Region:Global
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAB2050
Pages:92
Published On:January 2026
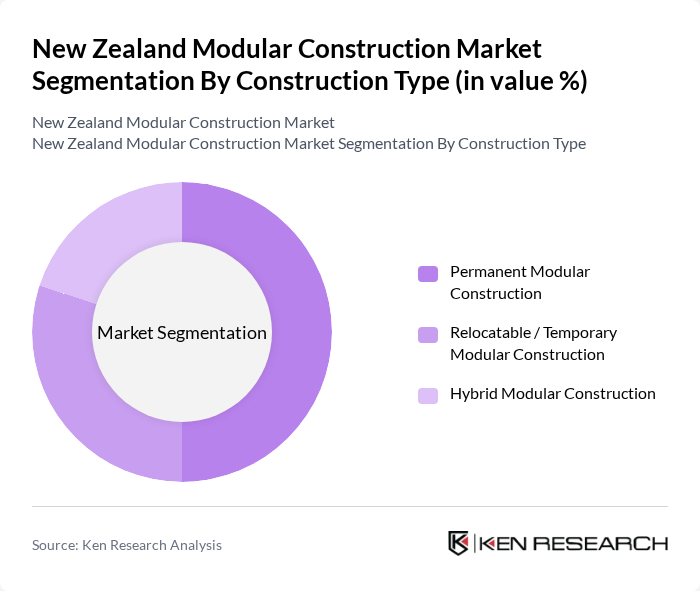
By Construction Type:The construction type segmentation includes Permanent Modular Construction, Relocatable / Temporary Modular Construction, and Hybrid Modular Construction. Permanent modular construction is gaining traction due to its durability, ability to meet full New Zealand Building Code performance requirements, and suitability for multi?unit residential, education, and healthcare projects. Relocatable and temporary modular solutions are increasingly used for classrooms, site facilities, disaster recovery accommodation, and other short? to medium?term uses where speed of deployment and redeployment is critical. Hybrid modular construction, which combines prefabricated volumetric units or panels with traditional on?site methods, is expanding in higher?spec residential and commercial projects as it offers greater architectural flexibility while retaining programme and cost advantages.
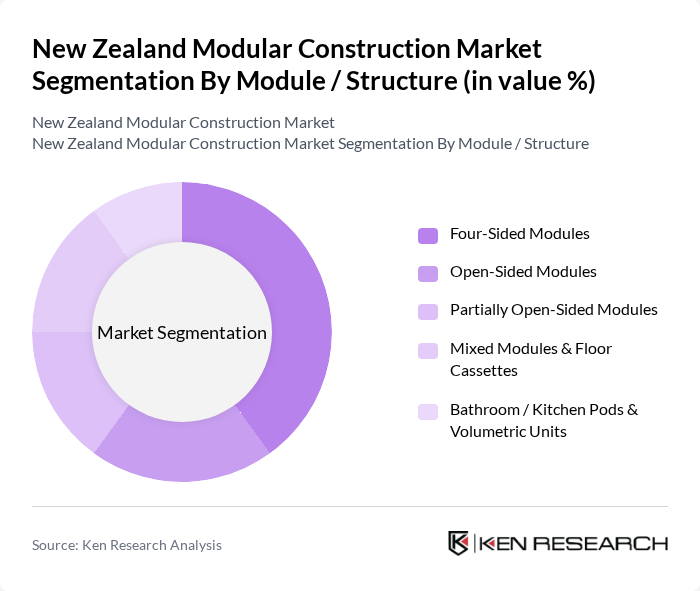
By Module / Structure:The module/structure segmentation includes Four-Sided Modules, Open-Sided Modules, Partially Open-Sided Modules, Mixed Modules & Floor Cassettes, and Bathroom / Kitchen Pods & Volumetric Units. Four-sided modules are a key format globally and in New Zealand, as they provide complete volumetric units that can be stacked and combined, offering versatility and speed of assembly for residential, hospitality, and commercial schemes. Open-sided and partially open?sided modules are often used where larger internal spans or extensive glazing are needed, such as offices, education buildings, and communal residential areas. Bathroom and kitchen pods, as well as other volumetric service modules, are gaining popularity in New Zealand multi?unit housing, build?to?rent, and student accommodation, because they improve quality control, reduce site labour demands, and shorten interior fit?out times.
