Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAE3009
Pages:82
Published On:February 2026
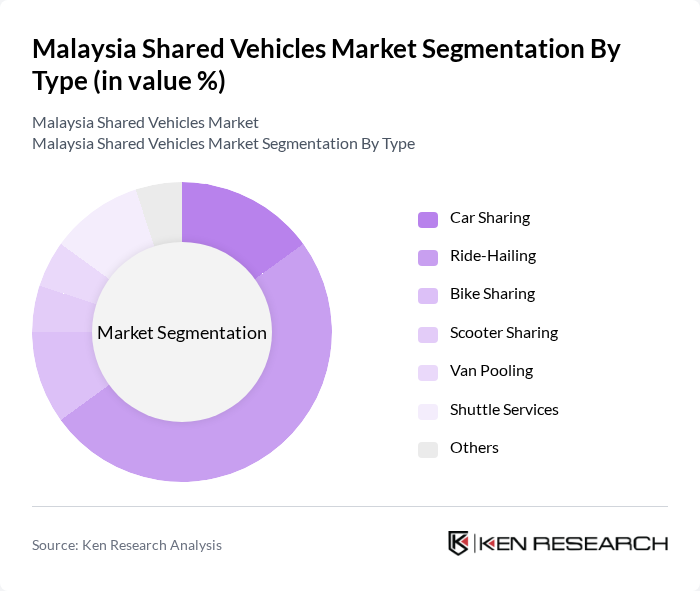
By Type:The shared vehicles market can be segmented into various types, including car sharing, ride-hailing, bike sharing, scooter sharing, van pooling, shuttle services, and others. Among these, ride-hailing has emerged as the dominant segment due to its convenience and widespread adoption among urban commuters. The increasing reliance on mobile applications for transportation has further fueled the growth of this segment.
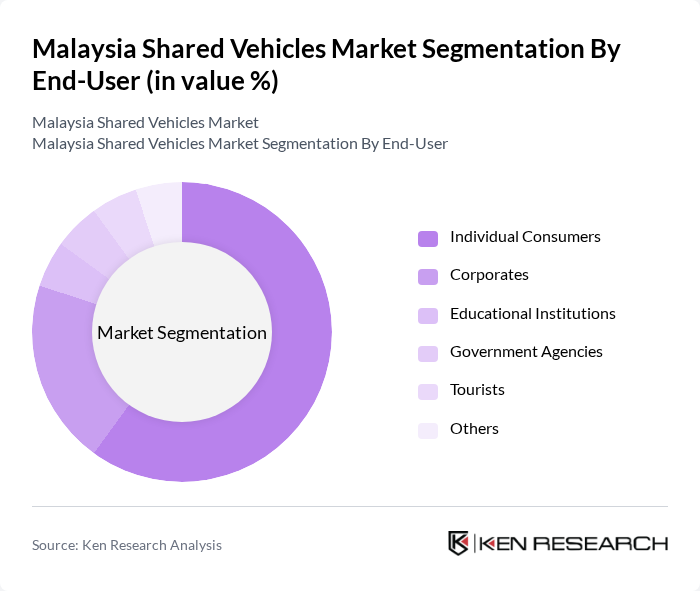
By End-User:The end-user segmentation includes individual consumers, corporates, educational institutions, government agencies, tourists, and others. Individual consumers represent the largest segment, driven by the increasing preference for flexible transportation options and the rise of the gig economy. Corporates are also increasingly utilizing shared vehicle services for employee transportation, contributing to the overall market growth.
The Malaysia Shared Vehicles Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Grab Holdings Inc., Go-Jek, Socar Mobility, MyCar, BeepBeep, MUV, Uber Technologies Inc., Carriage, Easybook, Tada, Lalamove, Drive.my, Waze Carpool, Ofo, Mobike contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the shared vehicles market in Malaysia appears promising, driven by urbanization and environmental initiatives. As the government continues to invest in infrastructure and regulatory frameworks, the market is likely to see increased participation from both traditional and new players. The integration of technology, such as mobile applications for seamless booking, will enhance user experience. Furthermore, the rise of electric vehicle sharing will align with sustainability goals, making shared mobility a key component of Malaysia's transport landscape in the future.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Type | Car Sharing Ride-Hailing Bike Sharing Scooter Sharing Van Pooling Shuttle Services Others |
| By End-User | Individual Consumers Corporates Educational Institutions Government Agencies Tourists Others |
| By Vehicle Size | Compact Cars Sedans SUVs Vans Others |
| By Duration of Use | Short-Term Rentals Long-Term Rentals Subscription Services Others |
| By Payment Model | Pay-Per-Use Membership-Based Subscription-Based Others |
| By Geographic Coverage | Urban Areas Suburban Areas Rural Areas Others |
| By Technology Integration | Mobile App-Based Services IoT-Enabled Vehicles AI-Based Routing Others |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Ride-sharing User Insights | 150 | Frequent Users, Occasional Users |
| Car-sharing Service Feedback | 100 | Members of Car-sharing Platforms, New Users |
| Regulatory Impact Assessment | 80 | Government Officials, Policy Makers |
| Urban Mobility Trends | 70 | Urban Planners, Transportation Analysts |
| Consumer Behavior Analysis | 120 | General Public, Non-users of Shared Vehicles |
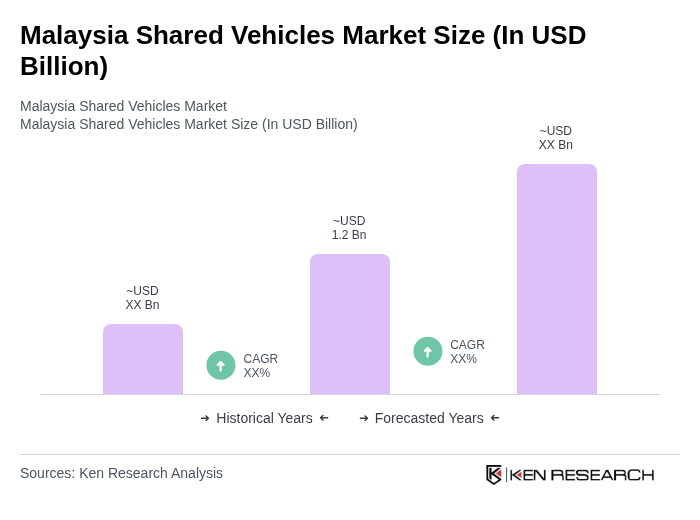
The Malaysia Shared Vehicles Market is valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion, reflecting significant growth driven by urbanization, demand for convenient transportation, and the trend towards shared mobility among consumers, particularly in urban areas.