Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAC0729
Pages:80
Published On:August 2025
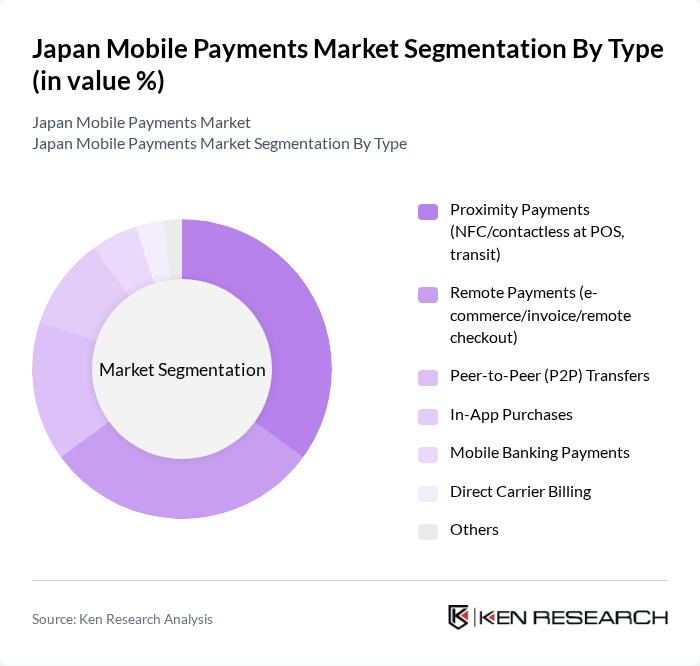
By Type:The mobile payments market can be segmented into various types, including proximity payments, remote payments, peer-to-peer transfers, in-app purchases, mobile banking payments, direct carrier billing, and others. Each of these sub-segments caters to different consumer needs and preferences, with proximity payments and remote payments being the most prominent due to their convenience and ease of use; strong smartphone penetration, transport wallet integration (e.g., transit cards in mobile wallets), and e-commerce growth underpin these two segments’ leadership.
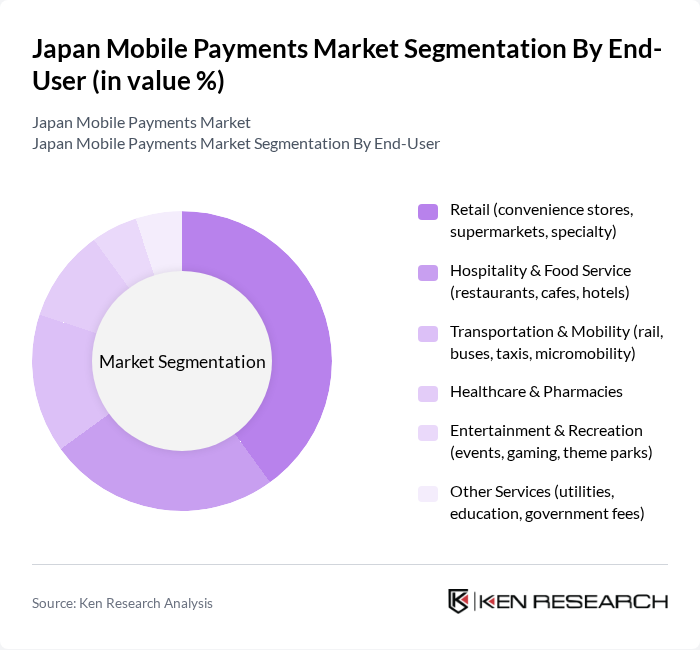
By End-User:The end-user segmentation of the mobile payments market includes retail, hospitality & food service, transportation & mobility, healthcare & pharmacies, entertainment & recreation, and other services. Retail is the leading segment, driven by the increasing number of merchants accepting mobile payments and the growing consumer preference for cashless transactions, with urban transit integration and QR/NFC acceptance supporting usage across convenience stores, supermarkets, and specialty retail.
