Region:Asia
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAB0503
Pages:91
Published On:August 2025
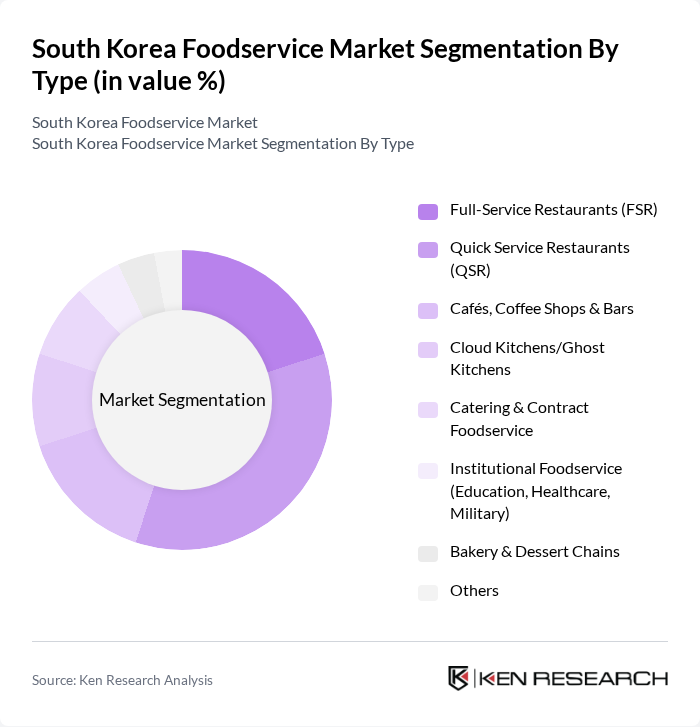
By Type:The foodservice market can be segmented into various types, including Full-Service Restaurants (FSR), Quick Service Restaurants (QSR), Cafés, Coffee Shops & Bars, Cloud Kitchens/Ghost Kitchens, Catering & Contract Foodservice, Institutional Foodservice (Education, Healthcare, Military), Bakery & Dessert Chains, and Others. Among these, Quick Service Restaurants (QSR) have emerged as the dominant segment due to their convenience, affordability, and the growing trend of fast food consumption among busy urban dwellers.
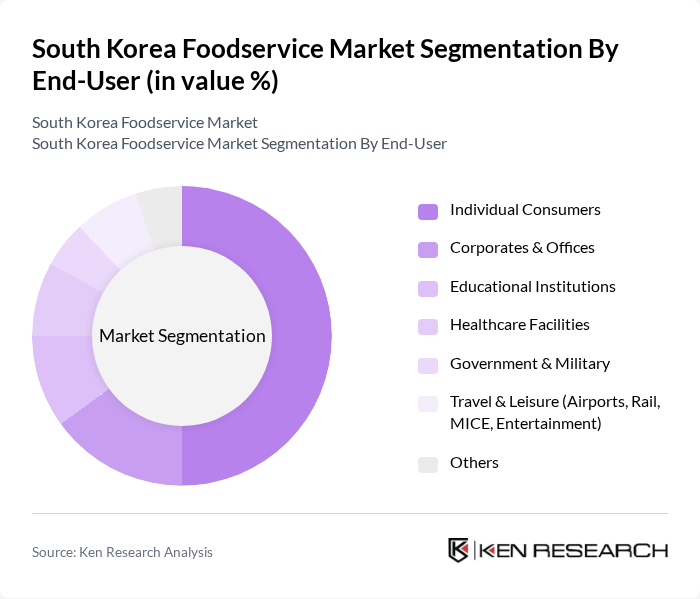
By End-User:The foodservice market is also segmented by end-users, which include Individual Consumers, Corporates & Offices, Educational Institutions, Healthcare Facilities, Government & Military, Travel & Leisure (Airports, Rail, MICE, Entertainment), and Others. Individual Consumers represent the largest segment, driven by the increasing trend of dining out and the convenience of food delivery services, particularly among younger demographics.
The South Korea Foodservice Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as CJ Foodville (VIPS, Bibigo Restaurants, The Place), Shinsegae Food (E-Mart24 Foodservice, Olbaan, Peacock Kitchen), LOTTE GRS (Lotteria, Angel-in-us Coffee, Krispy Kreme Korea), Samyang Foods Co., Ltd. (Foodservice & franchise partnerships), Ottogi Co., Ltd. (Foodservice sauces, HMR supply), Daesang Corporation (Foodservice solutions; Jongga), Nongshim Co., Ltd. (Foodservice channels; Baeksul partners), HiteJinro Co., Ltd. (On-premise beverage distribution), Sempio Foods Company (Foodservice condiments & sauces), BGF Retail (CU-affiliated foodservice, ready-to-eat), GS Retail (GS25-affiliated foodservice, GS Fresh), E-Mart Inc. (SSG Food Market; food halls), Paris Baguette (SPC Group), Starbucks Coffee Korea (Joint venture with E-Mart ? now SCK Company), McDonald’s Korea, KFC Korea, Burger King Korea (BKR Co., Ltd.), No Brand Burger (Shinsegae Food), Ediya Coffee, Mega Coffee, Compose Coffee, Paik’s Coffee (Theborn Korea Inc.), The Venti, Baedal Minjok (Woowa Brothers Corp.), Yogiyo (Delivery Hero Korea), Coupang Eats (Coupang Corp.), Ourhome Co., Ltd. (Contract catering), Hyundai Green Food Co., Ltd. (Contract catering), CJ Freshway (Contract catering & foodservice distribution), Sodexo Korea contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korea foodservice market is poised for dynamic growth, driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. As health-conscious dining becomes increasingly popular, establishments are likely to adapt their menus to include more nutritious options. Additionally, the integration of digital technologies in ordering and payment processes will enhance customer experiences. The focus on sustainability and local sourcing will also shape the market, as consumers demand transparency and environmentally friendly practices from foodservice providers.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Full-Service Restaurants (FSR) Quick Service Restaurants (QSR) Cafés, Coffee Shops & Bars Cloud Kitchens/Ghost Kitchens Catering & Contract Foodservice Institutional Foodservice (Education, Healthcare, Military) Bakery & Dessert Chains Others |
| By End-User | Individual Consumers Corporates & Offices Educational Institutions Healthcare Facilities Government & Military Travel & Leisure (Airports, Rail, MICE, Entertainment) Others |
| By Distribution Channel | Online Delivery Platforms & Aggregators On-Premise (Dine-in) Takeaway/Click-and-Collect Convenience & Retail Affiliated Outlets Events and Catering Others |
| By Cuisine Type | Korean Cuisine Western Cuisine Asian (non-Korean) Cuisine Bakery, Dessert & Specialty Coffee Fast Food Others |
| By Service Type | Dine-In Takeaway Delivery Drive-Thru Vending/Unmanned Stores Others |
| By Price Range | Budget Mid-Range Premium Others |
| By Consumer Demographics | Age Groups Income Levels Lifestyle Preferences Household Size (Single-Person vs Family) Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Quick Service Restaurants | 150 | Franchise Owners, Store Managers |
| Full Service Restaurants | 100 | Restaurant Owners, Head Chefs |
| Catering Services | 80 | Catering Managers, Event Planners |
| Food Delivery Services | 120 | Operations Managers, Marketing Managers |
| Food Trucks and Street Vendors | 70 | Owner-Operators, Street Food Vendors |
The South Korea Foodservice Market is valued at approximately USD 120 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and changing consumer preferences towards dining out and convenience foods, particularly during the pandemic.