Japan Modular Construction Market Overview
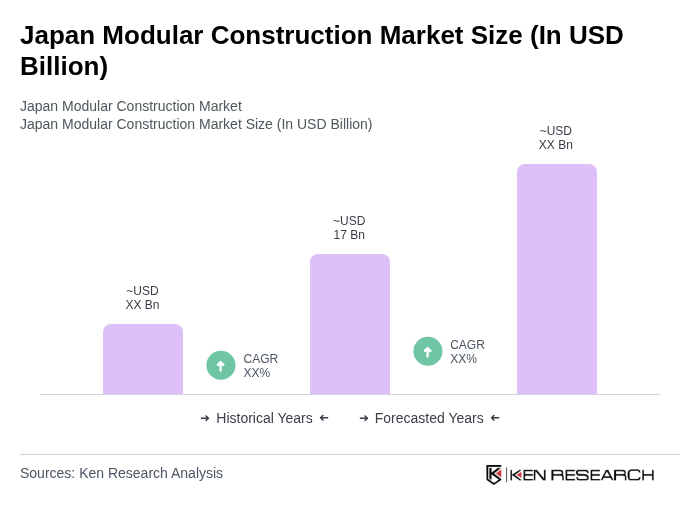
- The Japan Modular Construction Market is valued at USD 17 billion, based on a five-year historical analysis. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for efficient construction methods, urbanization in major metropolitan regions, labor shortages in the construction sector, and the need for sustainable building solutions. The market has seen a significant rise in modular construction projects, particularly in dense urban areas, as developers seek to reduce construction time and costs while meeting stricter energy performance and environmental standards through off-site prefabrication and higher quality control.
- Key demand hubs in this market include the Kanto Region (which covers Tokyo), the Kansai/Kinki Region (including Osaka), and the Chubu Region (including Nagoya), which dominate due to their high population density, large construction pipelines, and ongoing infrastructure and redevelopment projects. These urban regions are at the forefront of adopting modular construction techniques, driven by municipal and national initiatives to accelerate housing supply, renew aging building stock, improve seismic resilience, and enable rapid reconstruction and temporary housing deployment after natural disasters.
- The regulatory environment supporting sustainable building has been strengthened through instruments such as the Building Energy Efficiency Act (Act on the Improvement of Energy Consumption Performance of Buildings) enforced by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) and revised in 2022, which expands mandatory energy performance standards for new buildings and progressively requires compliance with specified energy efficiency criteria for a wider range of non-residential and residential buildings. These requirements aim to reduce carbon emissions and encourage the adoption of construction methods, including modular and prefabricated approaches, that can more easily integrate high-performance envelopes, factory-installed insulation, and energy-saving systems compared to conventional on-site building techniques.
Japan Modular Construction Market Segmentation
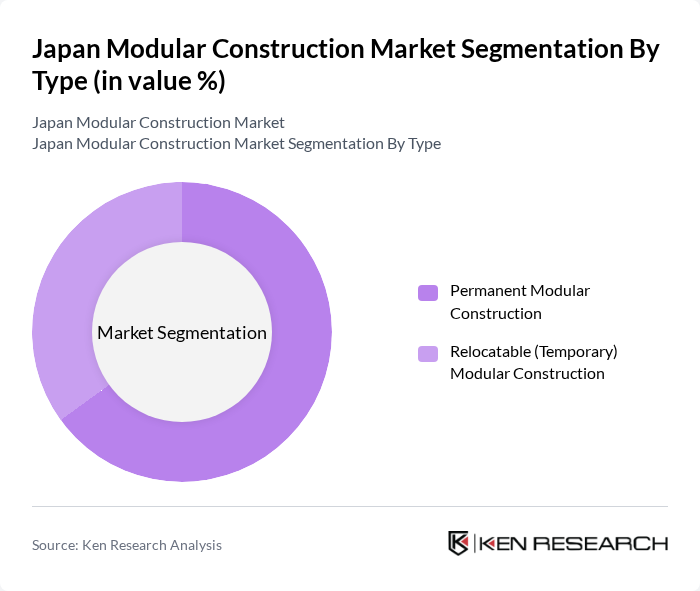
By Type:The modular construction market can be segmented into two primary types: Permanent Modular Construction and Relocatable (Temporary) Modular Construction. Permanent modular construction involves the off-site fabrication of building modules that are then transported and assembled on-site, providing a durable and long-lasting solution suitable for residential, commercial, and institutional buildings. Relocatable modular construction, on the other hand, focuses on temporary or semi-permanent structures that can be moved, reused, or reconfigured as needed, often for site offices, temporary housing, education, or disaster-relief facilities. The demand for permanent modular construction is currently leading the market due to its long-term cost benefits, improved quality, better energy performance, and increasing acceptance in sectors such as multi-family housing, healthcare, and hospitality.