The New Zealand Modular Construction Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as PrefabNZ / OffsiteNZ, Modulus Homes, T?maki Regeneration Company, Fletcher Building, G.J. Gardner Homes, A1 Homes, KiwiBuild Programme, BuildSmart, Advance Build, Urban Homes, Taitokerau Construction, K?inga Ora – Homes and Communities, Green Homes New Zealand, Concision Offsite Manufacturing, Matrix Homes / Other Emerging Modular Providers contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the New Zealand modular construction market appears promising, driven by increasing urbanization and a growing emphasis on sustainable building practices. As the government continues to support affordable housing initiatives, modular construction is likely to play a pivotal role in meeting these demands. Furthermore, advancements in technology will enhance efficiency and reduce costs, making modular solutions more appealing to developers and consumers alike, fostering a more robust market environment.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Construction Type | Permanent Modular Construction Relocatable / Temporary Modular Construction Hybrid Modular Construction |
| By Module / Structure | Four-Sided Modules Open-Sided Modules Partially Open-Sided Modules Mixed Modules & Floor Cassettes Bathroom / Kitchen Pods & Volumetric Units |
| By Material | Steel Concrete Timber / Engineered Wood Other Materials (Composite, Lightweight Panels, etc.) |
| By End-Use Sector | Residential (Single-Family & Multi-Family) Office & Commercial Education Healthcare Hospitality & Retail Public Sector & Social Housing |
| By Application | New Build Additions, Extensions & Infill Temporary Accommodation & Site Facilities |
| By Financing / Delivery Model | Direct Purchase (Capex-Funded) Lease / Hire Public–Private Partnership (PPP / P3) Government-Backed Housing Schemes & Grants |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Modular Construction | 120 | Architects, Home Builders, Project Managers |
| Commercial Modular Projects | 90 | Construction Managers, Developers, Real Estate Investors |
| Industrial Modular Solutions | 70 | Facility Managers, Operations Directors, Procurement Officers |
| Regulatory Compliance in Modular Construction | 50 | Regulatory Officials, Compliance Managers, Legal Advisors |
| Sustainability Practices in Modular Construction | 60 | Sustainability Officers, Environmental Consultants, Project Coordinators |
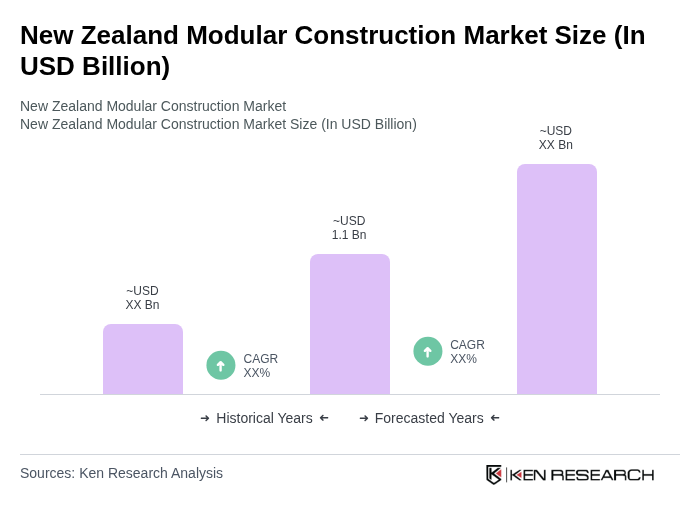
The New Zealand Modular Construction Market is valued at approximately USD 1.1 billion, reflecting a significant growth trend driven by the demand for affordable housing and efficient construction methods.