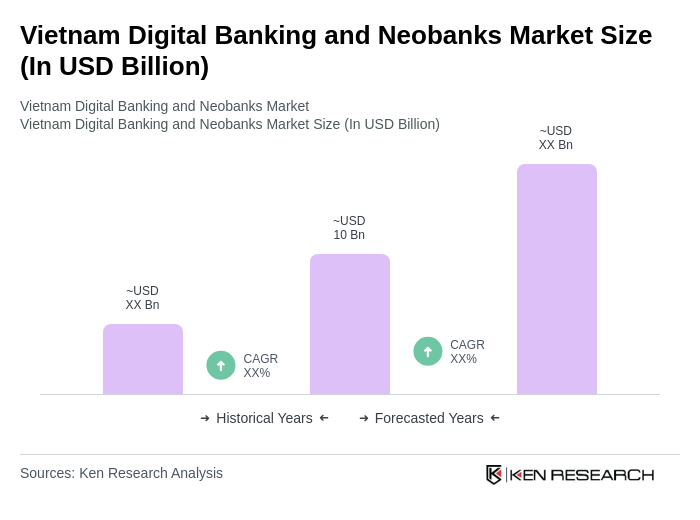
The Vietnam Digital Banking and Neobanks Market is valued at approximately USD 10 billion, driven by the increasing adoption of digital financial services, smartphone penetration, and a growing preference for cashless transactions among consumers.