Region:Asia
Author(s):Shubham
Product Code:KRAA0898
Pages:90
Published On:August 2025
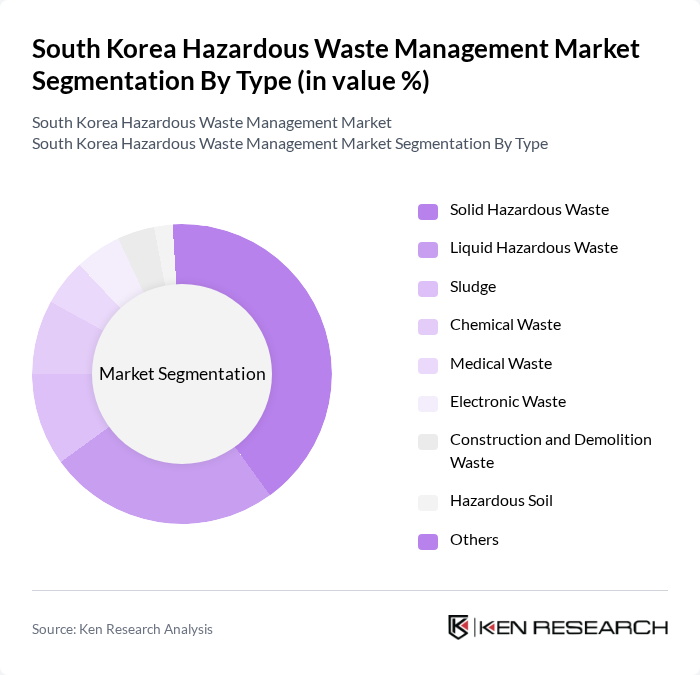
By Type:The hazardous waste management market is segmented into solid hazardous waste, liquid hazardous waste, sludge, chemical waste, medical waste, electronic waste, construction and demolition waste, hazardous soil, and others. Solid hazardous waste remains the largest segment, primarily due to the high output from manufacturing and municipal sources. Liquid hazardous waste is also significant, driven by the chemical, petrochemical, and industrial sectors. The growing emphasis on recycling and material recovery, especially for electronic and chemical waste, is shaping market dynamics .
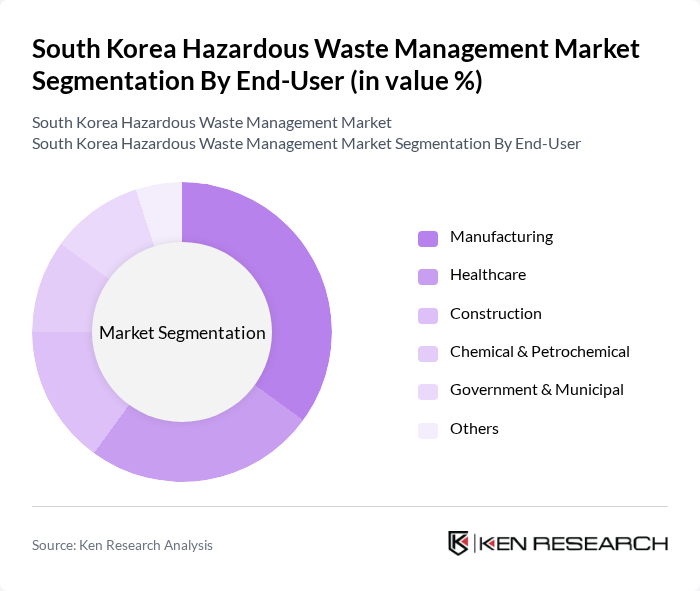
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes manufacturing, healthcare, construction, chemical & petrochemical, government & municipal, and others. Manufacturing is the leading contributor to hazardous waste generation, reflecting the scale of South Korea's industrial output. Healthcare is a significant segment due to strict protocols for medical waste disposal. Construction and demolition activities also contribute notably, while government and municipal sectors are increasingly adopting integrated hazardous waste management solutions in response to regulatory pressure .
The South Korea Hazardous Waste Management Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Korea Environment Corporation (KECO), SK ecoplant, SLC Co., Ltd., ECO Management Korea Co., Ltd., Korea Waste Management Corporation, Hanmi Global Environmental Co., Ltd., Daejeon Environmental Corporation, Veolia Korea, SUEZ Korea, GS E&C (GS Engineering & Construction), POSCO E&C (POSCO Engineering & Construction), Hyundai Engineering & Construction, LG Chem, Hanwha Solutions, Green Cross Corporation contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The South Korea hazardous waste management market is poised for significant transformation as regulatory frameworks tighten and public awareness continues to grow. In future, the integration of advanced technologies and sustainable practices will likely reshape waste management strategies. The shift towards a circular economy will encourage recycling and resource recovery, while public-private partnerships will enhance infrastructure development. These trends indicate a proactive approach to hazardous waste management, fostering innovation and collaboration within the industry, ultimately leading to improved environmental outcomes.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Solid Hazardous Waste Liquid Hazardous Waste Sludge Chemical Waste Medical Waste Electronic Waste Construction and Demolition Waste Hazardous Soil Others |
| By End-User | Manufacturing Healthcare Construction Chemical & Petrochemical Government & Municipal Others |
| By Disposal Method | Incineration Landfilling Recycling Treatment and Neutralization Others |
| By Collection Method | Scheduled Collection On-Demand Collection Drop-off Centers Others |
| By Region | Seoul Busan Incheon Daegu Gwangju Others |
| By Regulatory Compliance Level | Fully Compliant Partially Compliant Non-Compliant |
| By Policy Support | Government Subsidies Tax Incentives Grants for Technology Adoption Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Hazardous Waste Management | 100 | Plant Managers, Environmental Compliance Officers |
| Healthcare Waste Disposal Services | 60 | Healthcare Facility Administrators, Waste Management Coordinators |
| Construction and Demolition Waste Management | 50 | Construction Project Managers, Safety Officers |
| Electronic Waste Recycling | 40 | Recycling Facility Operators, Environmental Engineers |
| Government Regulatory Bodies | 40 | Policy Makers, Environmental Inspectors |
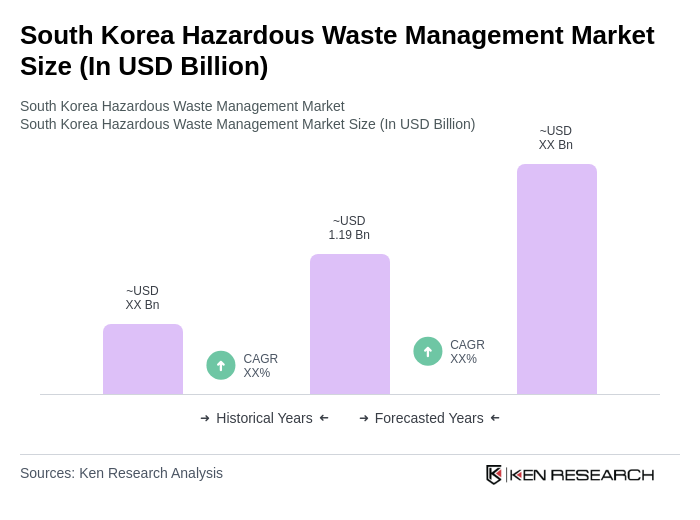
The South Korea Hazardous Waste Management Market is valued at approximately USD 1.19 billion, reflecting a significant growth driven by stringent environmental regulations, industrialization, and a focus on sustainable waste practices.