Region:Asia
Author(s):Rebecca
Product Code:KRAB2153
Pages:80
Published On:January 2026
By Storage Form:The storage form of hydrogen is critical in determining the efficiency and practicality of hydrogen storage solutions. The primary subsegments include Gas (Compressed Hydrogen), Liquid Hydrogen, and Solid / Material-based (Metal Hydrides, Chemical Carriers). This aligns with industry practice, where hydrogen energy storage in Australia is typically categorized into solid, liquid, and gas forms. Each of these forms has unique characteristics that cater to different applications and market needs.
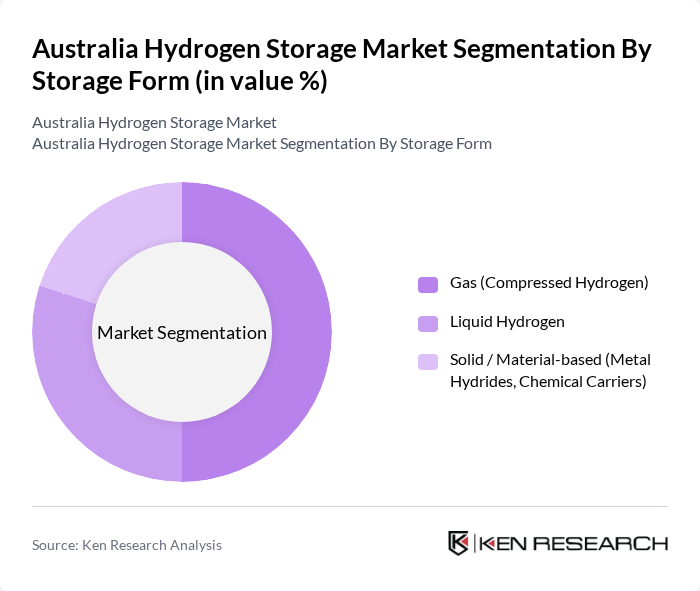
The Gas (Compressed Hydrogen) subsegment is currently dominating the market due to its widespread adoption in various applications, including blending into gas networks, mobility projects, and industrial uses, reflecting the maturity of compressed gas storage infrastructure. The relative ease of compression and storage at high pressures, compatibility with existing gas handling equipment, and suitability for hydrogen hubs make it a preferred choice for many companies and utilities. Liquid Hydrogen is also gaining traction, particularly in export-oriented and long-distance transport applications requiring high energy density and maritime shipment, while Solid / Material-based storage, including metal hydrides, ammonia, and other chemical carriers, is emerging as a viable option for long-term storage and international transport solutions where hydrogen is stored in bound form and released at the point of use.
By Technology:The technology used for hydrogen storage plays a significant role in determining the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of storage solutions. The main subsegments include Compression-based Storage, Liquefaction-based Storage, and Material-based Storage (Hydrides, Ammonia, LOHC). These technology groupings are consistent with industry segmentation, which differentiates between compression, liquefaction, and material-based approaches for hydrogen energy storage. Each technology has its advantages and is suited for specific applications.
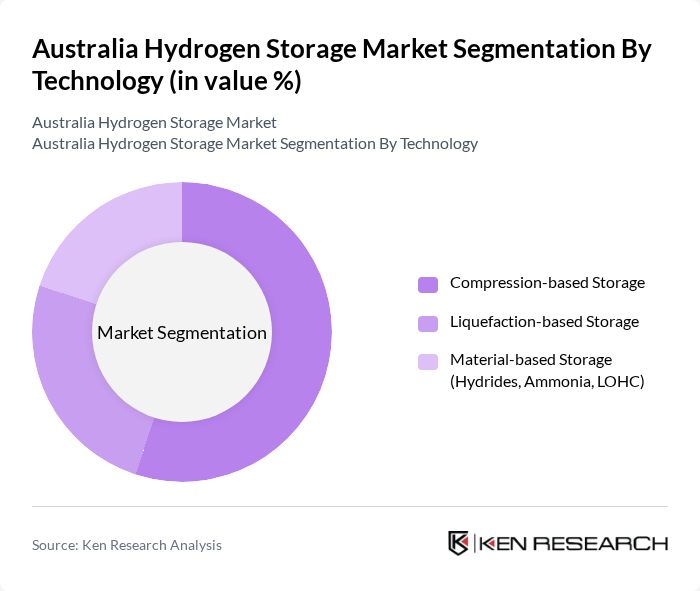
Compression-based Storage is leading the market due to its established technology, relatively lower capital intensity compared with cryogenic systems, and the ability to leverage existing gas pipelines, cylinders, and high-pressure vessels for hydrogen storage. This method is widely used in various applications, including fuel cell vehicle refuelling, industrial processes, and grid-support hydrogen hubs. Liquefaction-based Storage is also significant, particularly for export and mobility applications requiring high volumetric energy density and long-distance transport, while Material-based Storage is gaining interest for its potential in long-term storage and transport solutions using carriers such as ammonia and liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHC), which can simplify shipping and handling.
