Region:Middle East
Author(s):Dev
Product Code:KRAA8381
Pages:100
Published On:November 2025
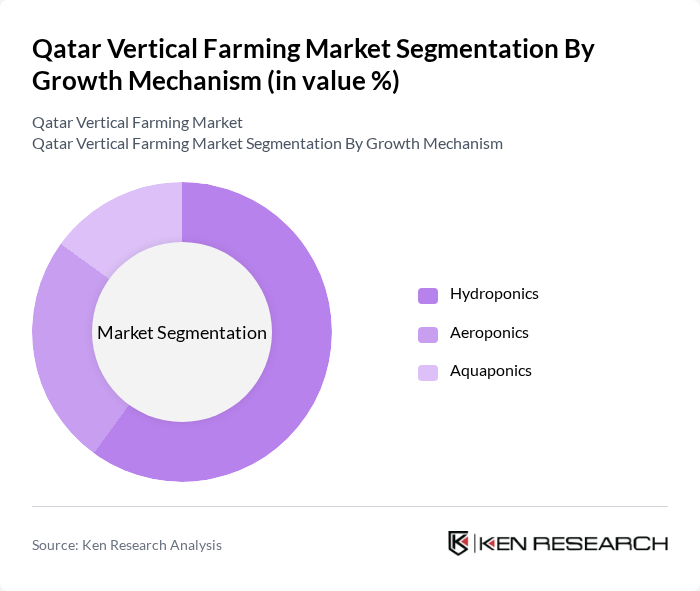
By Growth Mechanism:The growth mechanisms in the vertical farming market include hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. Hydroponics is the most widely adopted method due to its efficiency in water usage and nutrient delivery, making it suitable for urban environments. Aeroponics, while gaining traction, is still in the early stages of adoption, primarily used for high-value crops. Aquaponics combines fish farming with plant cultivation, appealing to niche markets focused on sustainability .
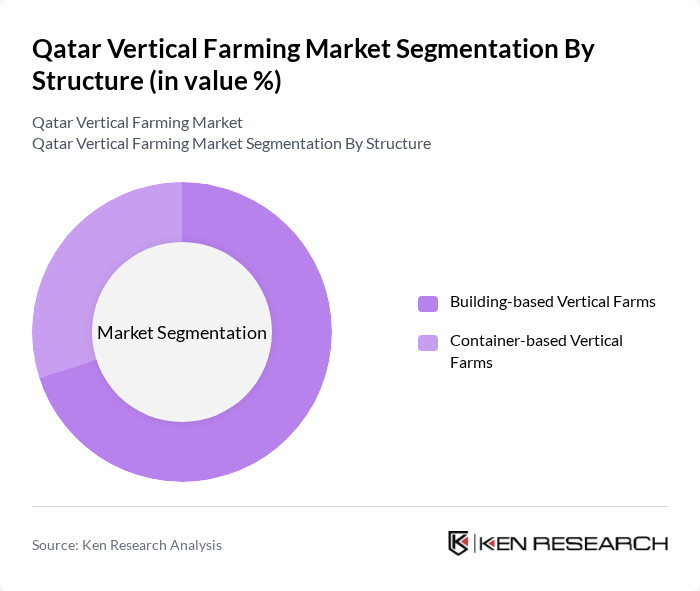
By Structure:The vertical farming market is segmented into building-based and container-based vertical farms. Building-based vertical farms dominate the market due to their ability to utilize existing urban infrastructure, allowing for efficient land use and reduced transportation costs. Container-based farms are emerging as a flexible solution for urban agriculture, appealing to businesses looking for scalable and mobile farming options. Building-based vertical farms account for the majority share, reflecting the market’s preference for permanent infrastructure and centralized distribution .
The Qatar Vertical Farming Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Agrico Qatar, Safwa Farms, Qatar Greenhouse Company, YAS Holding (Elite Agro Projects Qatar), Agritecture Qatar, Future Green Solutions, Qatar National Food Security Program, Al Sulaiteen Agricultural & Industrial Complex (SAIC), Baladna Food Industries, Qatar University Agricultural Research Center, Green Oasis Establishment, Eco Farm Qatar, Agrico Hydroponics, Vertical Harvest Qatar, and Smart Farm Qatar contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of vertical farming in Qatar appears promising, driven by increasing urbanization and a growing demand for sustainable food sources. As technological advancements continue to evolve, the integration of AI and IoT in farming practices will enhance efficiency and productivity. Furthermore, government initiatives aimed at promoting food security and sustainability will likely bolster investment in this sector, paving the way for innovative solutions that address local agricultural challenges and improve food accessibility.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Growth Mechanism | Hydroponics Aeroponics Aquaponics |
| By Structure | Building-based Vertical Farms Container-based Vertical Farms |
| By Component | Irrigation Systems Lighting (LED, Fluorescent, etc.) Sensors & Monitoring Climate Control Systems Building Materials (Glass, Plastic Greenhouse) Others |
| By Crop Type | Leafy Greens (Lettuce, Spinach, Kale, etc.) Herbs (Basil, Mint, etc.) Fruits (Strawberries, Tomatoes, etc.) Microgreens Flowers & Ornamentals Others |
| By Application | Indoor Outdoor |
| By End-User | Supermarkets & Hypermarkets Restaurants & Hotels Direct-to-Consumer (Online, Farm-to-Table) Institutional Buyers (Schools, Hospitals, etc.) Others |
| By Region | Ad Dawhah (Doha) Al Rayyan Al Wakrah Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Farming Operators | 70 | Farm Managers, Business Development Executives |
| Agricultural Technology Providers | 60 | Product Managers, R&D Specialists |
| Government Policy Makers | 40 | Agricultural Policy Analysts, Urban Development Officials |
| Academic Researchers | 50 | University Professors, Research Fellows |
| Retail Buyers of Fresh Produce | 70 | Procurement Managers, Category Buyers |
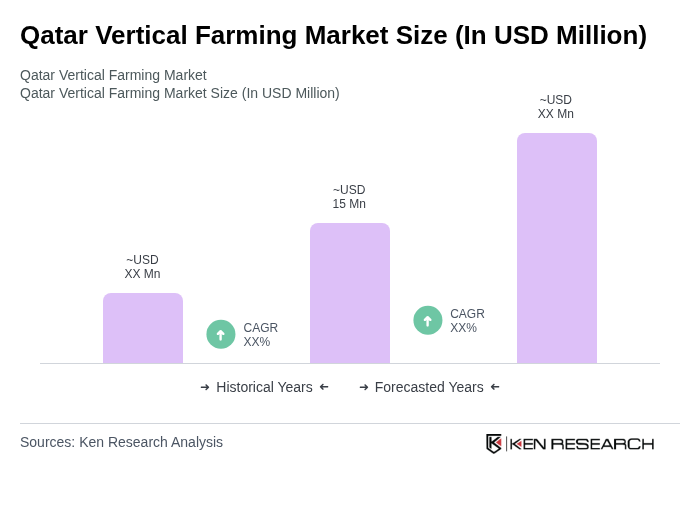
The Qatar Vertical Farming Market is valued at approximately USD 15 million, reflecting a growing trend towards sustainable agriculture and local food production driven by technological advancements and increasing urbanization.