The Japan Mobile Payments Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as PayPay Corporation, LINE Pay Corporation, Rakuten Payment, Inc. (Rakuten Pay / Rakuten Edy), Apple Pay (Japan), Google Pay (Japan), Square K.K. (Block, Inc.), Alipay+ (Ant Group) – Japan Acceptance, WeChat Pay (Tencent) – Japan Acceptance, JCB Co., Ltd. (QUICPay), East Japan Railway Company (JR East) – Suica Mobile, SoftBank Corp. (ecosystem partner for PayPay), NTT DOCOMO, Inc. (d?? / iD), MUFG Bank, Ltd. (MUFG / Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group), SB Payment Service Corp. (SoftBank Group), KDDI Corporation (au PAY / au PAY Card) contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Japan mobile payments market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. The integration of AI and machine learning is expected to enhance user experiences through personalized services, while the growth of digital wallets and contactless payments will further streamline transactions. Additionally, as rural areas gain better internet access, mobile payment adoption is likely to increase, creating new opportunities for service providers to expand their reach and customer base.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Proximity Payments (NFC/contactless at POS, transit) Remote Payments (e-commerce/invoice/remote checkout) Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Transfers In-App Purchases Mobile Banking Payments Direct Carrier Billing Others |
| By End-User | Retail (convenience stores, supermarkets, specialty) Hospitality & Food Service (restaurants, cafes, hotels) Transportation & Mobility (rail, buses, taxis, micromobility) Healthcare & Pharmacies Entertainment & Recreation (events, gaming, theme parks) Other Services (utilities, education, government fees) |
| By Sales Channel | Point of Sale (in-store) Online (web/mobile web) In-App (merchant/marketplace apps) Others |
| By Payment Method | Digital Wallets (PayPay, Rakuten Pay, d??, au PAY, LINE Pay) Card-on-File (credit/debit via tokenized wallets) Bank Account Transfers (J-Debit, account-to-account, Furikomi) Prepaid & Gift (Suica/Transit IC, prepaid e-money) Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Others |
| By Consumer Demographics | Age Groups Income Levels Urban vs Rural Others |
| By Security Features | Biometric Authentication Two-Factor Authentication Tokenization & Encryption Others |
| By Integration Level | Standalone Solutions Integrated Solutions (POS/ERP/loyalty) Custom Solutions Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Mobile Payment Usage | 150 | Smartphone Users, Age 18-64 |
| Merchant Acceptance of Mobile Payments | 120 | Small Business Owners, Retail Managers |
| Financial Institutions' Perspectives | 80 | Bank Executives, Payment Solution Managers |
| Technological Adoption Trends | 70 | IT Managers, Digital Transformation Officers |
| Regulatory Impact Assessment | 60 | Policy Makers, Compliance Officers |
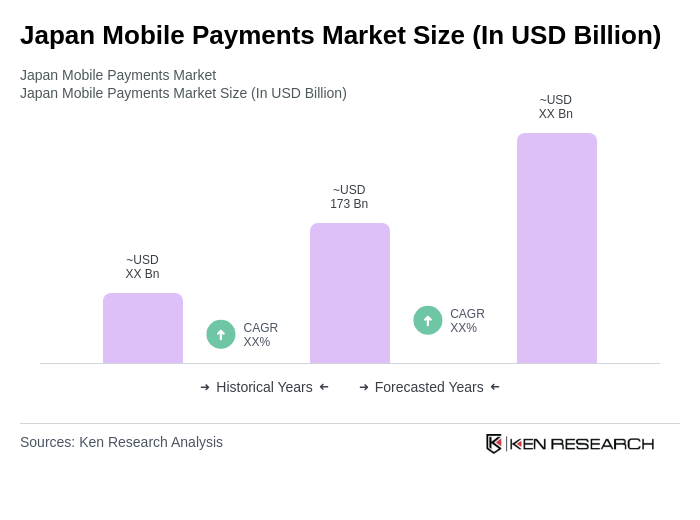
The Japan Mobile Payments Market is valued at approximately USD 173 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by smartphone adoption, e-commerce expansion, and a preference for contactless payment methods among consumers, particularly in urban areas.