Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAA6383
Pages:95
Published On:January 2026
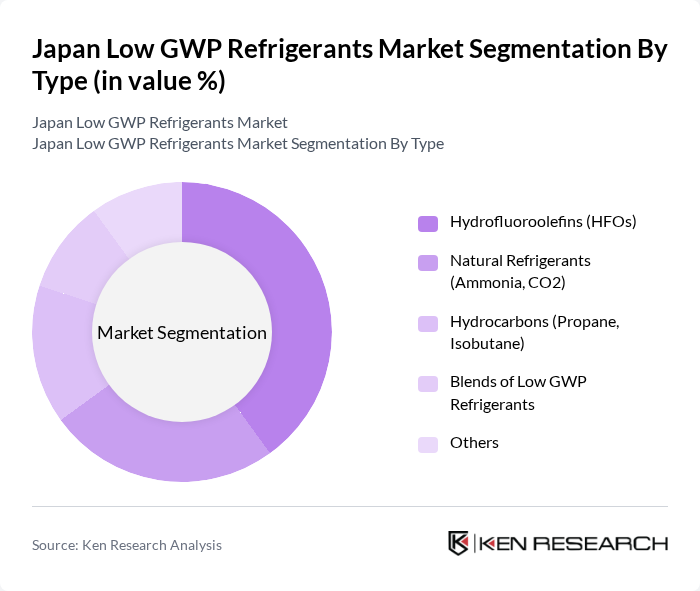
By Type:The market is segmented into various types of refrigerants, including Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs), Natural Refrigerants (Ammonia, CO2), Hydrocarbons (Propane, Isobutane), Blends of Low GWP Refrigerants, and Others. Among these, Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) are gaining traction due to their low environmental impact and efficiency in cooling applications. Natural refrigerants are also popular due to their sustainability and minimal environmental footprint.
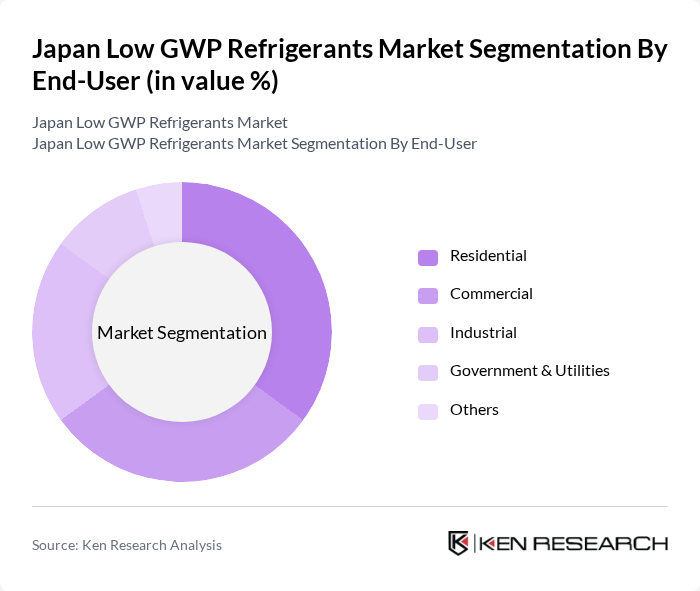
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Government & Utilities, and Others. The Residential segment is leading due to the increasing adoption of energy-efficient cooling systems in homes. The Commercial sector follows closely, driven by the need for sustainable refrigeration solutions in retail and food service industries.
The Japan Low GWP Refrigerants Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Daikin Industries, Ltd., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, Hitachi, Ltd., Toshiba Corporation, A-Gas, Honeywell International Inc., Chemours Company, Arkema S.A., Solvay S.A., Linde plc, Air Products and Chemicals, Inc., Koura Global, Refron, A-Gas (Japan) Ltd. contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the Japan low GWP refrigerants market appears promising, driven by increasing environmental awareness and technological advancements. As industries strive to meet stringent regulations, the demand for low GWP solutions is expected to rise. Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies in refrigeration systems will enhance efficiency and sustainability. With ongoing government support and incentives, the market is likely to witness significant growth, fostering innovation and collaboration among stakeholders in the coming years.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) Natural Refrigerants (Ammonia, CO2) Hydrocarbons (Propane, Isobutane) Blends of Low GWP Refrigerants Others |
| By End-User | Residential Commercial Industrial Government & Utilities Others |
| By Application | Air Conditioning Refrigeration Heat Pumps Chillers Others |
| By Distribution Channel | Direct Sales Distributors Online Sales Retail Others |
| By Region | Kanto Kansai Chubu Kyushu Others |
| By Technology | Vapor Compression Absorption Refrigeration Thermoelectric Refrigeration Magnetic Refrigeration Others |
| By Policy Support | Subsidies Tax Exemptions Research Grants Regulatory Support Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Refrigeration Users | 100 | Facility Managers, HVAC Technicians |
| Industrial Refrigerant Manufacturers | 80 | Production Managers, R&D Heads |
| Retail Sector Refrigeration Systems | 70 | Store Managers, Operations Directors |
| Environmental Regulatory Bodies | 40 | Policy Makers, Environmental Analysts |
| Consultants in HVAC Industry | 60 | Industry Analysts, Sustainability Consultants |
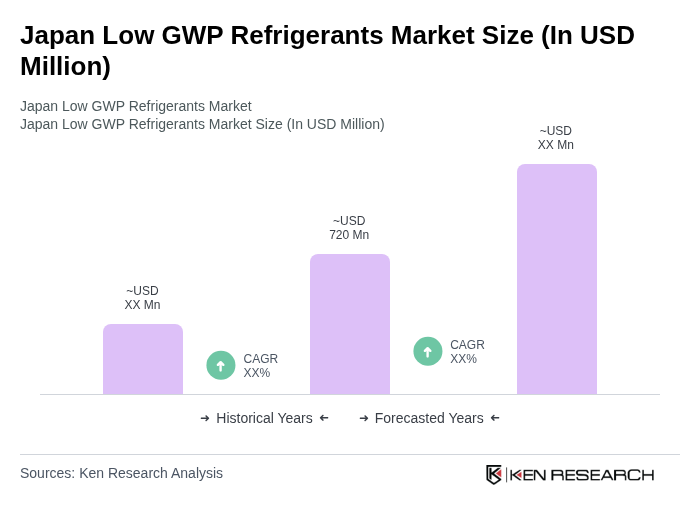
The Japan Low GWP Refrigerants Market is valued at approximately USD 720 million, reflecting a significant growth driven by environmental regulations, consumer awareness, and the demand for energy-efficient refrigeration systems across various sectors.