Region:Africa
Author(s):Geetanshi
Product Code:KRAB2739
Pages:82
Published On:October 2025
By Service Type:The service type segmentation includes digital payments and wallets, digital lending platforms, neobank services, mobile banking solutions, cross-border remittances, investment and wealth management, and digital insurance (insurtech). Each subsegment addresses distinct consumer needs, with digital payments and wallets leading due to the growing preference for cashless transactions, followed by lending platforms that enable quick credit access for individuals and SMEs .
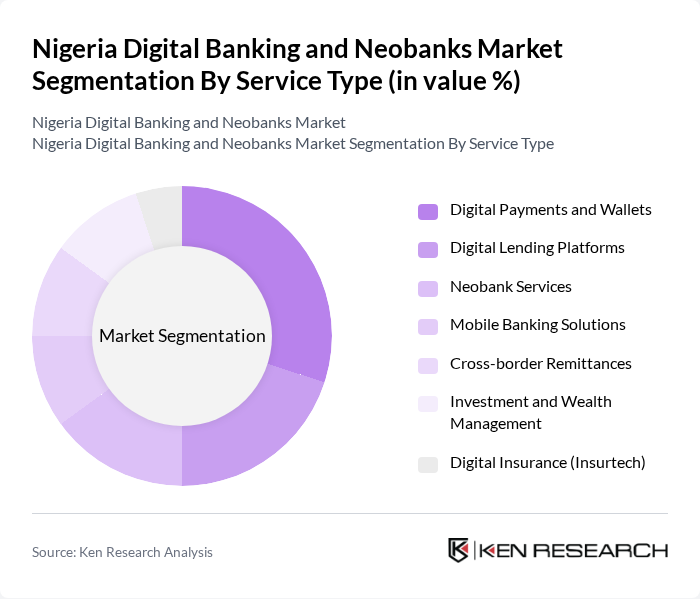
The digital payments and wallets segment remains the dominant player, driven by the surge in cashless transactions and the convenience of mobile wallets and payment apps. Younger demographics and urban consumers are increasingly adopting these solutions, contributing to the segment's growth. Digital lending platforms are also expanding rapidly, offering streamlined access to credit for individuals and small businesses, which further strengthens the competitive landscape .
By Customer Segment:The customer segment includes the unbanked population, underbanked (Y Generation), individual consumers, small and medium enterprises (SMEs), and micro-enterprises. Each group exhibits distinct financial needs and digital adoption patterns, with individual consumers leading in market share due to widespread use of digital banking for personal finance. The unbanked and underbanked segments are increasingly targeted by fintechs aiming to expand financial inclusion .
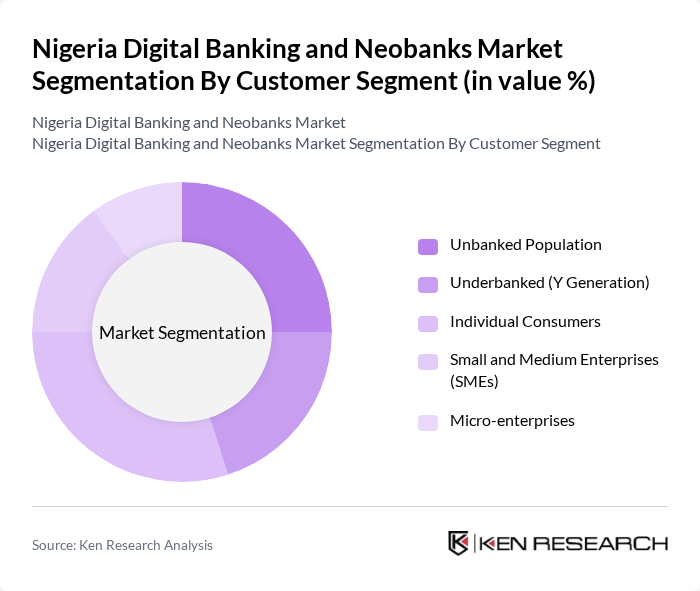
The individual consumers segment is the largest, reflecting the widespread adoption of digital banking for personal finance management. The unbanked population remains a critical focus area, with fintech companies deploying innovative solutions to reach this group. The underbanked, particularly younger generations, are increasingly utilizing digital platforms for their banking needs, driving further market expansion .
The Nigeria Digital Banking and Neobanks Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Kuda Bank, Opay, PalmPay, Carbon (formerly Paylater), VBank, Alat by Wema Bank, Flutterwave, Paystack, Moniepoint, Fairmoney, Branch International, Renmoney, Cowrywise, PiggyVest, TeamApt contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of Nigeria's digital banking and neobanks market appears promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. As artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies become more integrated into banking operations, personalized financial services will enhance customer experiences. Additionally, the rise of open banking platforms will foster collaboration between traditional banks and fintechs, creating a more competitive landscape that encourages innovation and improved service delivery for consumers across Nigeria.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Service Type | Digital Payments and Wallets Digital Lending Platforms Neobank Services Mobile Banking Solutions Cross-border Remittances Investment and Wealth Management Digital Insurance (Insurtech) |
| By Customer Segment | Unbanked Population Underbanked (Y Generation) Individual Consumers Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Micro-enterprises |
| By Technology Platform | Mobile Applications Web-based Platforms USSD Services Agent Banking Networks API-based Solutions |
| By Geographic Coverage | Urban Centers (Lagos, Abuja) Semi-urban Areas Rural and Farming Communities Northern Nigeria Southern Nigeria |
| By Business Model | B2C (Business-to-Consumer) B2B (Business-to-Business) B2G (Business-to-Government) Marketplace Models |
| By Regulatory Status | CBN Licensed Banks Payment Service Banks (PSB) Mobile Money Operators Fintech Companies |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Urban Digital Banking Users | 120 | Young Professionals, Tech-Savvy Consumers |
| Rural Neobank Adoption | 60 | Small Business Owners, Farmers |
| Fintech Entrepreneurs | 40 | Startup Founders, Product Managers |
| Traditional Bank Transition Strategies | 50 | Bank Executives, Digital Transformation Officers |
| Consumer Attitudes Towards Digital Banking | 90 | General Public, Financial Literacy Advocates |
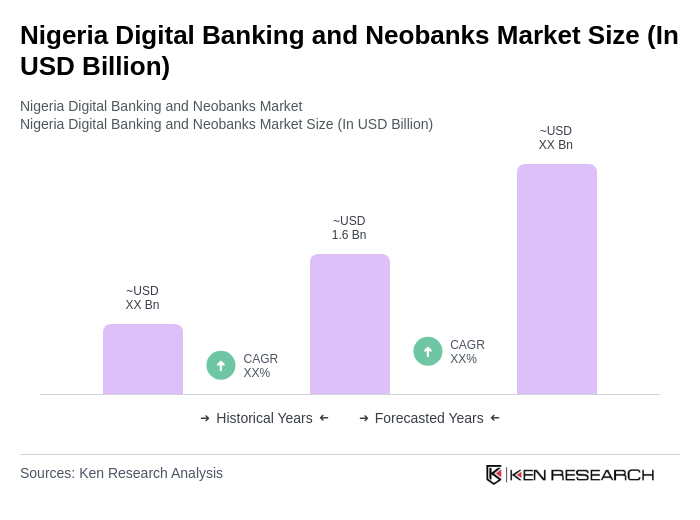
The Nigeria Digital Banking and Neobanks Market is valued at approximately USD 1.6 billion, driven by mobile technology adoption, internet penetration, and a growing demand for financial inclusion among the unbanked population.