The Australia Hydrogen Storage Market is characterized by a dynamic mix of regional and international players. Leading participants such as Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), Hydrogen Energy Supply Chain (HESC), Fortescue Metals Group (Fortescue Energy / Fortescue Future Industries), Woodside Energy, BOC Limited (a Linde company), Linde plc, ATCO Australia, Jemena, H2U – The Hydrogen Utility, CSIRO, AGL Energy, Origin Energy, Neoen Australia, Enel Green Power Australia, Siemens Energy contribute to innovation, geographic expansion, and service delivery in this space.
The future of the hydrogen storage market in Australia appears promising, driven by increasing investments in renewable energy and government support for hydrogen initiatives. In future, the integration of hydrogen storage with renewable energy sources is expected to enhance energy reliability and efficiency, supported by Australia’s growing renewable generation share and large?scale hydrogen export ambitions outlined in the National Hydrogen Strategy. Additionally, the growing interest in green hydrogen production will likely lead to innovative storage solutions, positioning Australia as a leader in the global hydrogen economy and fostering international collaborations.
| Segment | Sub-Segments |
|---|---|
| By Storage Form | Gas (Compressed Hydrogen) Liquid Hydrogen Solid / Material-based (Metal Hydrides, Chemical Carriers) |
| By Technology | Compression-based Storage Liquefaction-based Storage Material-based Storage (Hydrides, Ammonia, LOHC) |
| By Application | Stationary Power (Grid & Off-grid) Transportation (Mobility & Refueling) Industrial & Commercial |
| By End User | Utilities & Power Generators Industrial (Mining, Refining, Chemicals) Commercial & Logistics |
| By Storage Location | On-site / Onshore Storage Port & Export Hub Storage Underground Storage (Caverns, Reservoirs) |
| By Project Scale | Pilot & Demonstration Projects Commercial-scale Projects Utility-scale / Hub-scale Projects |
| Scope Item/Segment | Sample Size | Target Respondent Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Storage Technology Providers | 120 | Product Managers, R&D Directors |
| Energy Sector Stakeholders | 90 | Energy Analysts, Policy Makers |
| Industrial Users of Hydrogen | 80 | Operations Managers, Procurement Officers |
| Research Institutions and Academia | 70 | Research Scientists, Professors |
| Government Regulatory Bodies | 60 | Regulatory Affairs Managers, Energy Policy Advisors |
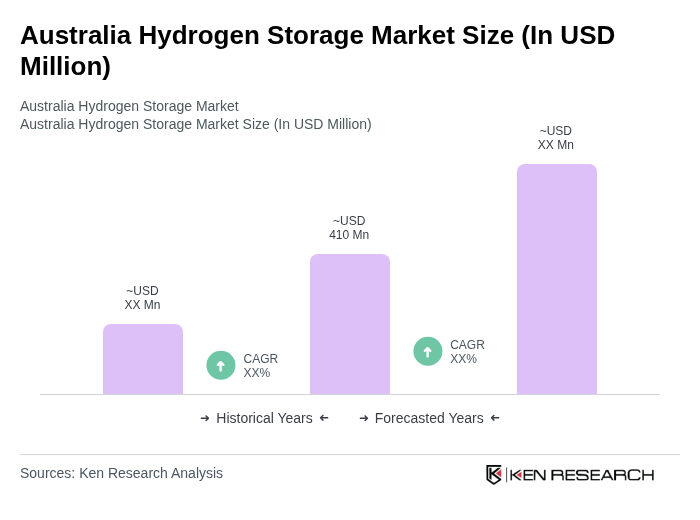
The Australia Hydrogen Storage Market is valued at approximately USD 410 million, driven by the increasing demand for clean energy solutions and advancements in hydrogen storage technologies, including compressed, liquefied, and material-based storage methods.