Region:Asia
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAA4507
Pages:92
Published On:September 2025
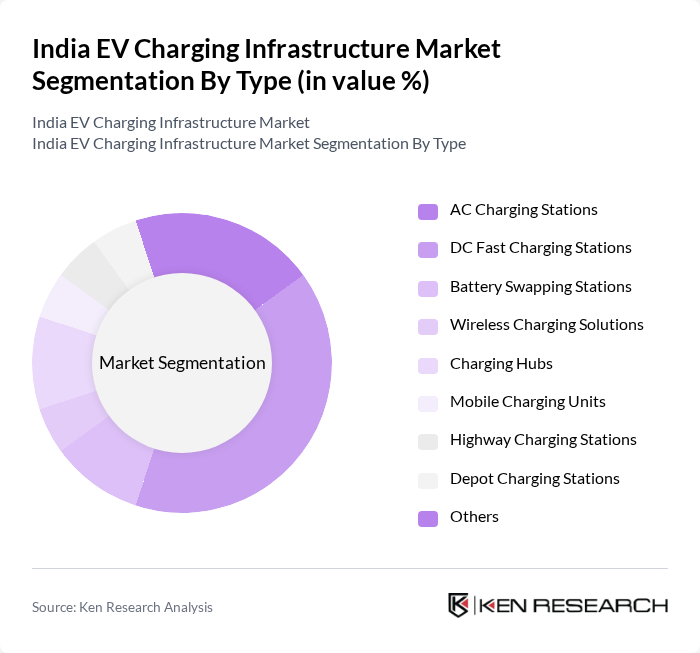
By Type:The market can be segmented into various types of charging stations, each catering to different consumer needs and technological advancements. The subsegments include AC Charging Stations, DC Fast Charging Stations, Battery Swapping Stations, Wireless Charging Solutions, Charging Hubs, Mobile Charging Units, Highway Charging Stations, Depot Charging Stations, and Others. Among these,DC Fast Charging Stationsare gaining significant traction due to their ability to charge vehicles quickly, making them ideal for urban areas and highways.
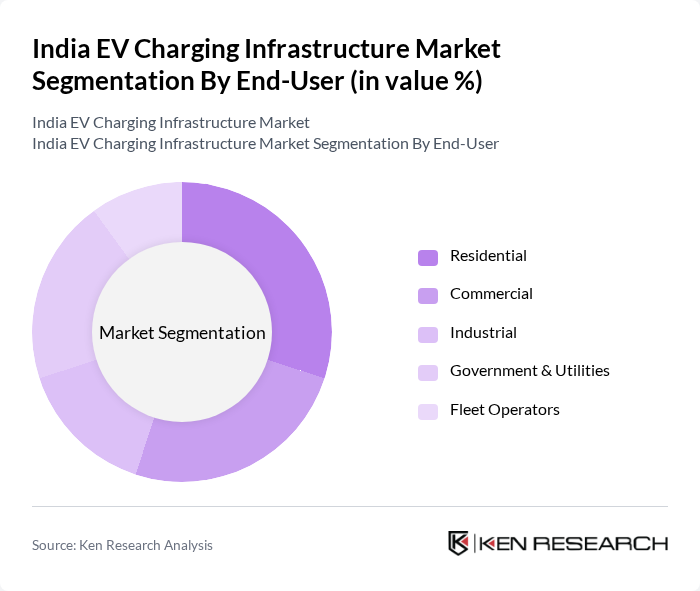
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Government & Utilities, and Fleet Operators. The residential segment is witnessing a surge in demand as more consumers opt for electric vehicles and seek convenient charging solutions at home. Commercial and fleet operators are also increasingly investing in charging infrastructure to support their electric vehicle fleets, driven by operational efficiency and sustainability goals.
The India EV Charging Infrastructure Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Tata Power, Fortum Charge & Drive India, ChargeZone, Magenta ChargeGrid, Exicom Power Systems, Delta Electronics India, ABB India, Siemens India, Hero Electric, Ather Energy, Amara Raja Batteries, EVRE, Statiq, Volttic, Bosch India contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the India EV charging infrastructure market appears promising, driven by increasing government support and technological innovations. In future, the integration of renewable energy sources into charging stations is expected to enhance sustainability. Additionally, the rise of smart charging solutions, which optimize energy use and reduce costs, will likely transform user experiences. As consumer acceptance grows, the market is poised for significant expansion, with a focus on enhancing accessibility and convenience for electric vehicle users.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | AC Charging Stations DC Fast Charging Stations Battery Swapping Stations Wireless Charging Solutions Charging Hubs Mobile Charging Units Highway Charging Stations Depot Charging Stations Others |
| By End-User | Residential Commercial Industrial Government & Utilities Fleet Operators |
| By Region | North India South India East and Central India West India |
| By Technology | Smart Charging Technology Renewable Energy Integration Battery Storage Solutions Grid Management Systems |
| By Application | Public Charging Stations Private Charging Solutions Fleet Charging Solutions Workplace Charging Highway Charging Depot Charging |
| By Investment Source | Domestic Investment Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Government Schemes |
| By Policy Support | Subsidies Tax Exemptions Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) Grants and Funding Programs |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Public Charging Station Operators | 60 | Operations Managers, Business Development Managers |
| Private Charging Solutions Providers | 50 | Product Managers, Technical Directors |
| EV Users and Owners | 100 | Individual Consumers, Fleet Managers |
| Government Policy Makers | 40 | Urban Planners, Environmental Policy Advisors |
| Energy Providers and Utilities | 45 | Energy Analysts, Infrastructure Development Managers |
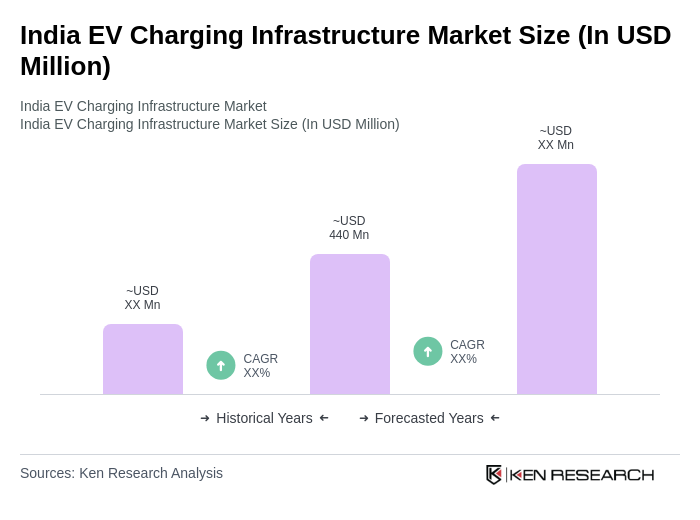
The India EV Charging Infrastructure Market is valued at approximately USD 440 million, driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, government initiatives, and consumer awareness regarding sustainable transportation.