Region:Asia
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAC0483
Pages:96
Published On:August 2025
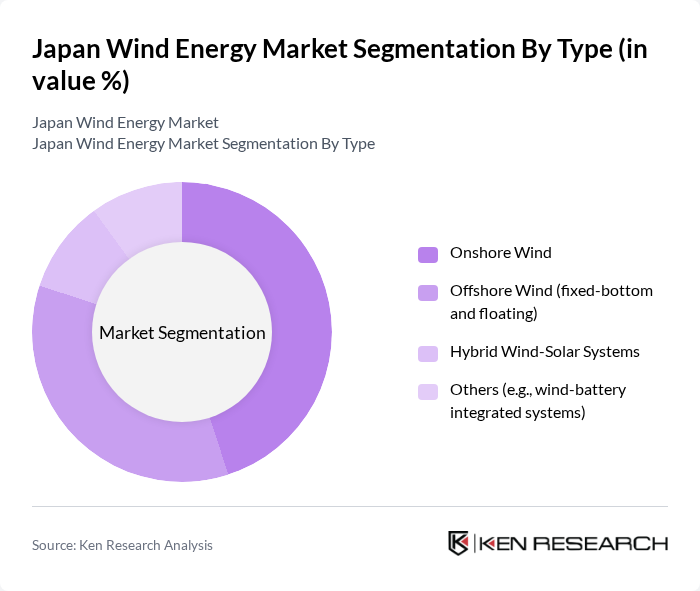
By Type:The market is segmented into various types, including Onshore Wind, Offshore Wind (fixed-bottom and floating), Hybrid Wind-Solar Systems, and Others (e.g., wind-battery integrated systems). Each type serves different energy needs and has unique characteristics that cater to specific market demands. Japan’s technical potential remains sizable (onshore and offshore), with policy and seabed conditions driving increasing emphasis on fixed-bottom and floating offshore development to meet decarbonization goals.
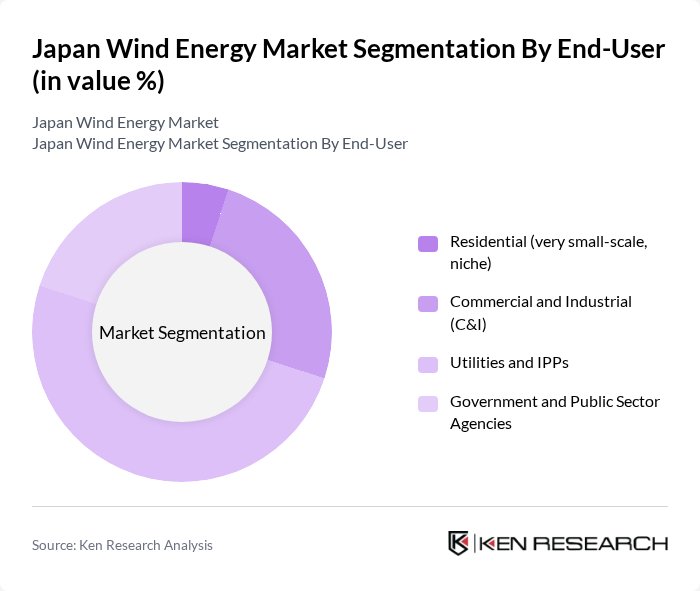
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Residential (very small-scale, niche), Commercial and Industrial (C&I), Utilities and IPPs, and Government and Public Sector Agencies. Each segment has distinct energy requirements and contributes differently to the overall market dynamics. In Japan, large-scale utility/IPPs dominate grid-connected wind capacity, with C&I participation growing via corporate PPAs and regional projects, while residential remains niche due to urban density and siting limits.