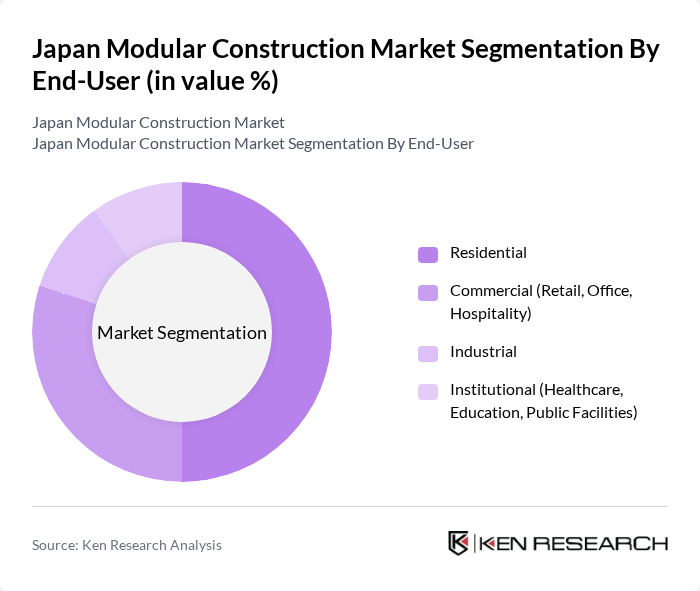
By End-User:The end-user segmentation of the modular construction market includes Residential, Commercial (Retail, Office, Hospitality), Industrial, and Institutional (Healthcare, Education, Public Facilities). The residential sector is currently the dominant segment, driven by the increasing need for affordable and space-efficient housing, redevelopment of aging stock, and strong demand in metropolitan areas such as greater Tokyo and Osaka. Additionally, the commercial sector is witnessing significant growth as developers and operators in offices, retail, and hospitality increasingly adopt modular solutions to shorten delivery times, respond quickly to changing tenant requirements, and reduce on-site labor dependence.
Japan Modular Construction Market Competitive Landscape
The Japan Modular Construction Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Sekisui House, Ltd., Daiwa House Industry Co., Ltd., Asahi Kasei Homes Corporation, Misawa Homes Co., Ltd., PanaHome Corporation (Panasonic Homes Co., Ltd.), Sumitomo Forestry Co., Ltd., Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd. (Housing Company), Toyota Housing Corporation, Kumagai Gumi Co., Ltd., Shimizu Corporation, Obayashi Corporation, Taisei Corporation, Takenaka Corporation, NTT Facilities, Inc., Haseko Corporation contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
Japan Modular Construction Market Industry Analysis
Growth Drivers
- Increased Demand for Affordable Housing:Japan faces a significant housing shortage, with over 8 million households classified as under-housed. The government aims to construct 1.5 million new homes annually in future, driving demand for modular construction. This method can reduce construction time by up to 50%, allowing for quicker responses to housing needs. Additionally, the average cost of modular homes is approximately ¥30 million, making them a viable option for many families seeking affordable housing solutions.
- Government Initiatives for Sustainable Construction:The Japanese government has committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 46% from previous levels in future. This commitment has led to increased funding for sustainable construction practices, including modular building techniques. In future, the government allocated ¥200 billion for green building initiatives, promoting energy-efficient designs and materials. Modular construction aligns with these goals, as it typically results in less waste and lower energy consumption during the building process, appealing to environmentally conscious developers.
- Technological Advancements in Construction Methods:The integration of advanced technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and robotics is revolutionizing the modular construction sector in Japan. In future, the adoption of BIM is expected to increase by 30%, enhancing project efficiency and accuracy. Furthermore, the use of robotics in assembly can reduce labor costs by 20%, making modular construction more attractive to developers. These technological advancements are crucial in addressing labor shortages and improving overall project timelines.
Market Challenges
- High Initial Investment Costs:Despite the long-term savings associated with modular construction, the initial investment remains a significant barrier. The average upfront cost for modular projects can reach ¥40 million, which is often higher than traditional construction methods. This financial hurdle can deter potential investors and developers, especially in a market where cost efficiency is paramount. Additionally, securing financing for these projects can be challenging, further complicating market entry for new players.
- Regulatory Compliance and Bureaucracy:Navigating Japan's complex regulatory landscape poses a challenge for modular construction. The country has stringent building codes and zoning laws that can delay project approvals. In future, it is estimated that compliance costs could account for up to 15% of total project expenses. This bureaucratic red tape can discourage investment and slow down the adoption of modular construction, as developers may face lengthy approval processes that hinder timely project execution.
Japan Modular Construction Market Future Outlook
The future of the modular construction market in Japan appears promising, driven by increasing urbanization and a growing emphasis on sustainability. As cities expand, the need for efficient housing solutions will intensify, pushing developers to adopt modular techniques. Furthermore, advancements in technology will continue to enhance construction efficiency and reduce costs. By future, the integration of smart technologies in modular designs is expected to become standard, further attracting investment and fostering innovation in the sector.
Market Opportunities
- Expansion into Rural Areas:With approximately 30% of Japan's population residing in rural areas, there is a significant opportunity for modular construction to address housing shortages. By targeting these regions, developers can meet local demands while benefiting from lower land costs. This expansion can lead to increased market penetration and foster community development, creating a win-win scenario for both builders and residents.
- Adoption of Green Building Practices:The growing trend towards sustainability presents a lucrative opportunity for modular construction. As more developers seek to comply with environmental regulations, the demand for eco-friendly modular solutions is expected to rise. In future, the market for green building materials is projected to reach ¥1 trillion, indicating a robust potential for modular construction firms that prioritize sustainable practices and materials in their offerings.