The Japan Wind Energy Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI), Hitachi, Ltd. (Hitachi Energy/Hitachi Power Solutions), Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, S.A. (Siemens Energy), Vestas Wind Systems A/S, GE Vernova (Wind segment), Nordex SE, Envision Energy, J-POWER (Electric Power Development Co., Ltd.), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO), Chubu Electric Power Co., Inc., The Kansai Electric Power Company, Incorporated, Shikoku Electric Power Company, Incorporated, Kyushu Electric Power Company, Incorporated, Japan Wind Development Co., Ltd. (Nihon Wind Development), Eurus Energy Holdings Corporation, Toda Corporation, Sumitomo Corporation, Marubeni Corporation, RENOVA, Inc., Japan Renewable Energy Corporation (JRE) contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of Japan's wind energy market appears promising, driven by increasing investments in offshore wind projects and advancements in energy storage technologies. By future, Japan aims to have 10 GW of installed wind capacity, with a significant portion coming from offshore installations. The integration of smart grid technologies is expected to enhance energy management and efficiency, while international collaborations will facilitate knowledge transfer and innovation, positioning Japan as a leader in renewable energy solutions.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Onshore Wind Offshore Wind (fixed-bottom and floating) Hybrid Wind-Solar Systems Others (e.g., wind-battery integrated systems) |
| By End-User | Residential (very small-scale, niche) Commercial and Industrial (C&I) Utilities and IPPs Government and Public Sector Agencies |
| By Application | Utility-Scale Projects Distributed Generation (behind-the-meter, community wind) Remote/Island and Off-Grid Solutions Others |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Investment (utilities, trading houses, developers) Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Government Programs and Funds (e.g., Green Innovation Fund) |
| By Policy Support | Feed-in Tariff (FIT) / Feed-in Premium (FIP) Tax Incentives and Accelerated Depreciation Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) and Corporate PPAs Others (grid enhancement schemes, port upgrades) |
| By Market Maturity | Emerging (floating offshore clusters) Growth (onshore repowering, fixed-bottom offshore) Mature (legacy onshore sites) Others |
| By Financing Model | Equity Financing Project Finance (non-recourse debt) Lease and Leasing-Back Structures Others (green bonds, transition bonds, infrastructure funds) |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Onshore Wind Farm Operators | 100 | Project Managers, Operations Directors |
| Offshore Wind Development Firms | 80 | Technical Leads, Business Development Managers |
| Government Energy Policy Makers | 60 | Regulatory Affairs Specialists, Energy Policy Analysts |
| Wind Energy Equipment Manufacturers | 70 | Product Managers, Sales Directors |
| Environmental Consultants in Renewable Energy | 50 | Sustainability Consultants, Environmental Engineers |
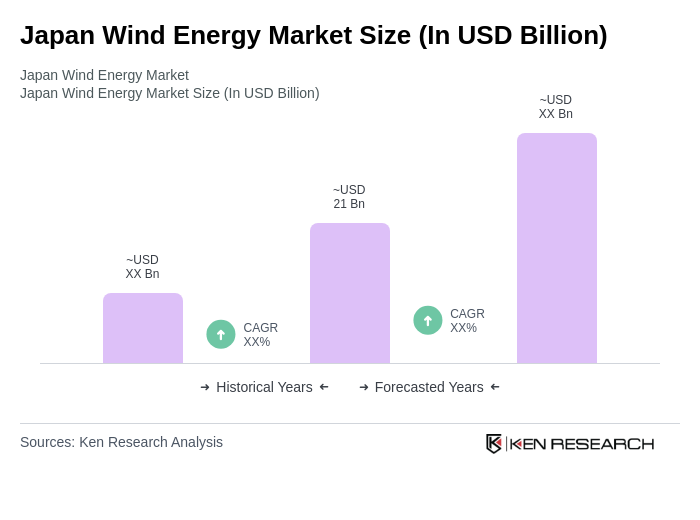
The Japan Wind Energy Market is valued at approximately USD 21 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by the increasing demand for renewable energy, government initiatives to reduce carbon emissions, and advancements in wind turbine technology.